0. Abstract
Summary
- DeepSeekV2의 효율성
- 연산 요율 확보: MoE 채택하여 전체 규모는 236B인데 inference시 실제 activate되는 파라미터는 9% 정도인 21B 정도.
- 학습 비용 절감: 이전 모델인 67B 대비 42.5% 줄였다.
- KV-caching: inference 시 사용하는 메모리를 93.3% 줄임.
- throughput 향상: 이전 모델 대비 5.76배 많은 토큰 처리량을 확보.
- Core Methods:
- Multi-Head Latent Attention: Kv-cache를 압축하여 저장해서 KV-cache에 할당되는 메모리를 줄임.
- DeepSeekMoE : MoE 장점을 누림.
- Data & Alignment
- 데이터는 8.1T 규모의 다국어 고품질 코퍼스로 pre-train됨.
- SFT하고 RL(GRPO from DeepSeekMath paper)을 통해 Human-Alignment 됨.
1. Introduction
Summary
Scaling Law등으로 규모가 확보되면 성능이 오르니, 모델 파라미터를 계속 늘리는 방향으로 발전하고 잇는데, 문제는 리소스가 많이 필요해지고, inference throughput이 저하되는 문제.
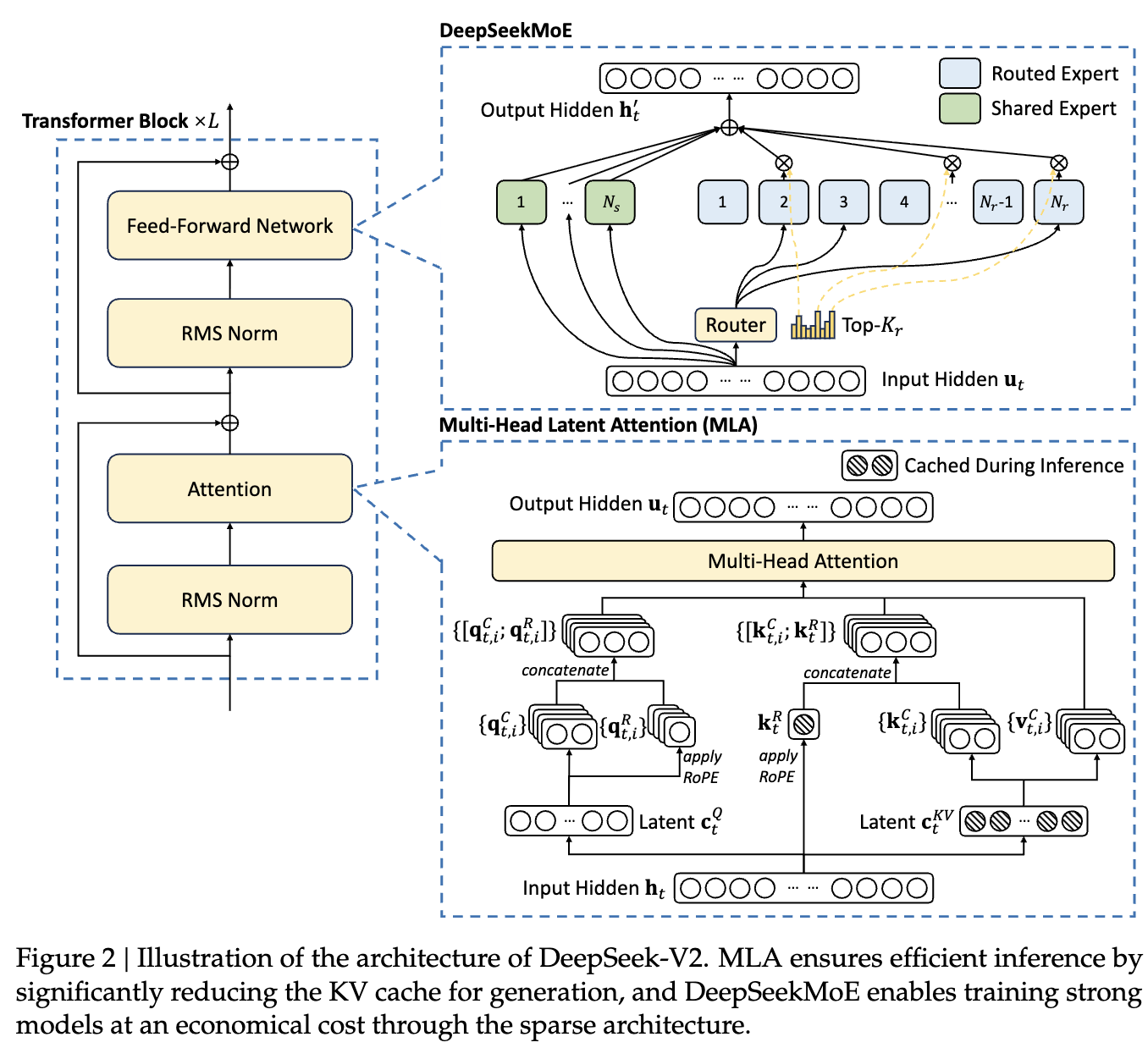
→ 를 해결하기 위해 DeepSeek에서는 MoE, MLA 제안.구조 자체는 Transformer(Attention + FFN)를 따르고,
- KV-cache 가 메모리를 많이 잡아먹으니 이를 해결하기 위해 기존에는
- GQA(Group-Query Attention)
- MQA(Multi-Query Attention) 등이 제안됨.
