RNN
Motivation
Language Modeling
Summary
다음 단어를 예측하는 task.
- NTP(Next Token Prediction)..
- 대표적인 benchmark task
- 많은 NLP task의 subcomponent 이다.
- predictive typing
- speech recognition
- handwriting recognition
- spelling/grammar correctopm
- machine translation
- etc..
formal 하게는 아래와 같이 정의됨.
원본 링크NOTE
give a sequence of words ,
compute the probability distribution of the next word :
where can be any word in voca
A system that does this called a Language Model.
- Language model : a system that assigns a probability to a piece of text.
Traditional approach
n-gram
Summary
Definition:
- An n-gram is a chunk of consecutive words.
Example
text : “the students opened their ”
- unigrams : “the”, “students”, “opened”, “their”
- bigrams: “the students”, “students opened”, “opened their”
- trigram: “the students opened”, “students opened their”
- 4-gram: “the student opened their”
Important
Idea: 서로 다른 n-gram의 빈도를 사용하여 NSP(Next token prediction.)
Tip
일반적으로 sparsity problem으로 인해 4-gram이 한계.
Assumption
Summary
n-gram 모델은 기본적으로 Markov 가정을 가져가는데, 개의 전 단어만이 다음 단어 예측에 관여한다.
조건부 확률의 정의에 의해 위 식은, joint-probability로 다음과 같이 쓰여진다.
이건 대규모 코퍼스에서 count로 근사되고.
Limits
Sparsity problem
Summary
일반적으로 생각해봐도, 4단어의 window, context는 너무 짧다.
Storage Problem
Summary
각 n-gram 마다 빈도를 저장해야 하니, 코퍼스 크기에 비례해 저장 용량이 커진다.
Text Generating
Summary
n-gram model은 n-gram마다 출현 빈도를 저장하고 있으니, 이를 사용해서 다음 단어 생성을 할 수 있다.
n-gram model이 저장하고 있는 출현빈도(probability distribution)을 기반으로 다음 단어를 생성하는데 2가지 방법이 있는데,
- 빈도를 그대로 사용해서 하나를 추출.(deterministic)
- 이렇게 하면 동일 input에 대해 항상 같은 response.
- 빈도 분포에서 sampling
- 현재의 gpt등의 생성형 LLM이 채택하여, 동일 input에 대해서도 다양한 응답.
원본 링크Example
문법적으로는 꽤 맞지만, 말이 되지 않는 말(incoherent)들을 뱉는다.
그렇다고 window size 을 키우면 sparse해지면서 모델 크기도 동시에 커진다.Question
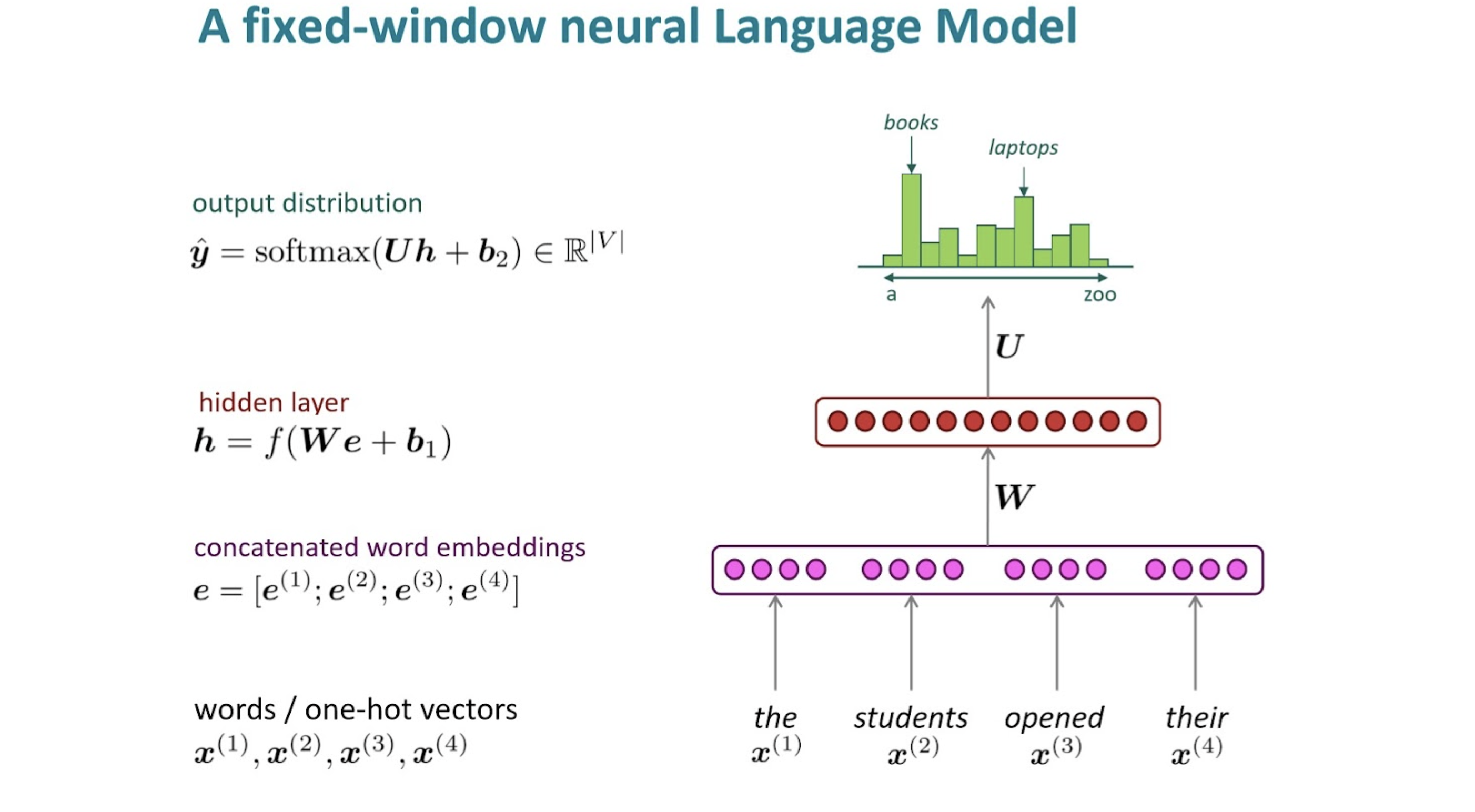
window based NN을 사용해보는 건?(e.g. FC, CNN)
- window-based : fix된 context를 처리. FC도, CNN도 한 번에 처리하는 단위가 정해져 있으니, 또한 n-gram 역시 fixed window-size를 가지고 있고.
Example
- sparsity problem 해결
- n-gram과는 달리 모든 n-gram들의 정보를 저장할 필요도 없음.
- 그런, 여전히 fixed-window,,, context 길이가 제한적임.
- 또한, 대칭적 input에 대한 정보가 다뤄지지 않는다.
- FC layer를 사용한다고 가정하면, an apple, apple an 같이 순서가 바뀐 것에 대해 완전히 독립적인 parameter(weight)가 관여하는 거라, 이게 맞을까?
Summary
“Need a neural architecture that can process any length input.”
RNN
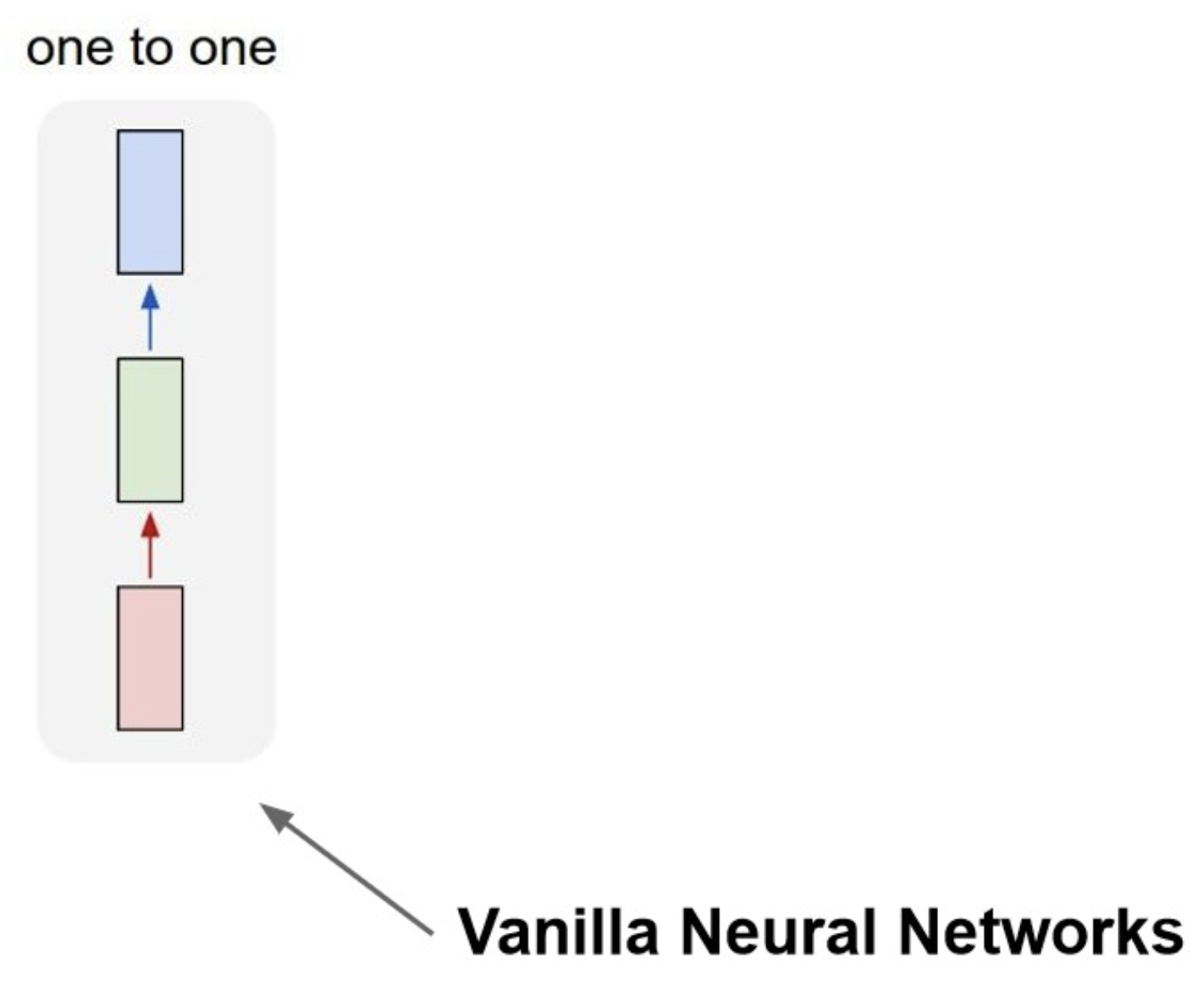
- 기존 vanila한 NN 구조에서 input과 output의 개수에 집중해서 나눠보자.
