Activation Functions
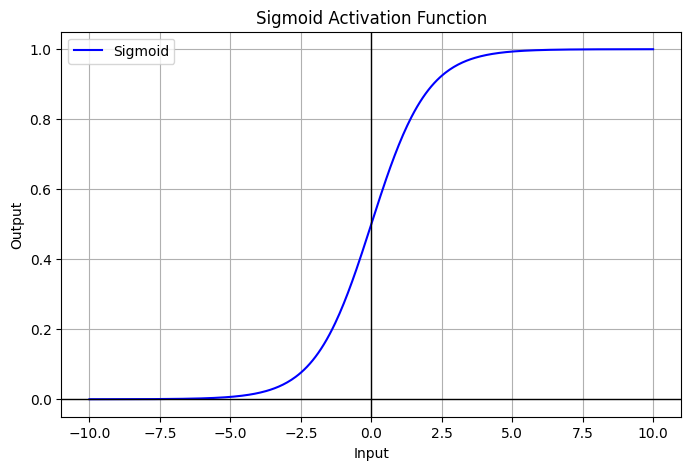
Sigmoid
Sigmoid
- activation 중 하나로 대표적으로 많이 사용됨.
- range:
- Neuroscience interpretation as saturating “firing rate” of neurons
Problems
- Saturation “kills” gradient : 입력 값의 절댓값이 커질수록 기울기 소실
- 특히나 layer가 깊어질수록, chain-rule에 의해 곱해지는 term들이 많아질텐데, 그러면 앞 쪽에 있는 layer 들일수록 learning되지 않을 수 있지.
- Outputs are not zero-centered → introduces bias after the layer
- sigmoid와 그 gradient는 항상 positive이기 때문에 model wight의 bias
- 라 할 때, =
- 모든 gradient는 동일한 부호를 가짐.
다음과 같이 구현.
원본 링크Sigmoid
def sigmoid(x: float) -> float: return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
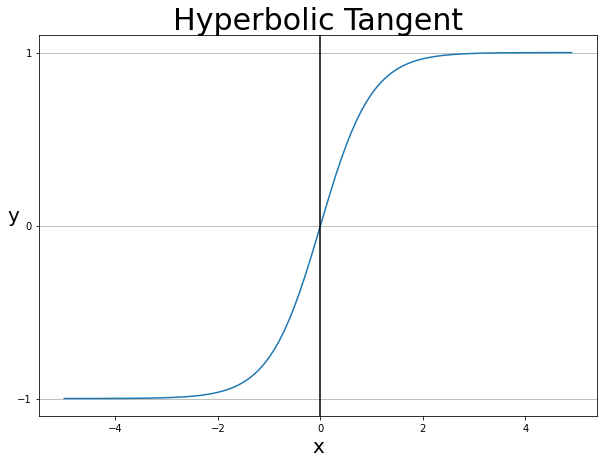
tanh
tanh(hyperbolic tangent)
- activation 중 하나로 대표적으로 많이 사용됨.
- range:
- anti-symmetric
- zero-centered
Problems
- Saturation “kills” gradient : 입력 값의 절댓값이 커질수록 기울기 소실
- 특히나 layer가 깊어질수록, chain-rule에 의해 곱해지는 term들이 많아질텐데, 그러면 앞 쪽에 있는 layer 들일수록 learning되지 않을 수 있지.
다음과 같이 구현.
원본 링크tanh
def tanh(x: float) -> float: return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
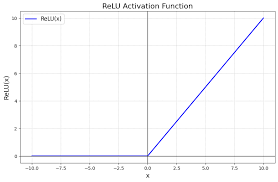
ReLU
ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit)
- activation 중 하나로 대표적으로 많이 사용됨.
- Does not saturate(for )
- Leads to fast convergence
- Computationally efficient
Problems
- No learning for → dead/dying ReLU
- downstream gradient가 0(input이 0 이하일 때,)
- often initialize with pos. bias ()
- Outputs are not zero-centered → introduces bias after the layer
- sigmoid와 그 gradient는 항상 positive이기 때문에 model wight의 bias
- 라 할 때, =
- 모든 gradient는 동일한 부호를 가짐.
다음과 같이 구현.
ReLU
def relu(x: float) -> float: return np.maximum(0, x)
- 단점들 보안을 위해 Leaky ReLU 등이 있음.
