Gradient
In 1-dim:
the derivative of function:
In multiple-dim:
the gradient is a vector of (partial derivatives) along each dimension
Direction of gradient
Gradient의 방향 = 값이 가장 가파르게 증가하는 방향.
따라서 gradient-descent는 neg-gradient 방향으로 가야지.
Implementation
Numerical Calculation
optimization의 target인 의 gradient를 직접 numerically 계산하는 것은 매우 힘들다.(gradient vector의 ndim 만큼 만큼씩 계산해야 하니, loop를 너무 많이 돌아야 함.)
- approximate
- slow
- easy to write
Numerical Differentiation
Newton’s difference quotient에 따르면,
이지만, 아래처럼 대칭으로 계산하는게 더 낫다고 한다. Why??
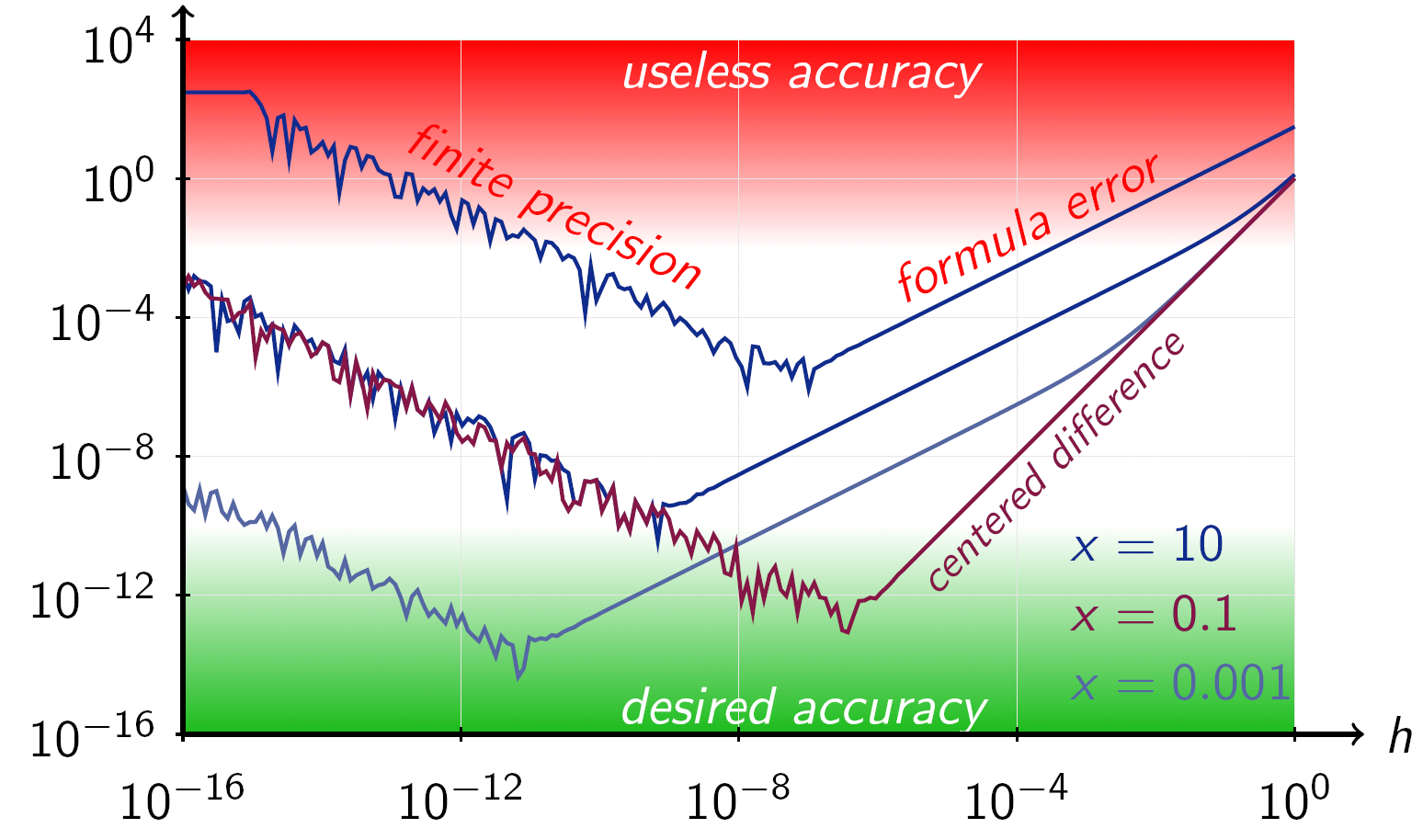
How to choose ?
For is undefined
Choose is trade-off:
- Rounding error(finite precision)
- Approximation error(wrong)
Elbow: with the machine precision
ex)
- . for single precision(32 bits)
- . for double precision(64 bits)
Analytic Calculation
where
- Data loss: ,
- Regularization:
라고 할 때, target은tips!) Loss는 의 함수이다.
it is,
- exact
- fast
- error-prone
Gradient check!
항상 gradient를 analytic하게 구할 줄 알아야 하지만, implementation을 numerical 하게 한다는 점을. 그리고 대응시켜본 다는 것을.