Multi column
One to One(Vanila NN)
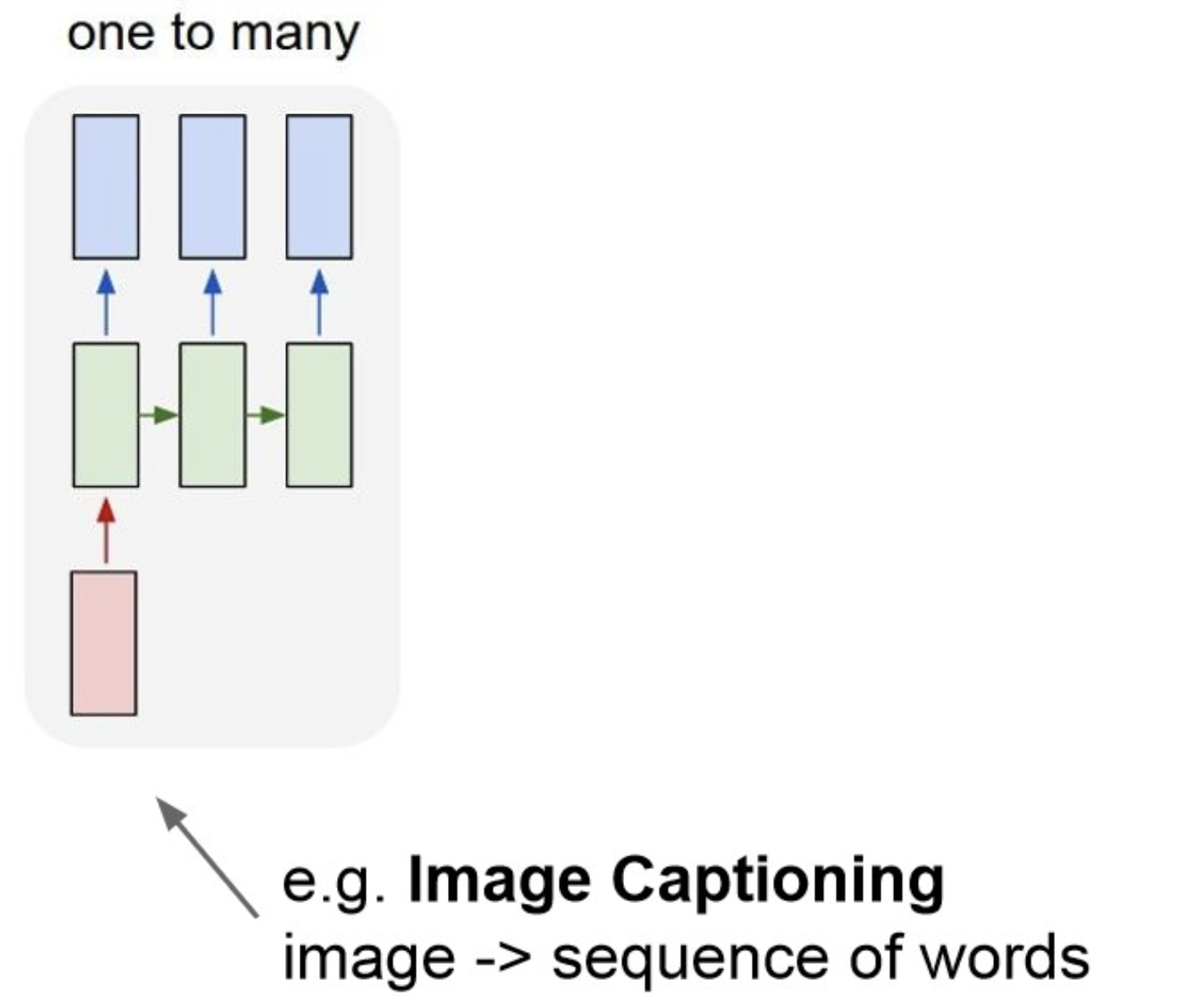
One to Many
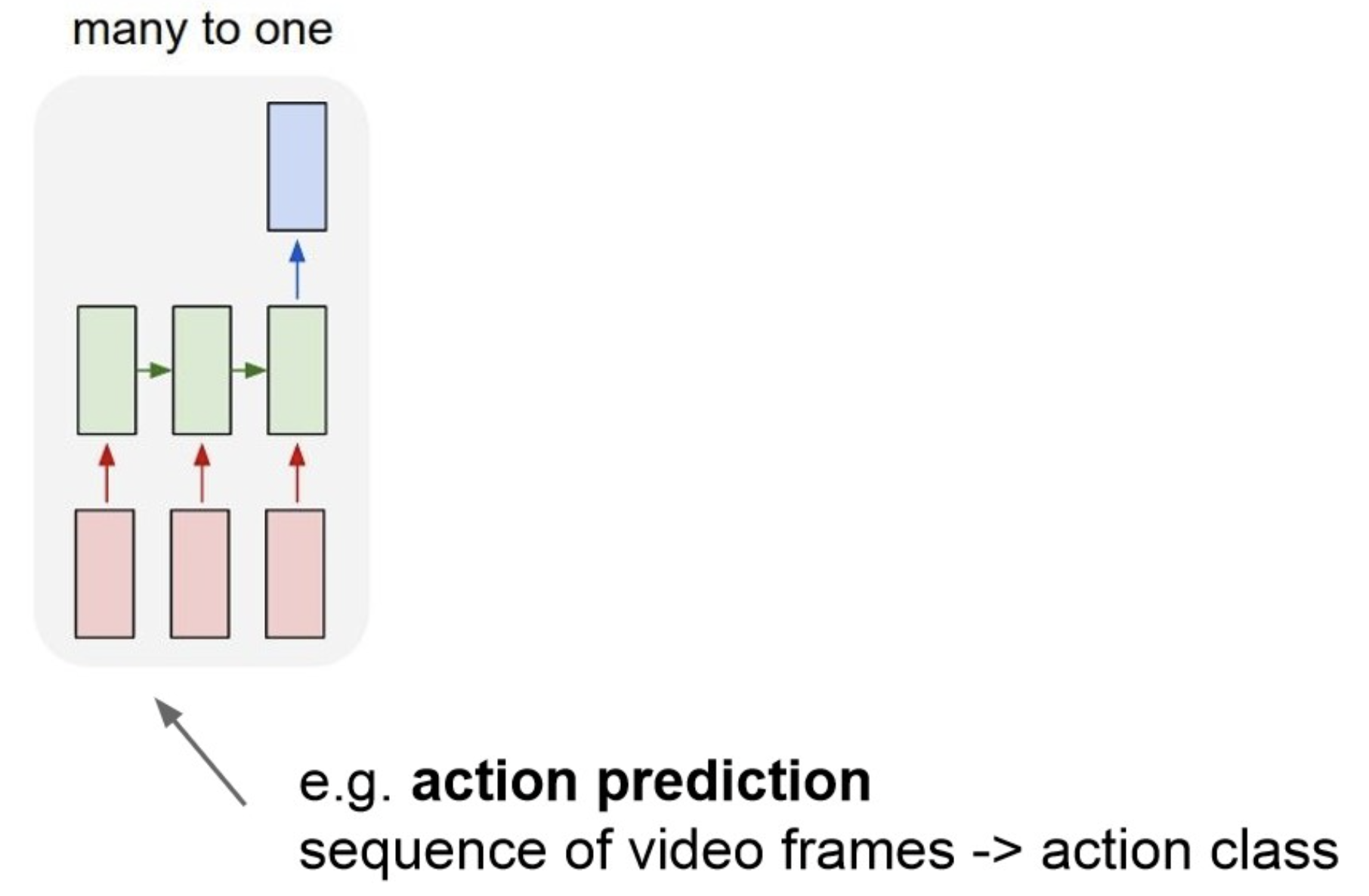
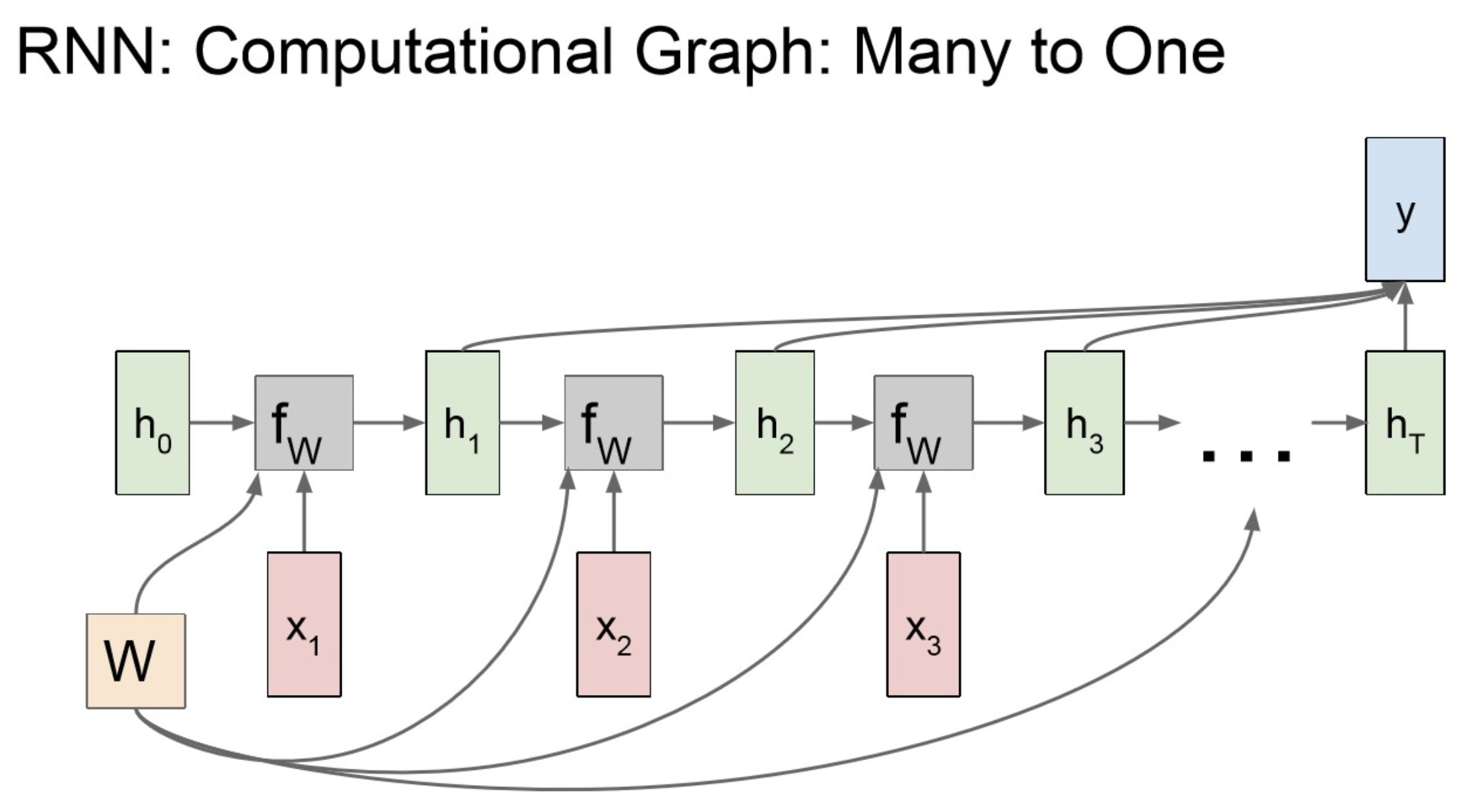
Many to One
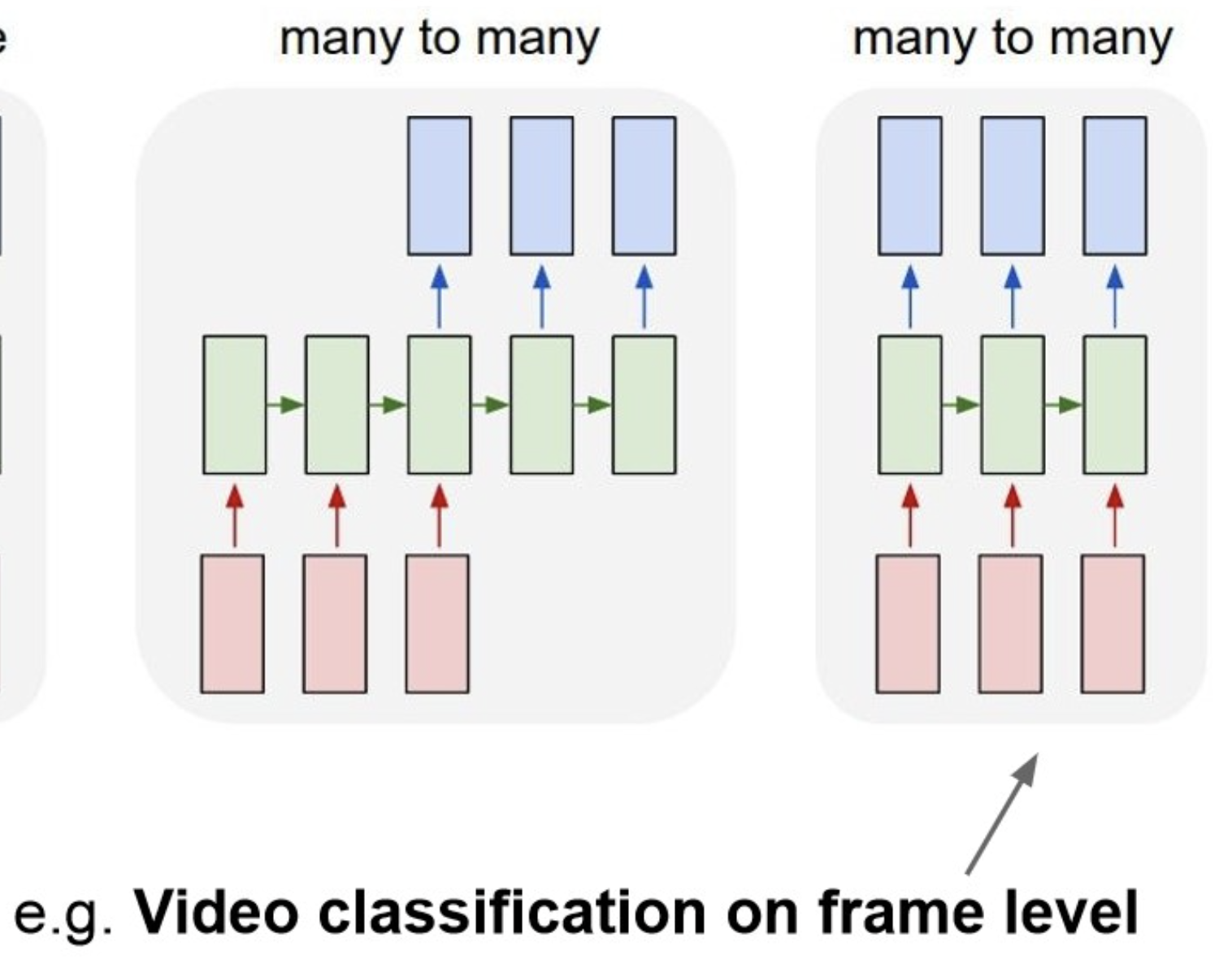
Many to Many
- 구현 방법이 그림 처럼 여러 방법.