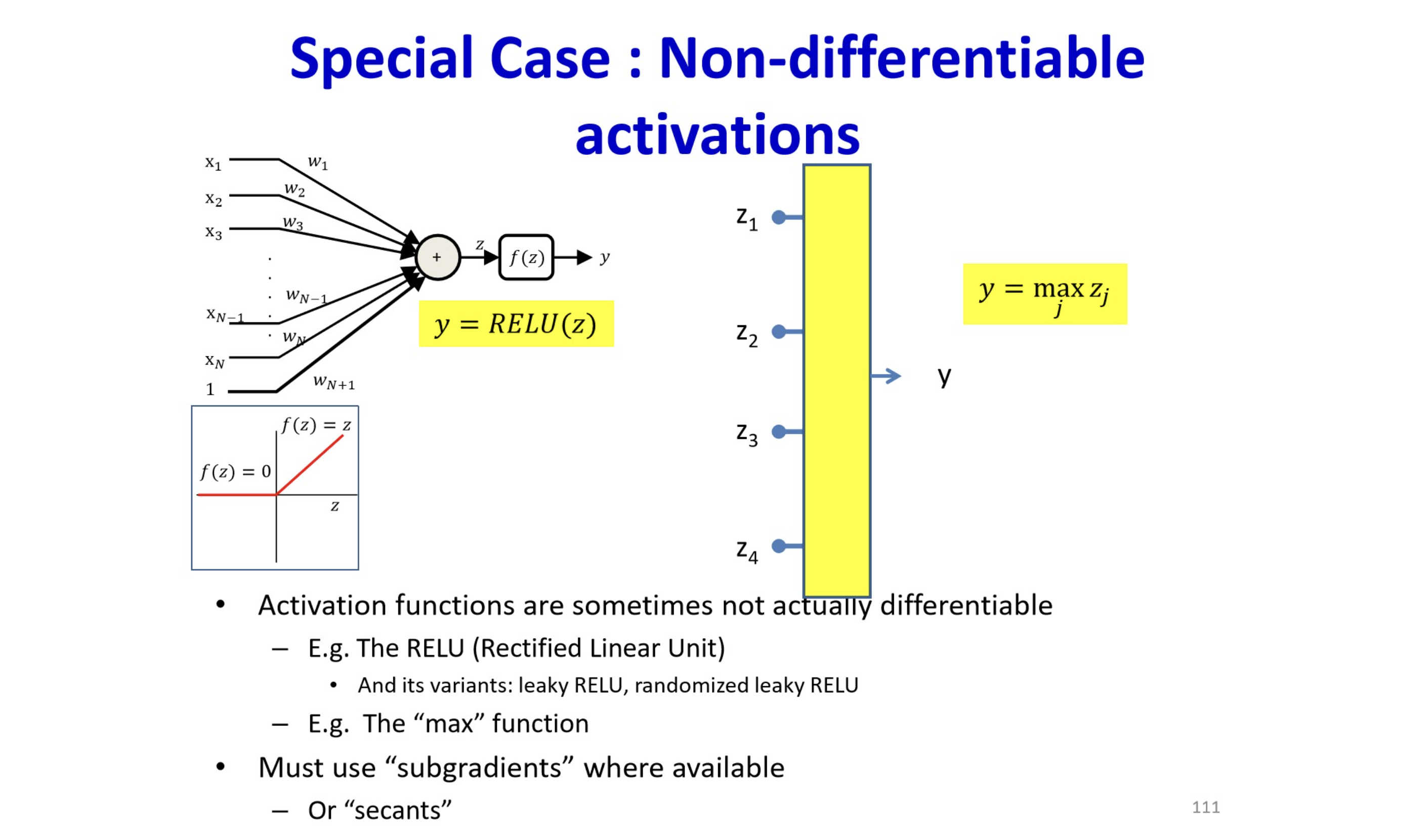
원본 링크How can we calculate non-differentiable function (like ReLU)?
Leaky ReLU
Leaky ReLU
- ReLU 보완형.
- Does not saturate(i.e., will not die)
- Closer to zero-centered outputs
- Leads to fast convergence
- Computationally efficient
원본 링크Parametric ReLU
좀 더 generalized 된 버전이고, Leaky에서 0.01에 해당하는 것 조차 모델이 학습시킴.
- Does not saturate(i.e., will not die)
- Parameter learned from data
- Leads to fast convergence
- Computationally efficient
ELU
원본 링크ELU(Exponential Linear Units)
x & \text{if } x > 0\\ \alpha (\text{exp}(x)-1) & \text{if } x \leq 0\\ \end{cases}$$ - All benefits of Leaky ReLU - Adds some robustness to noise - Default $\alpha = 1$
- Leaky ReLU 보완형.