- 그러나 종종 성능의 희생이 뒤따름.
→ MLA 라는 low-rank key-value joint compression 을 사용한 attention을 제안함.
- FFN에는 DeepSeekMoE를 적용해서,
- fine-grained expert segmentation and shared expert isolation for higher potential in expert specialization
Train-Flow
- 8.1T 고품질 multi-source data로 pre-train
- 1.5M 규모의 다양한 대화 내용(math, code, reasoning 등) corpus로 SFT
- GRPO 사용해서 Human-alilgnmet 함.
Key Word
- Attention에는
- MLA-block
- FFN에는 DeepSeekMoE
- RMSNorm을 pre-norm 구조로 달고, Skip-Connection
- Decoupled Rotary Positional Encoding
- FFN
- DeepSeekMoE 구조이고,
- experts는
- Shared Experts : 항상 activate되는 모델.
- Routed Experts: router가 선택한 상위 개의 experts만 사용됨.
Check
Transformer가 크게 attention layer랑 FFN으로 구성되어 있어서, 각 파트에서
- global한 정보처리
- point-wise 정보처리 부분을 구분해 놓았으니,
현재 paradigm은 그 두 부분을 각각 나눠서 upgrade하는 느낌.
→ CNN 계열에서도 depth-wise separable convolution이란 개념도 흐름은 비슷.
→ global한 relation을 파악하고, 각 채널 별 정보를 따로 처리하고.
2. Architecture
Summary
- MLA
- DeepSeekMoE
2. 1. Multi-Head Latent Attention : Boosting Inference Efficiency
2. 1. 1. Preliminaries: Standard Multi-Head Attention
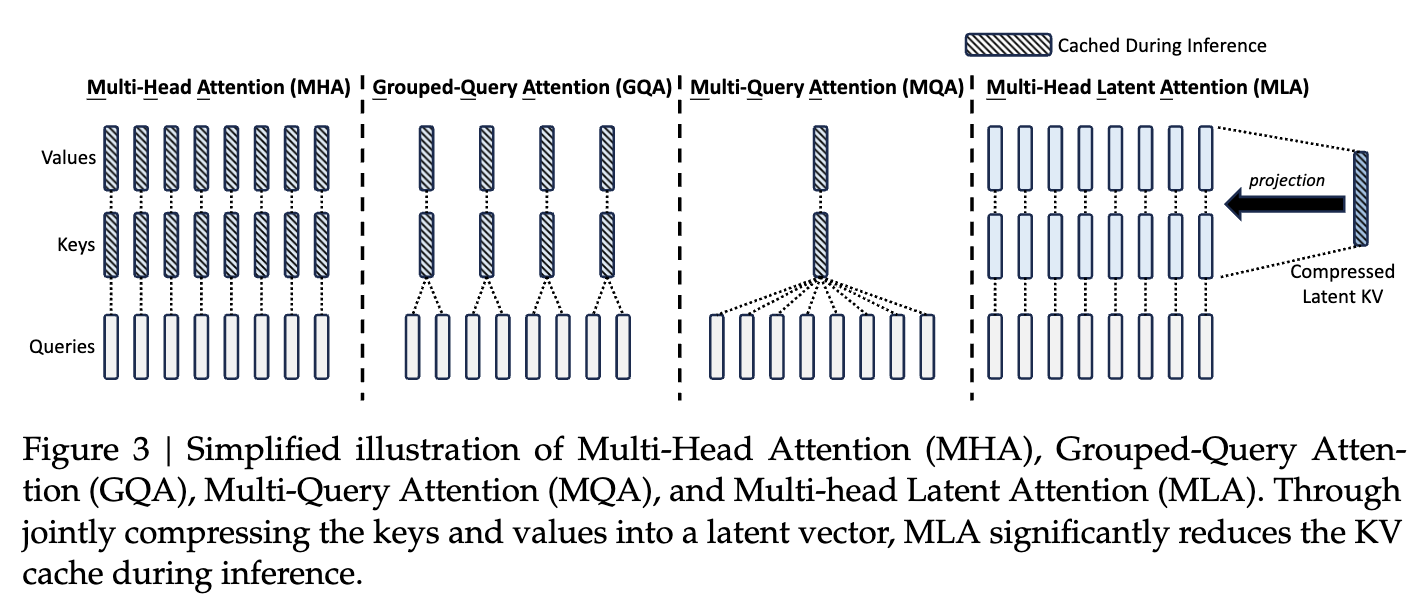
- 기존의 여러 방법들 중 MHA 및 더 효율적인 MHA 대체 방법들.
Summary
수식을 정리해보자면,
- q, k, v는 pojection-layer를 사용해서 hidden-state를 projection함.
- , ,
2. 1. 2. Low-Rank Key-Value Joint Compression
Summary
where
- : Compressed KV
- :