model structure
Multi column
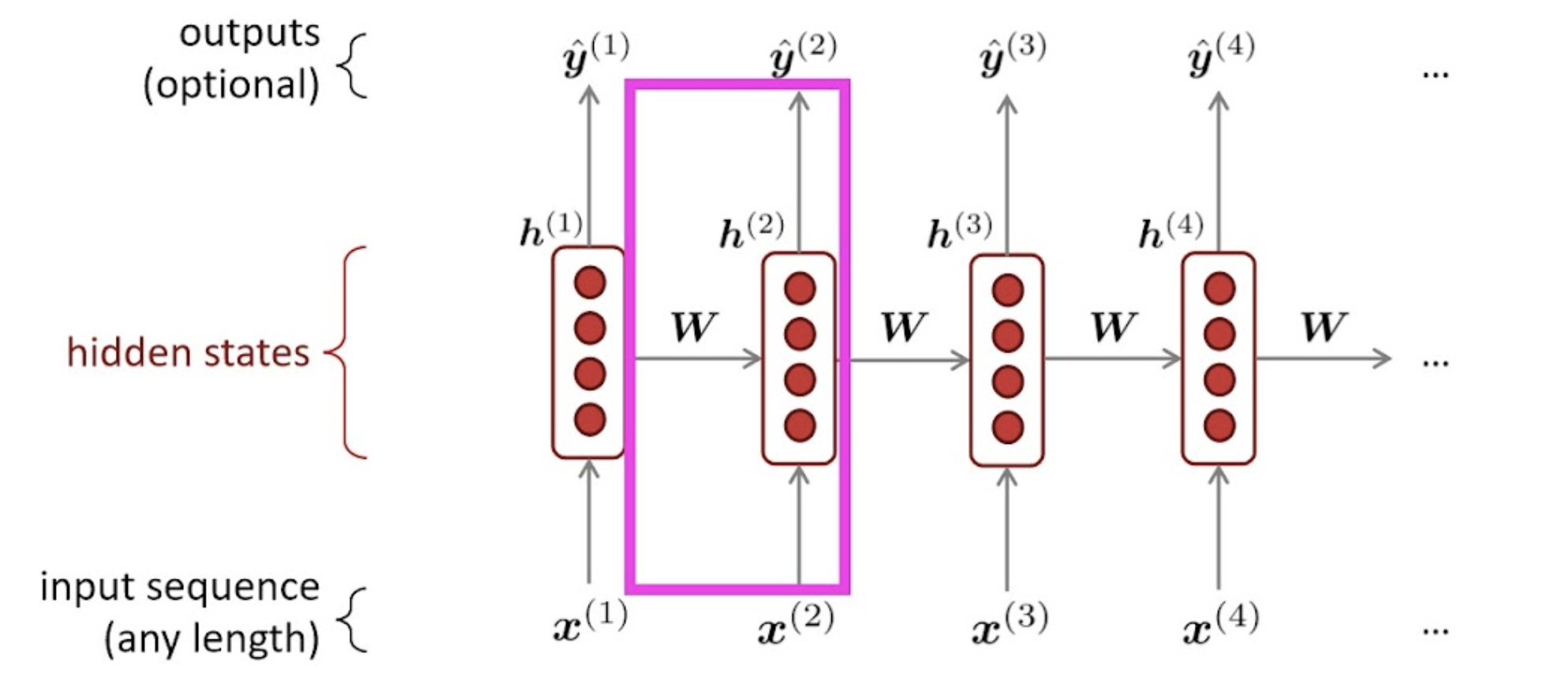
folded-form
unfolded-form
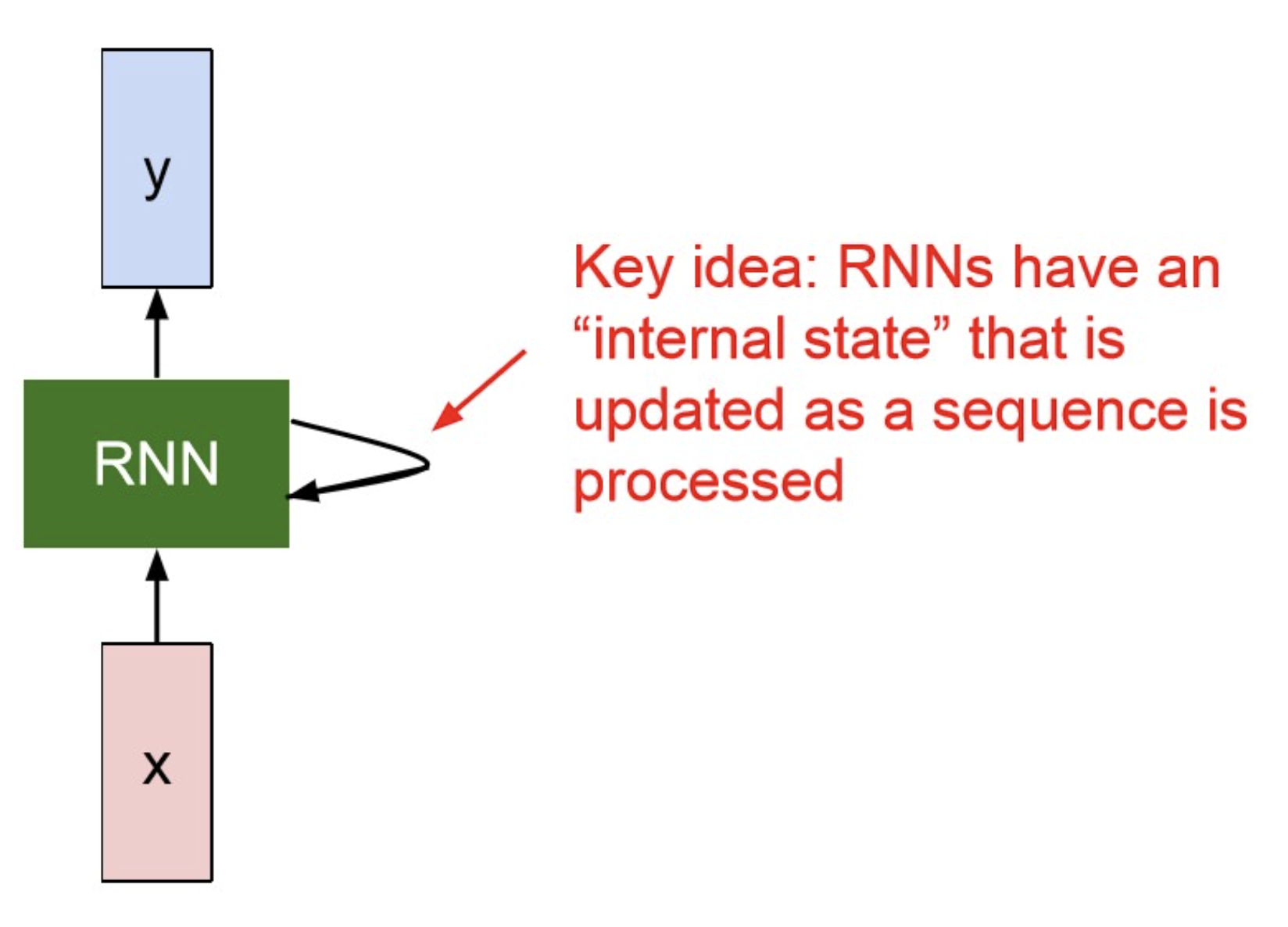
Key Idea
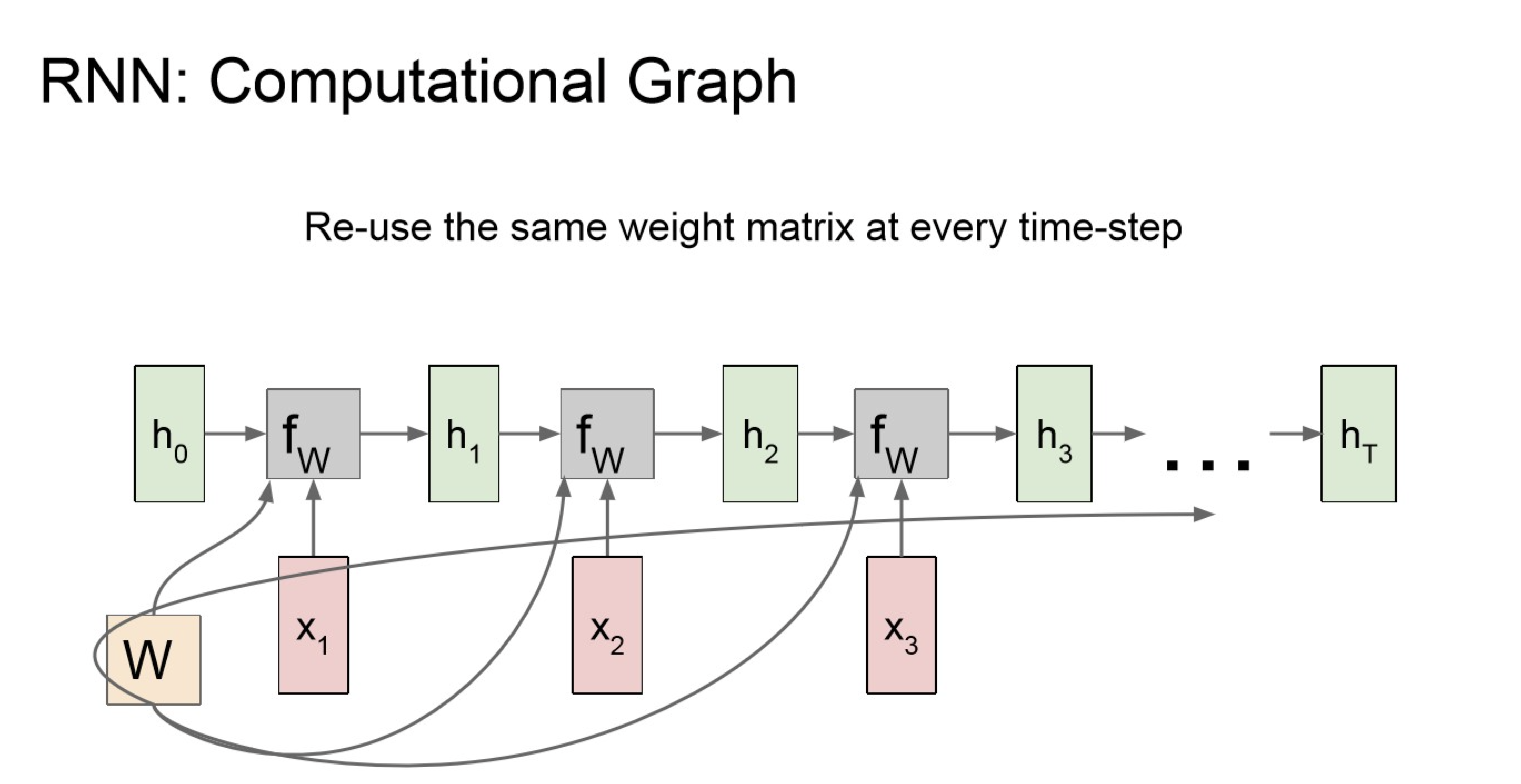
“Apply the same weights repeatively.”
구체적으로는 파라미터를 아래처럼 사용한다.