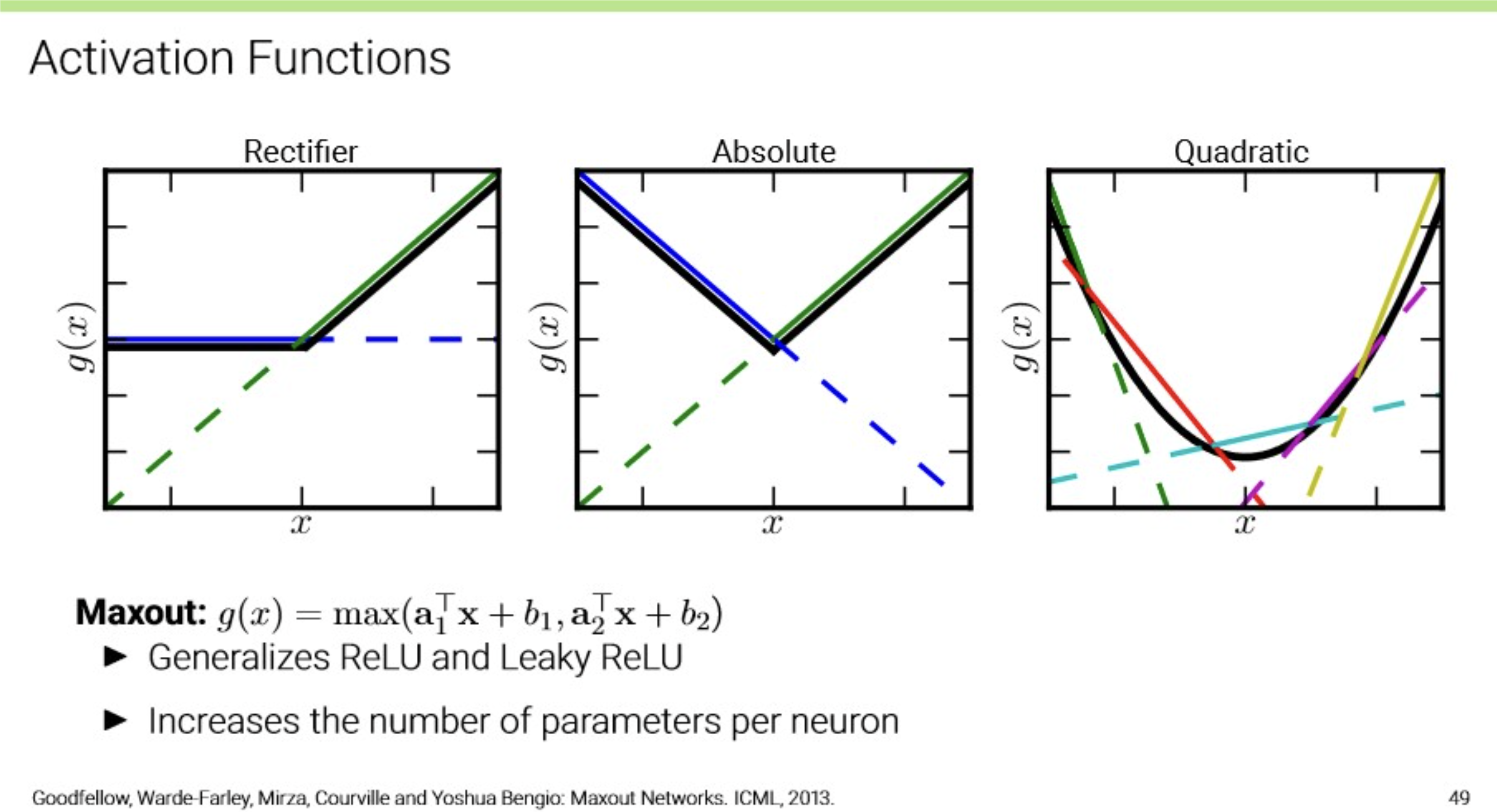
Maxout
Maxout
- Generalizes ReLU and Leaky ReLU
- Increases the number of parameters per neuron
원본 링크
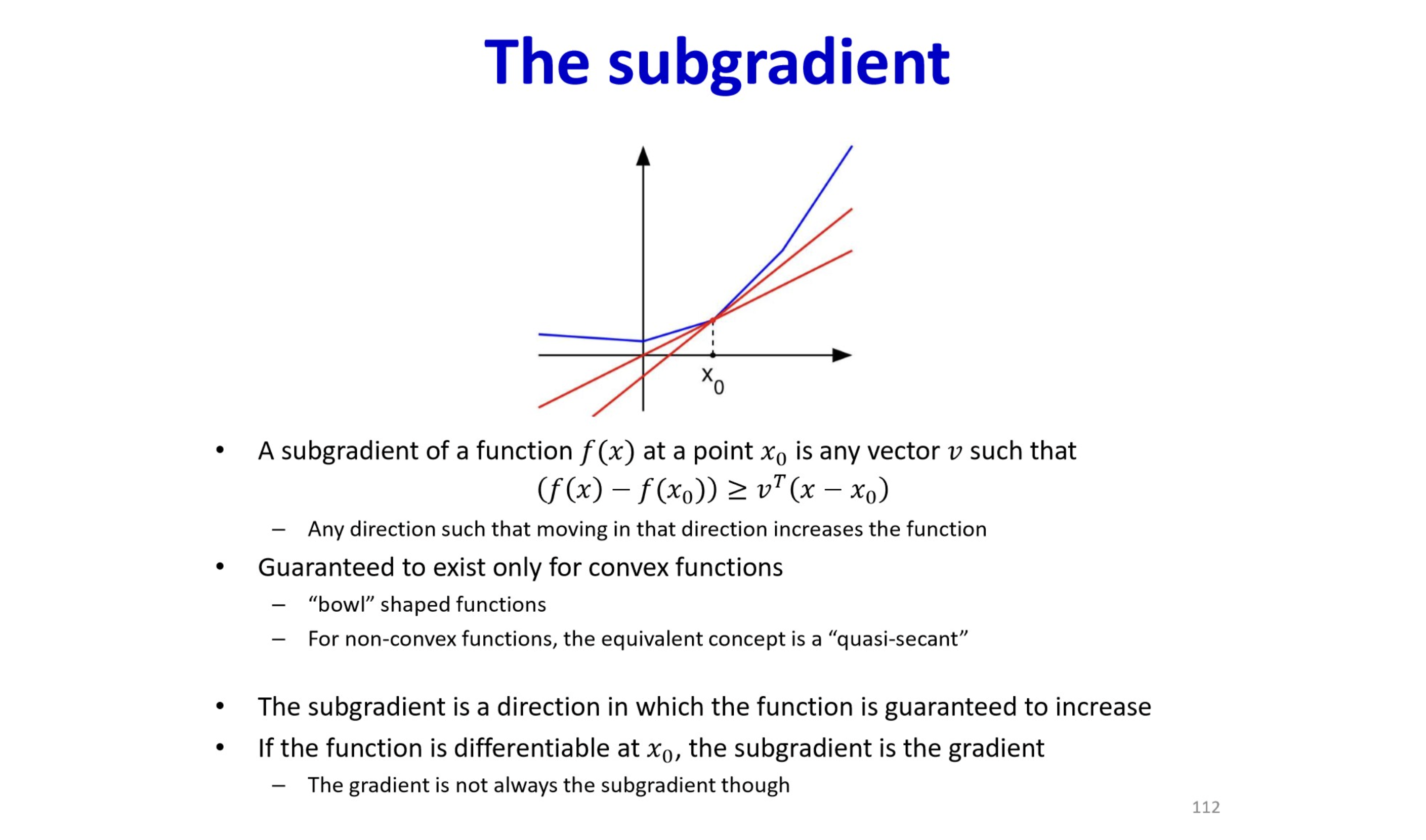
Subgradient
Subgradient
원본 링크
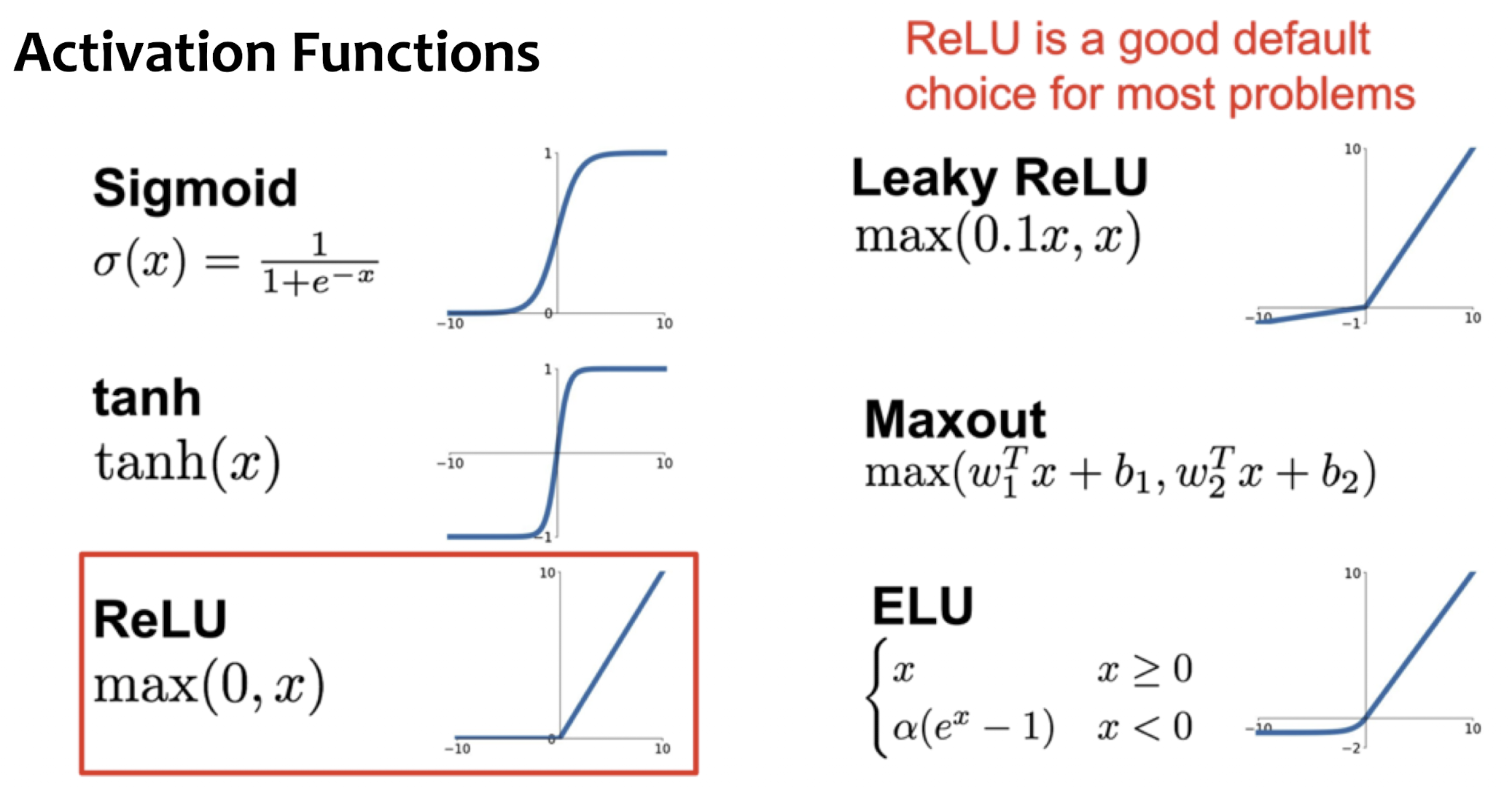
Activation Functions
- 나중에 transformer 계열에 최근 가장 많이 사용되는 GeLU 계열이나 찾아볼 것.
Summary
- No one-size-fits-all: Choice of activation function depends on problem.
- We only showed the most common ones, there exist many more
- Best activation function / model is often using trial-and-error in practice