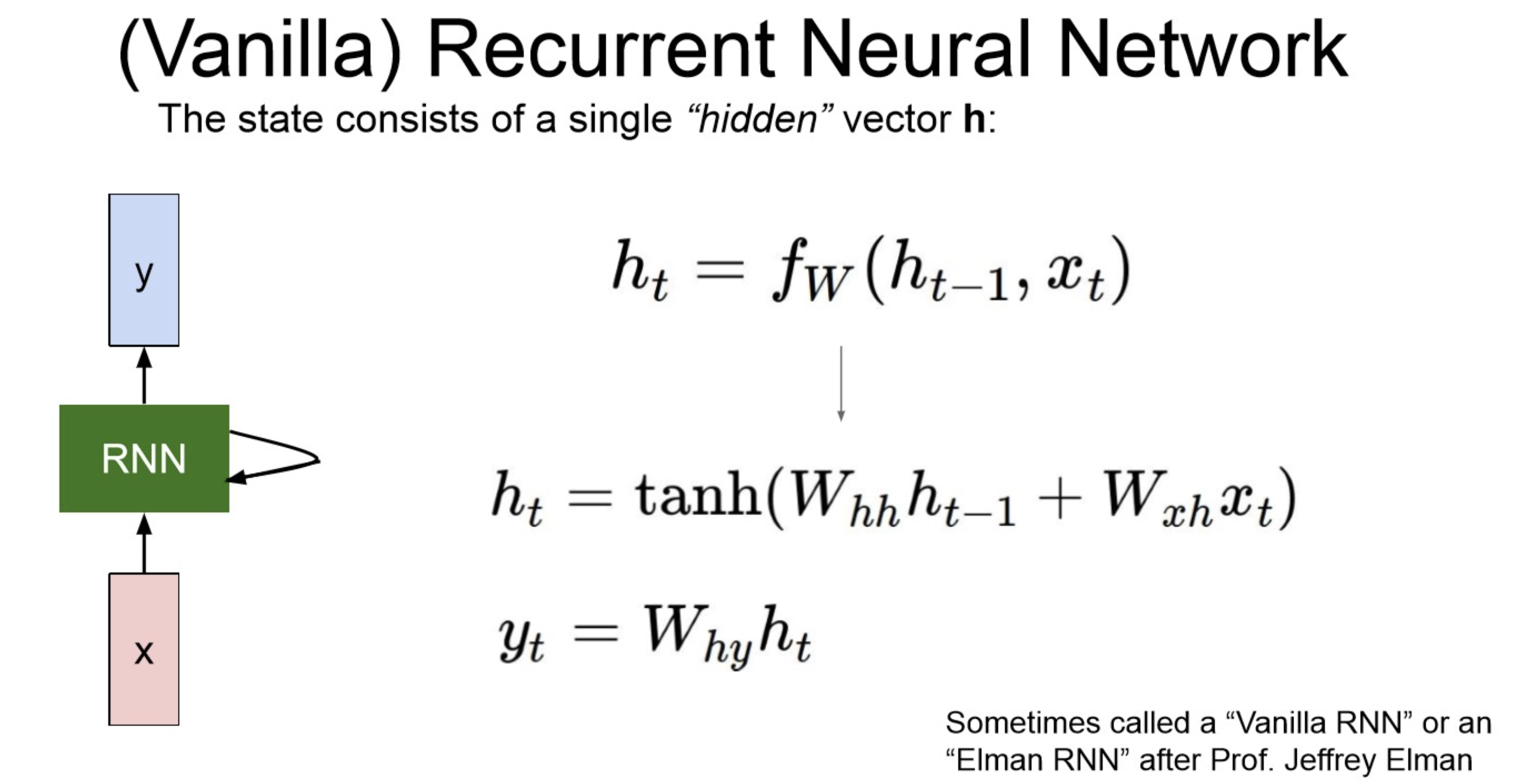
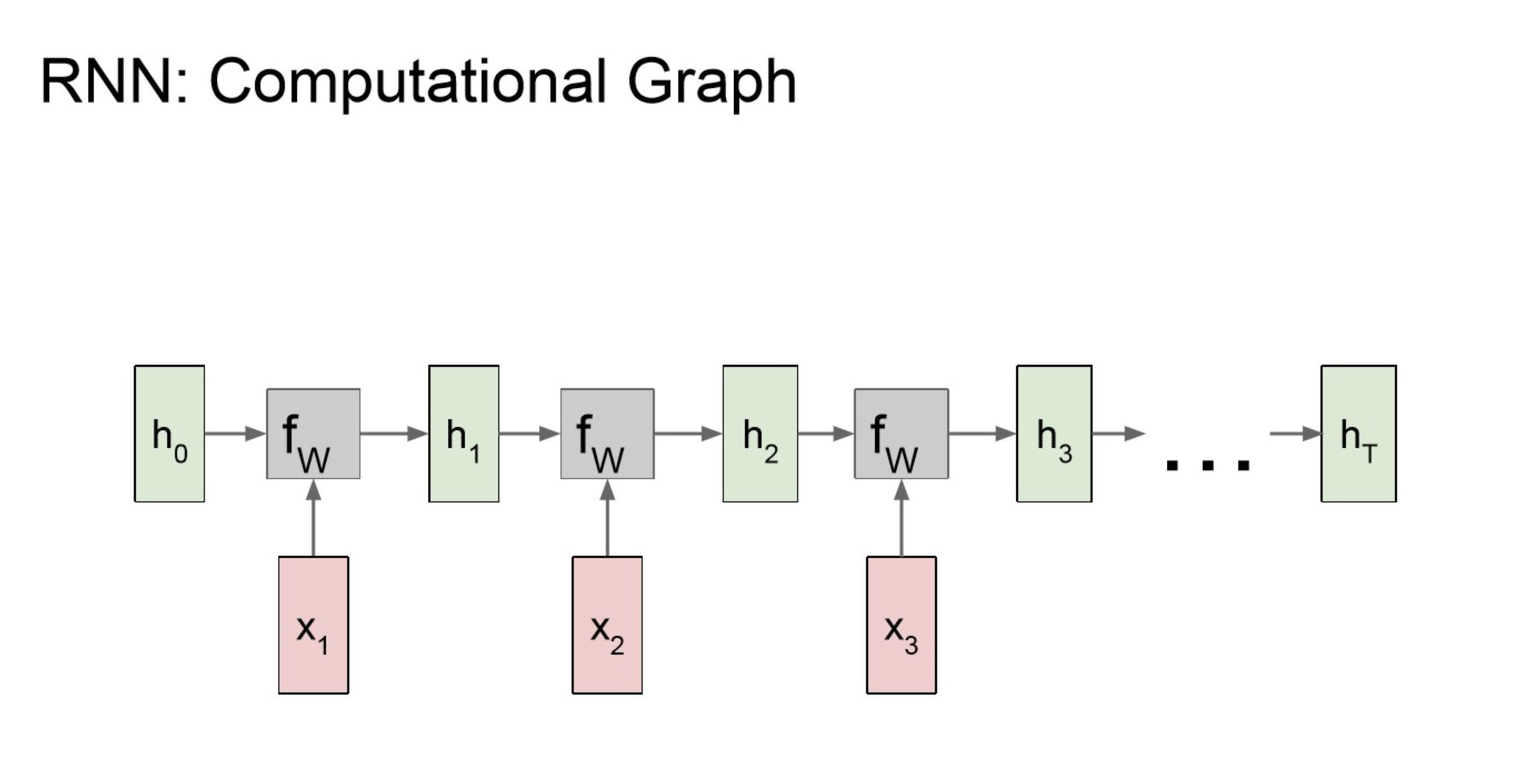
Recurrence Formula
: t step에서의 hidden state
: W로 구성된 함수(layer)
: t step의 input
: t step에서 output
: hidden to y, 방향으로 갈 때 곱해주는 파라미터.
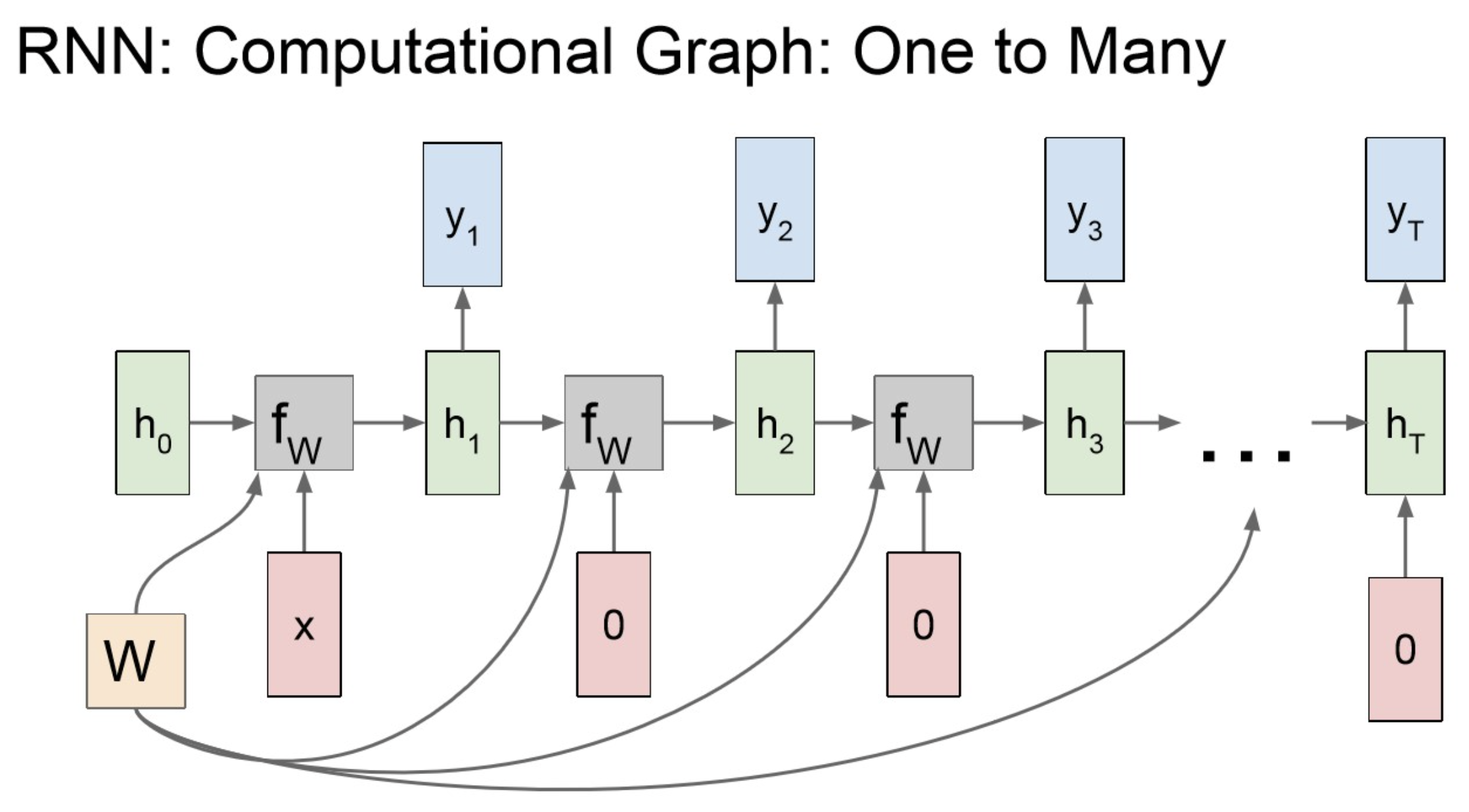
Computational Graph
NOTE
아래와 같은 순서로 연산이 되고,
중간 중간에 적용하는 함수에 관여하는 것이 항상 동일한
여기서 처음 본 (input, output) 의 종류에 따라 아래처럼 분기.
Multi column
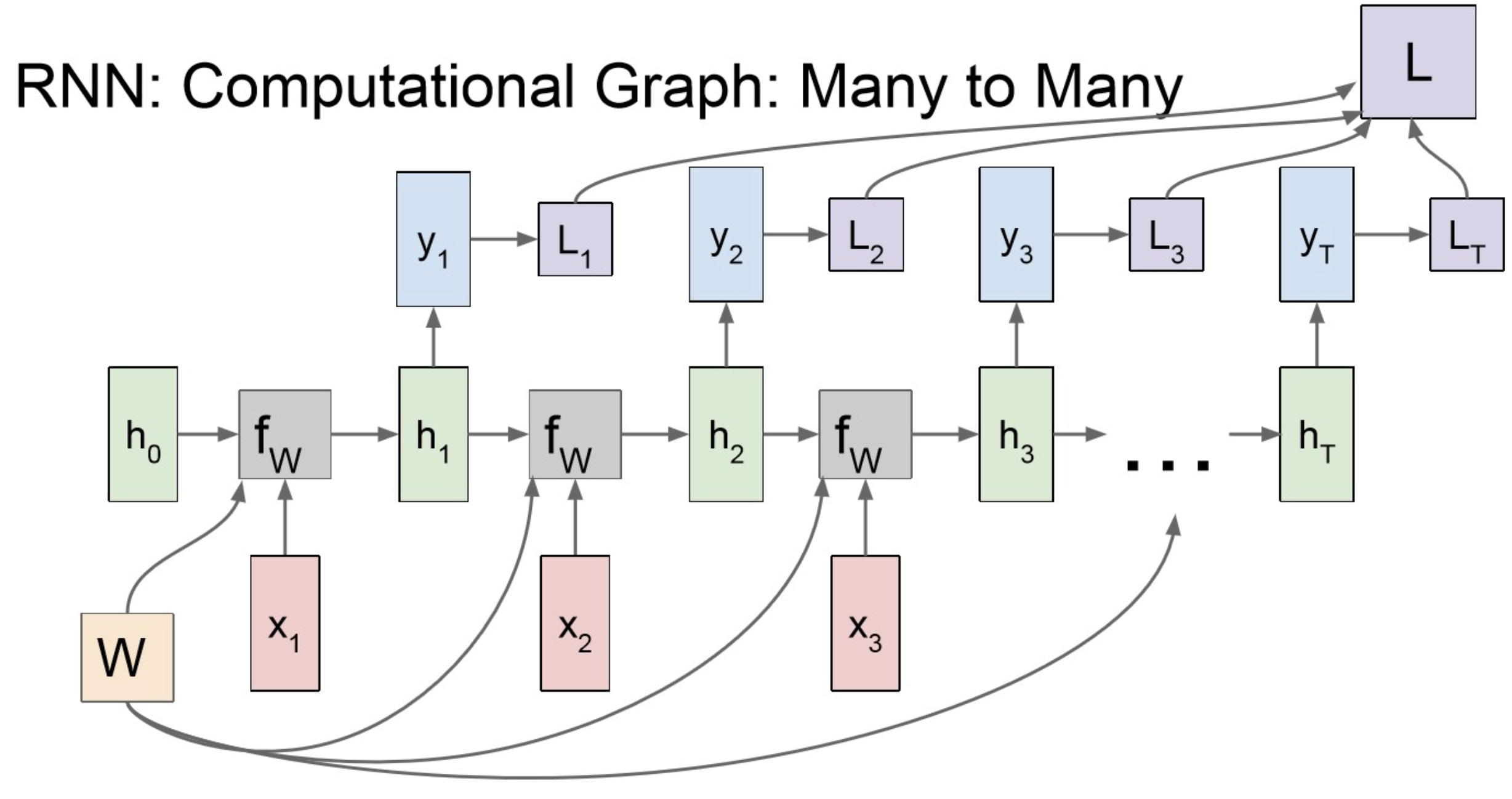
Many to Many
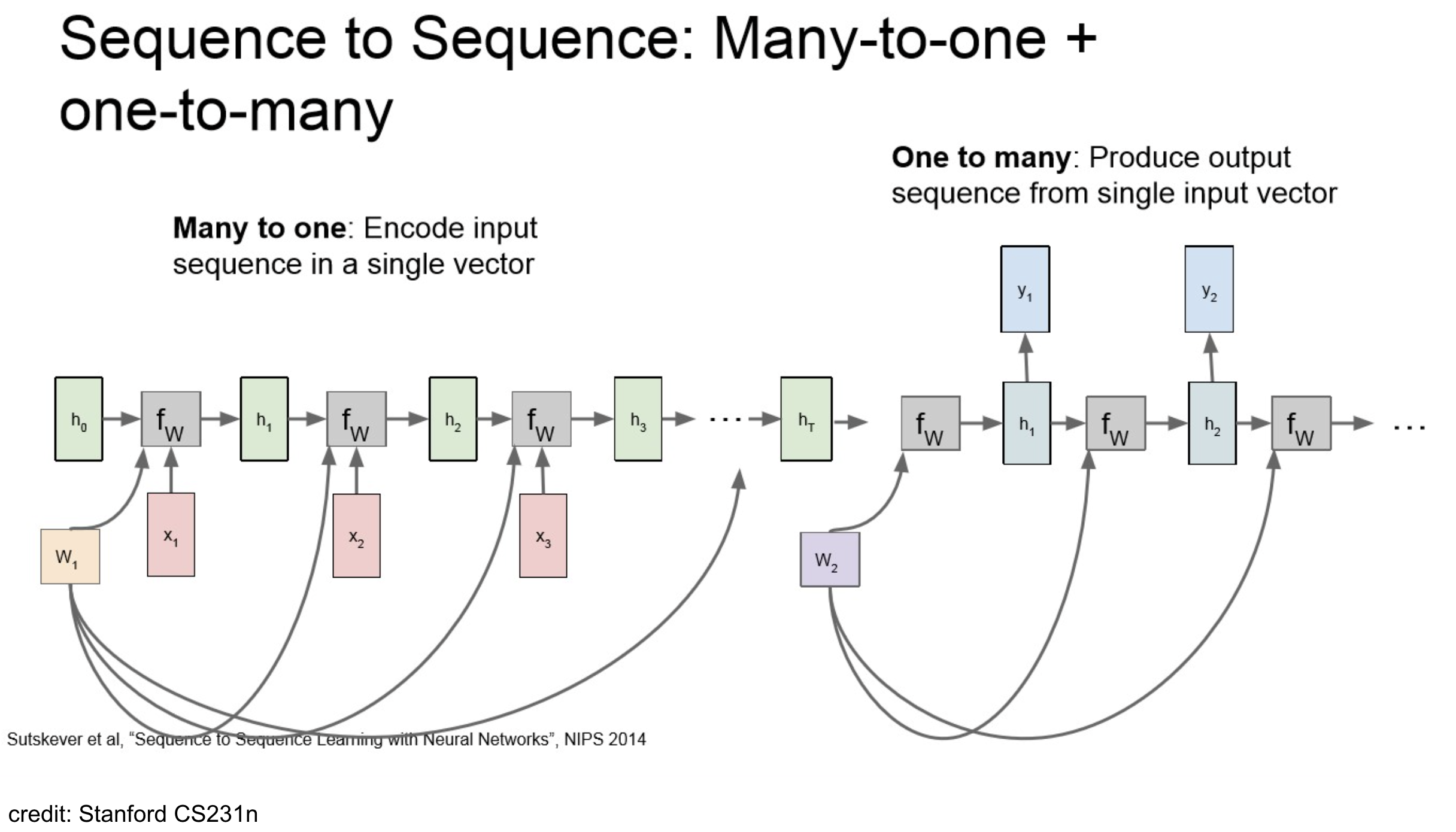
Many to One
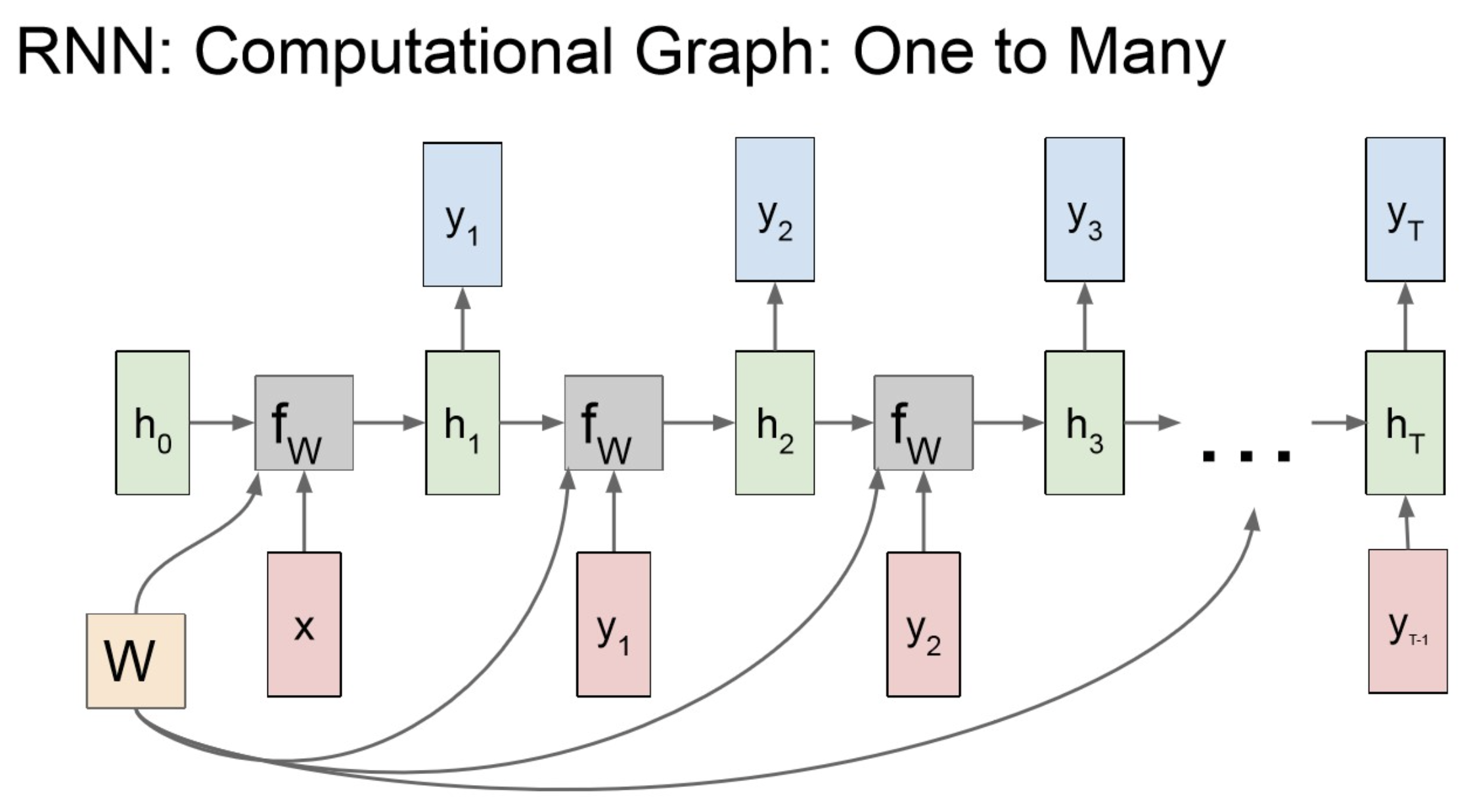
One to Many-1
One to Many-2
Tip
RNN 구조에서 Many-to-One 구조에다 One-to-Many 구조를 합치면 아래와 같이 seq2seq.
benefifts: translation 작업 같은 경우, 나라별 어순이나 문장 내 정보 위치가 다를 수 있으니 한 번 번주 압축해서 encoding(context vector)를 만들고 일르 decode 하는 방식이 유리한 부분이 있음.
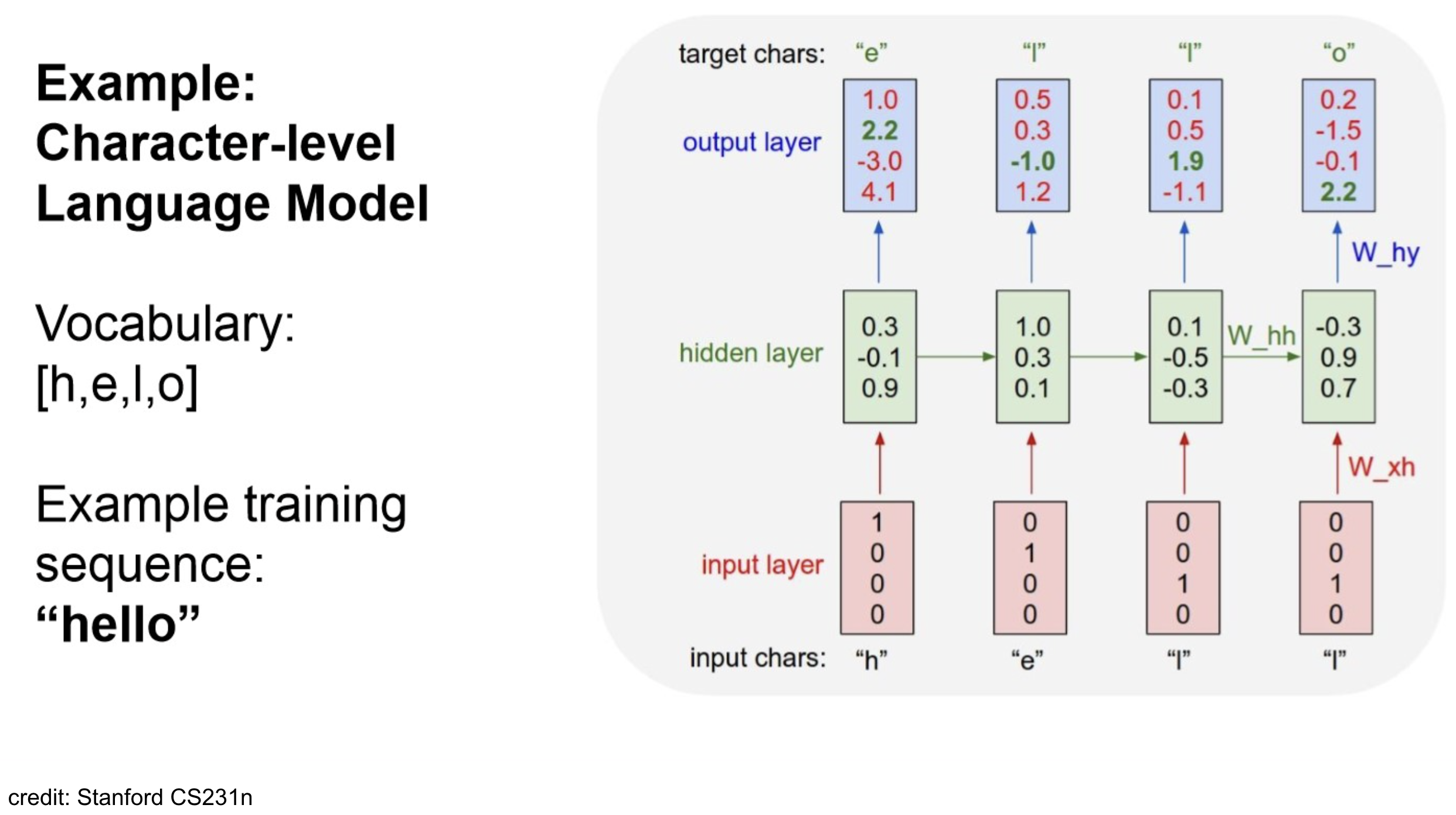
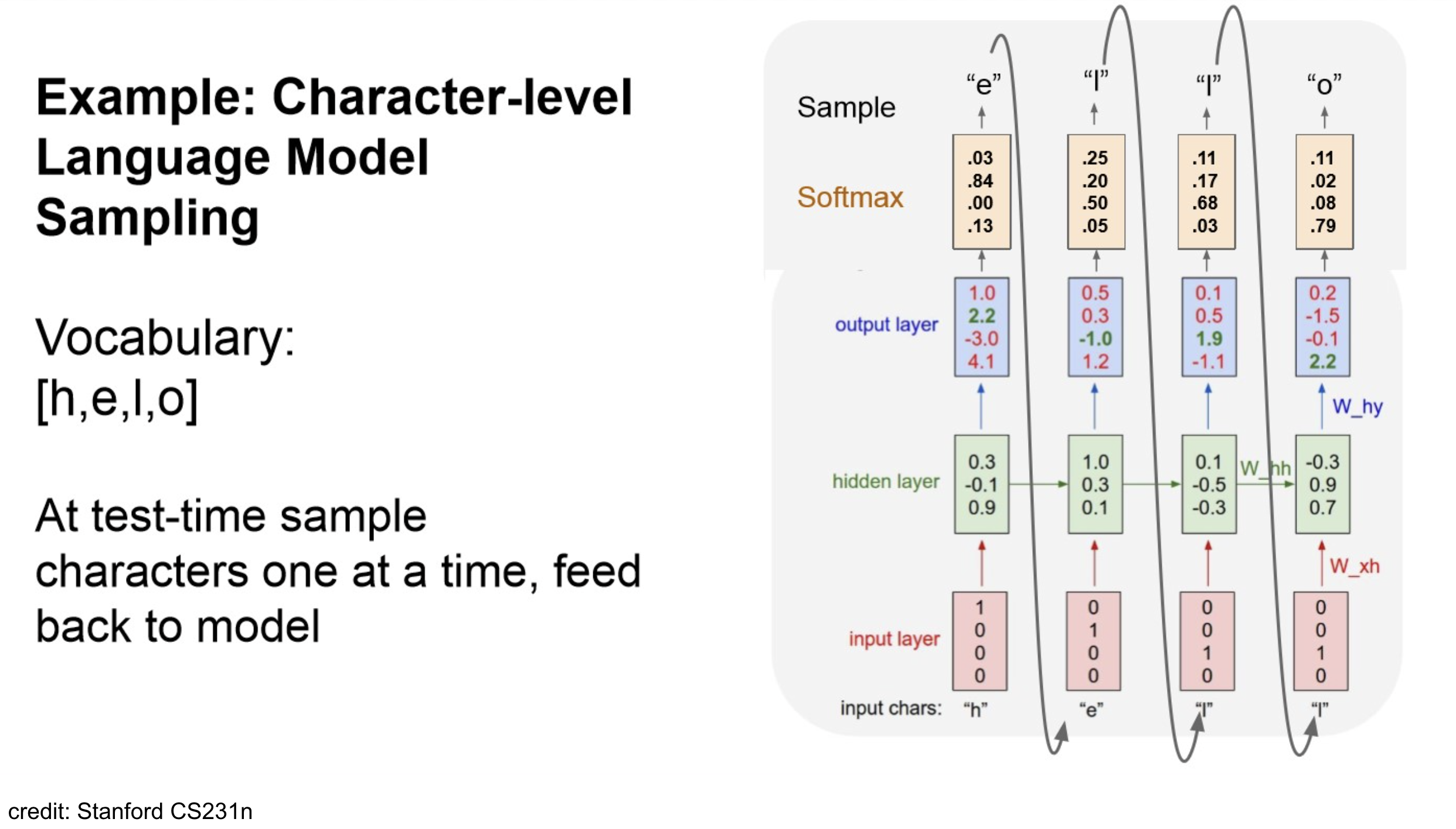
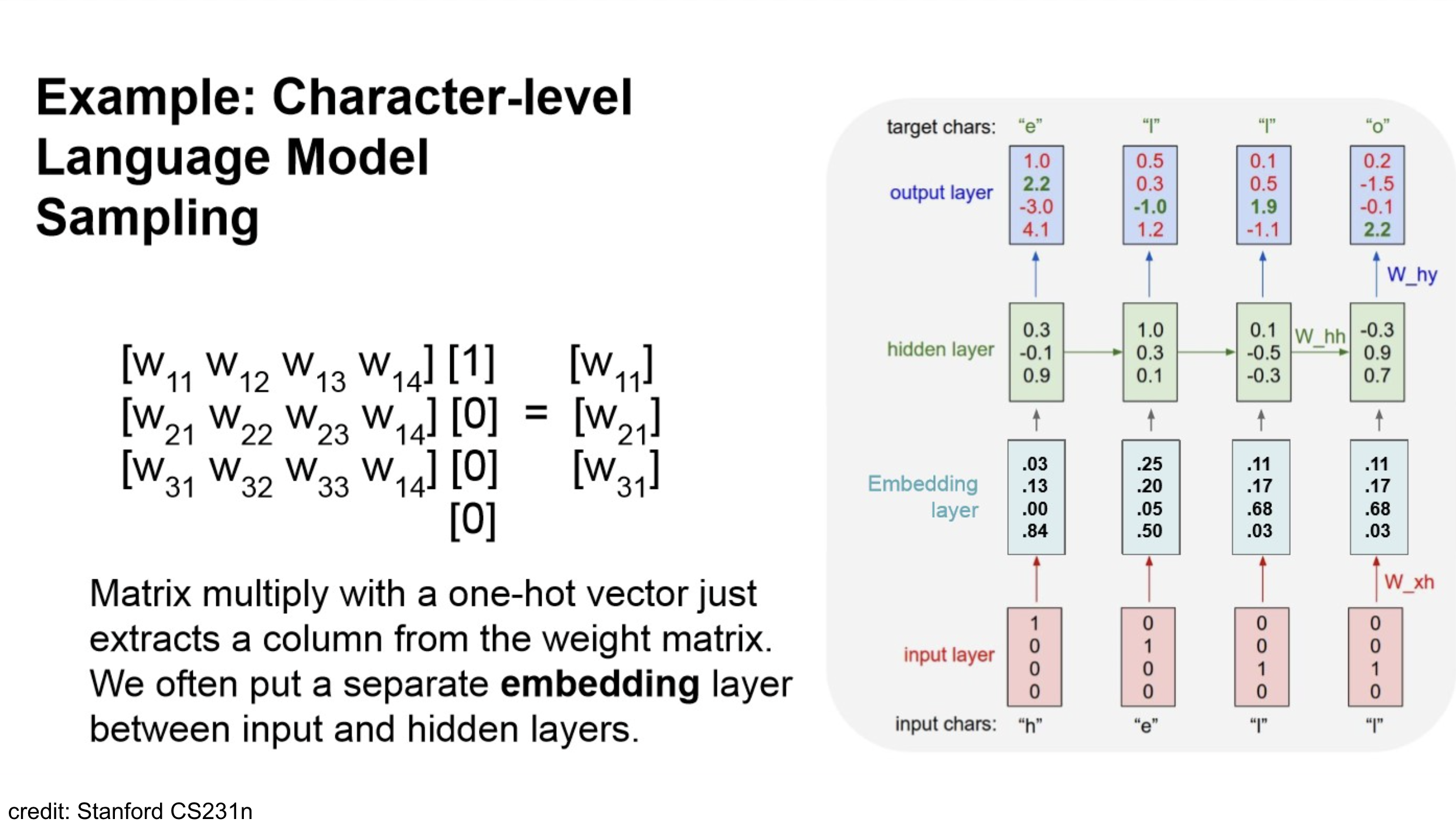
Example
Example
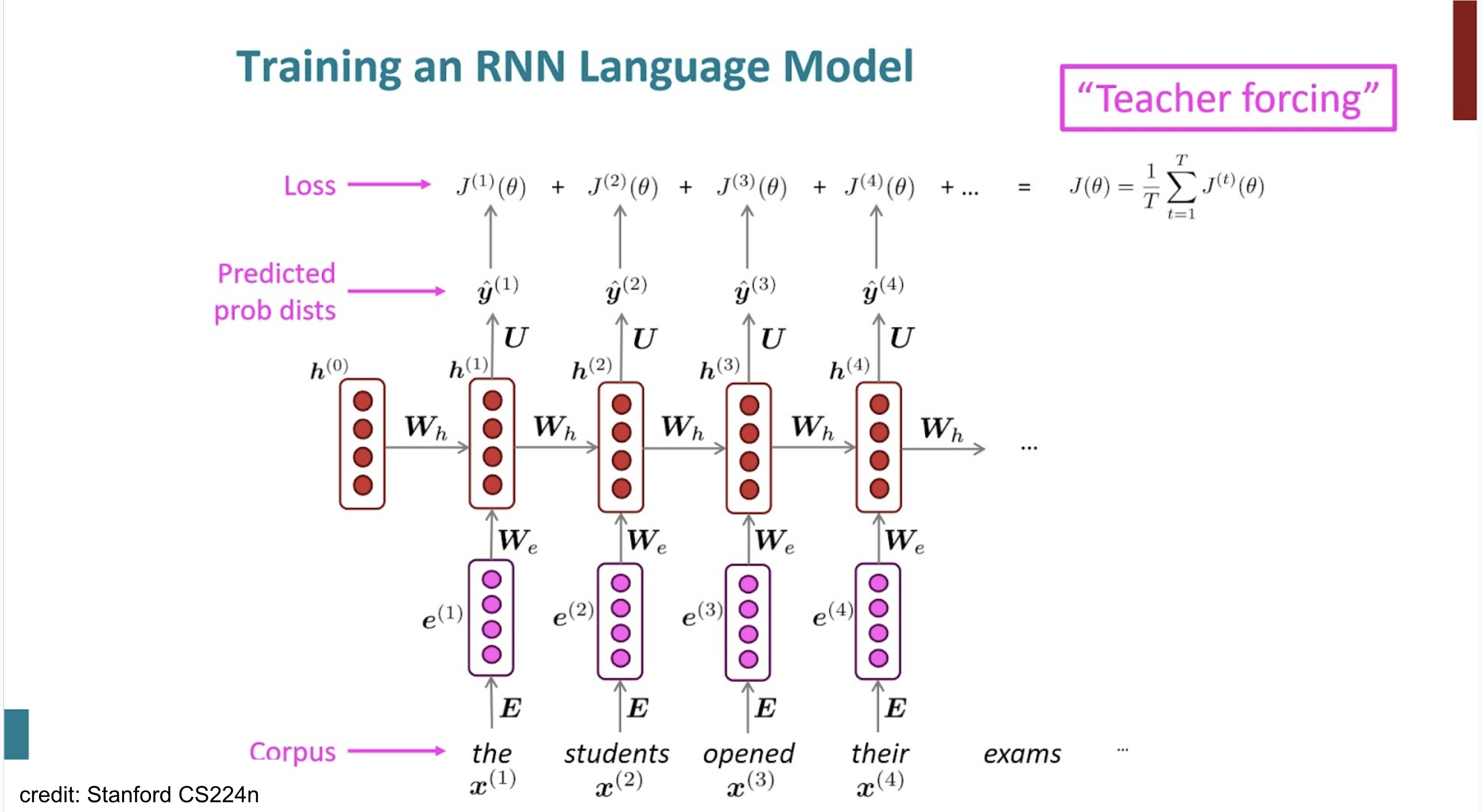
Training RNN
NOTE
각 는 neg log prob of wordTip
teacher forcing : 다음 step input에 model의 prediction이 아니라, ground truth label을 사용.(train시에만)
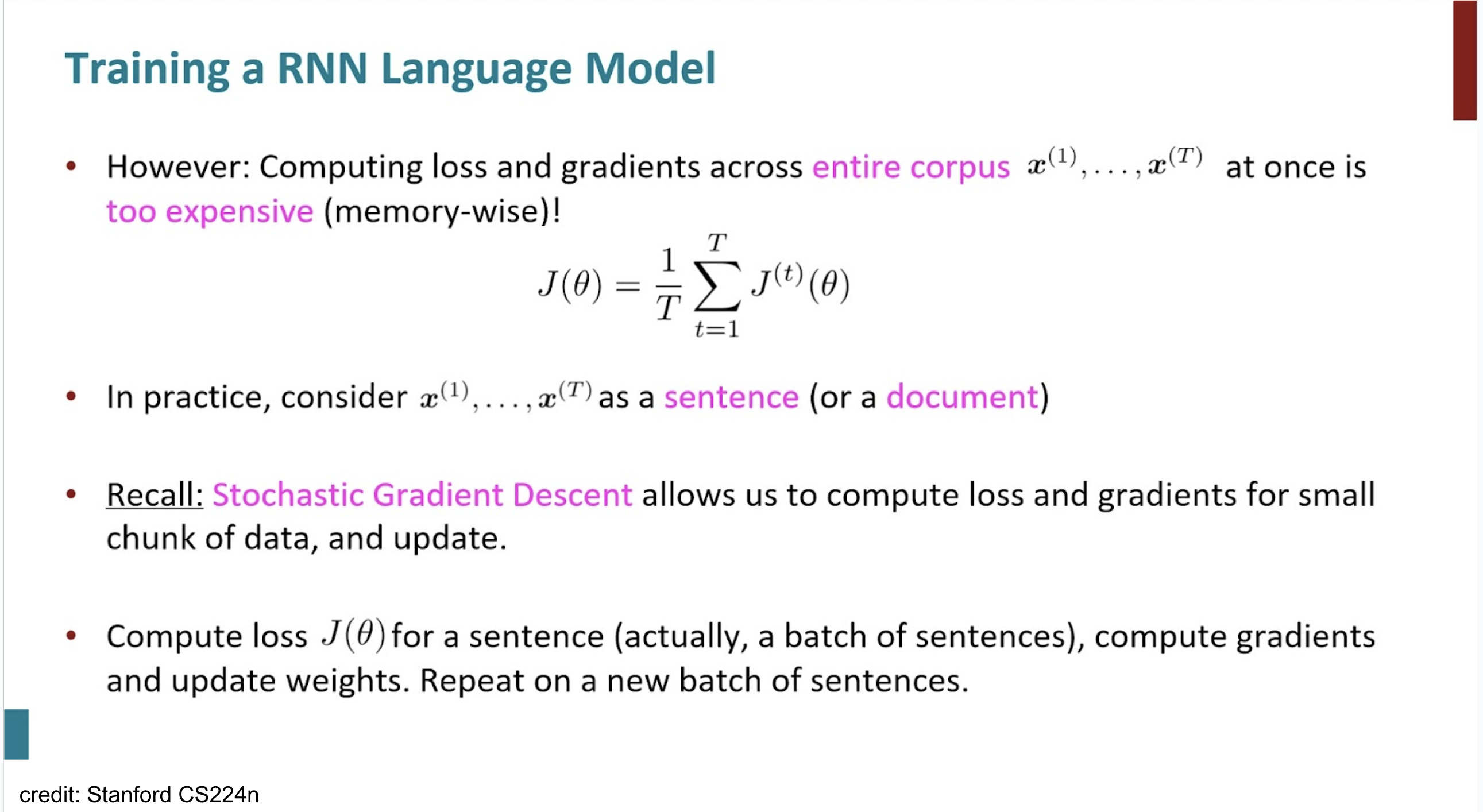
NOTE
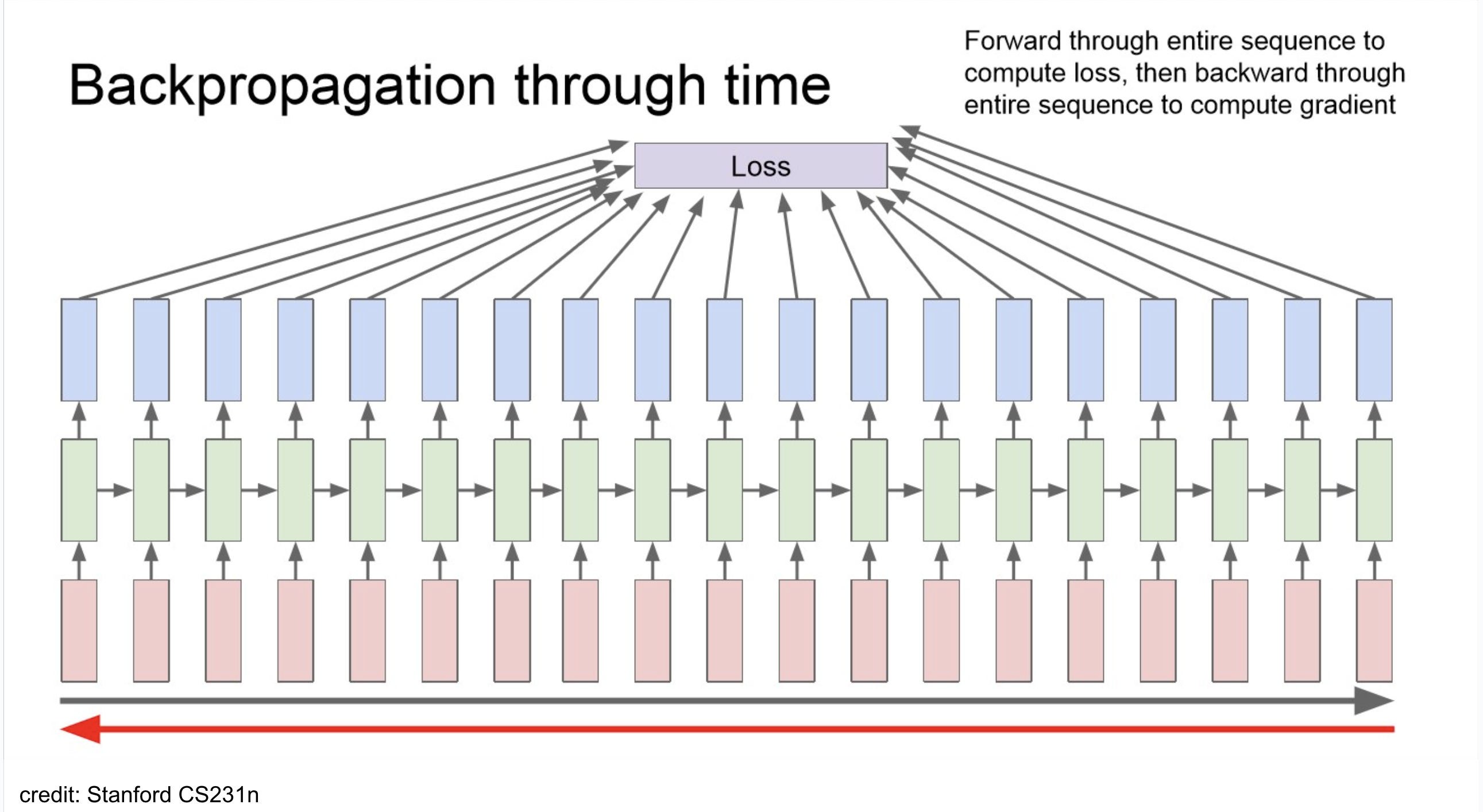
- large corpus내의 단어별로 backpropagation을 하는 건 너무 computation cost가 크다. 따라서 실제에는 문장 단위 정도로 이를 진행.
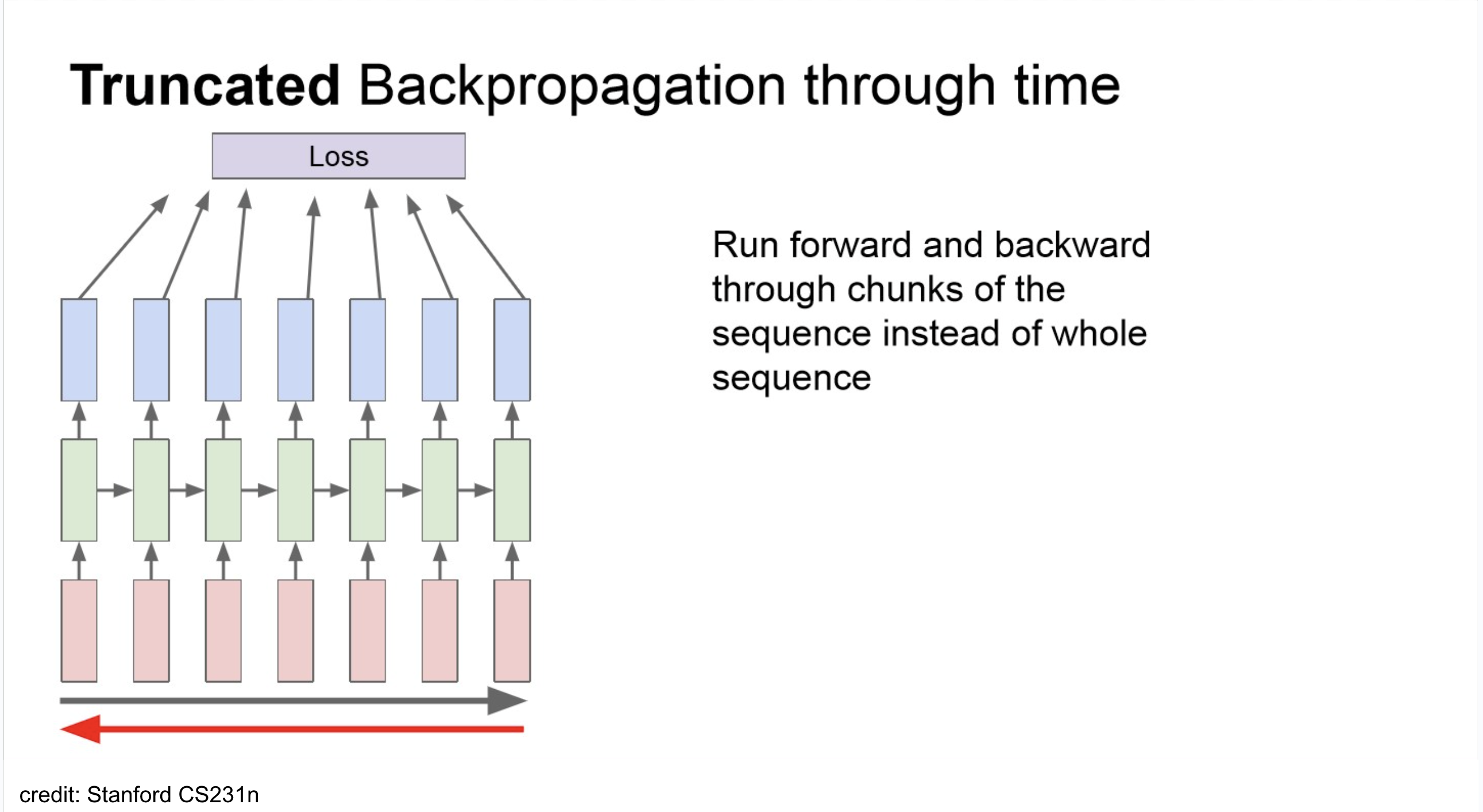
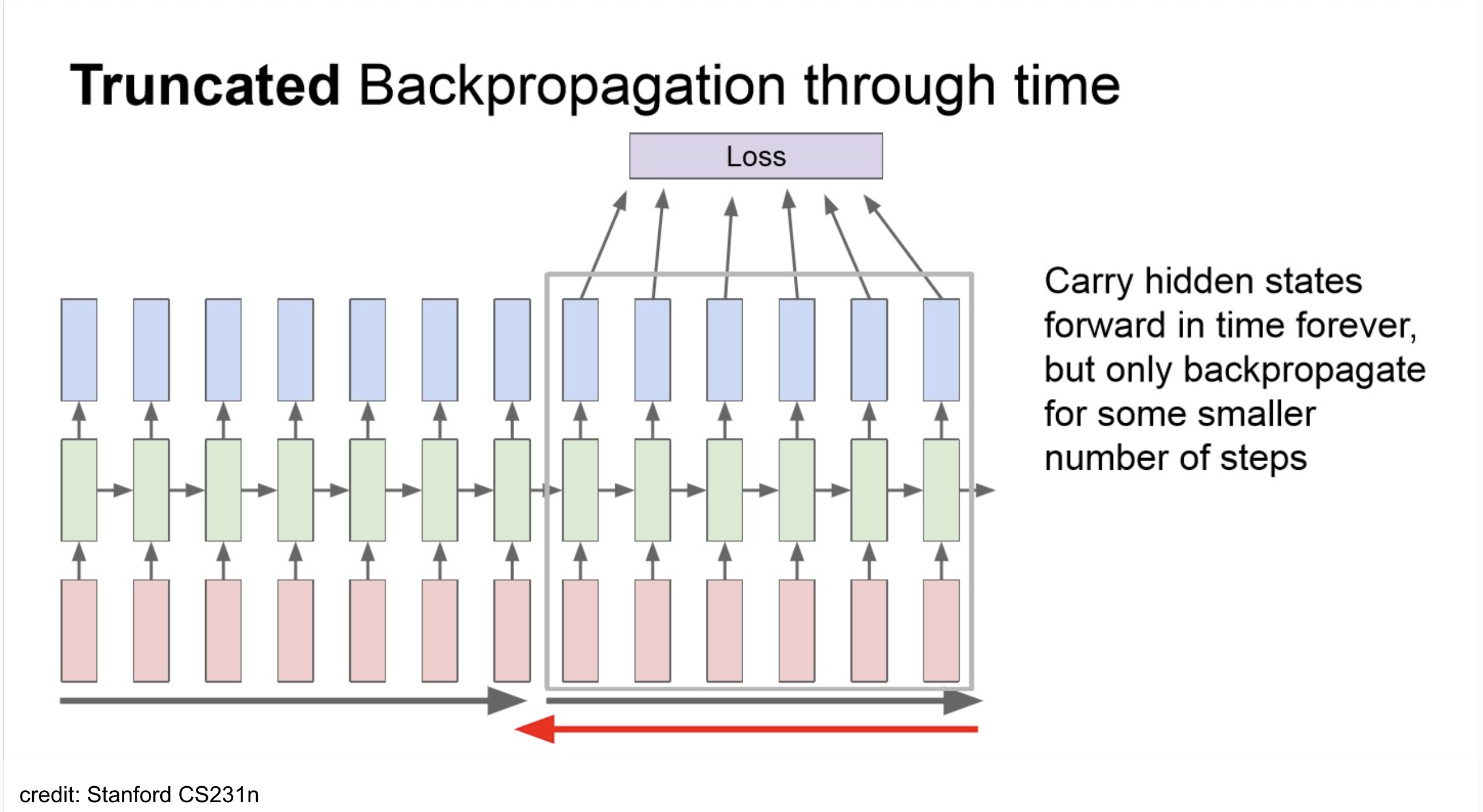
truncated backpropagation
NOTE
total loss를 다 하면 아래와 같겠지만,
implementation에서는 보통 아래처럼 쪼개서 backprop.
NOTE
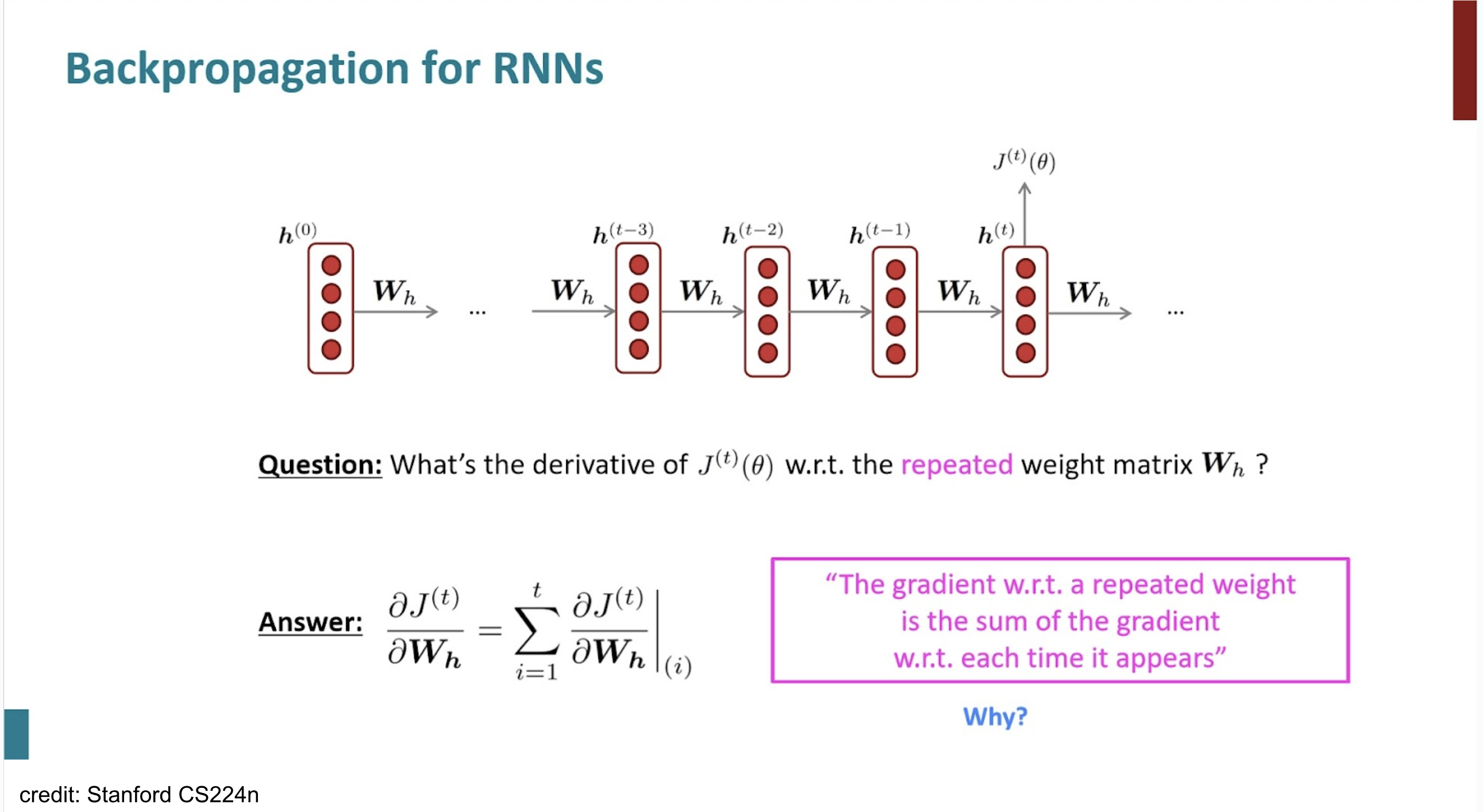
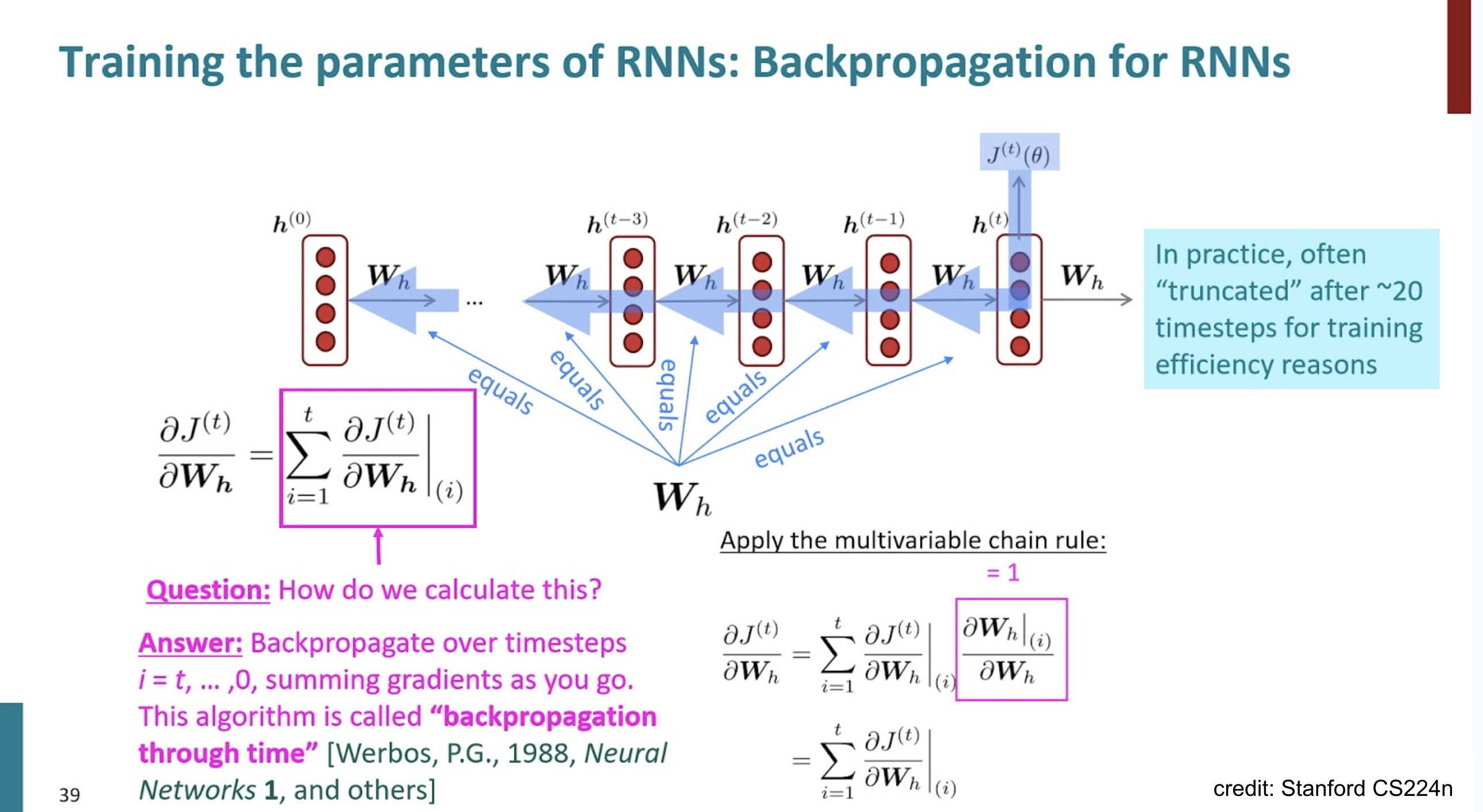
Backpropagation - gradient
Evaluation Metric
PerplexityTradeoffs of RNN
Success
- Can process any length input
- Computation for step t can (in theory) use information from many steps back
- Model size doesn’t increase for longer input
- Same weights applied on every timestamp, so there is symmetry in how inputs are precessed.
원본 링크Failure
- Recurrent computation is slow.
- In practice, difficult to access information from many steps back.
.png)
.png)
.png)