- It is important to ensure a good “gradient flow” during optimization
Rule of Thumb
- Use ReLU by default(with small enough lr)
- Try Leaky ReLU, Maxout, ELU for some small additional gain
- Prefer Tanh over sigmoid(Tanh often used in RNNs)
ReLU
ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit)
- activation 중 하나로 대표적으로 많이 사용됨.
- Does not saturate(for )
- Leads to fast convergence
- Computationally efficient
Problems
- No learning for → dead/dying ReLU
- downstream gradient가 0(input이 0 이하일 때,)
- often initialize with pos. bias ()
- Outputs are not zero-centered → introduces bias after the layer
- sigmoid와 그 gradient는 항상 positive이기 때문에 model wight의 bias
- 라 할 때, =
- 모든 gradient는 동일한 부호를 가짐.
다음과 같이 구현.
ReLU
def relu(x: float) -> float: return np.maximum(0, x)
- 단점들 보안을 위해 Leaky ReLU 등이 있음.
원본 링크How can we calculate non-differentiable function (like ReLU)?
Sigmoid
Sigmoid
- activation 중 하나로 대표적으로 많이 사용됨.
- range:
- Neuroscience interpretation as saturating “firing rate” of neurons
Problems
- Saturation “kills” gradient : 입력 값의 절댓값이 커질수록 기울기 소실
- 특히나 layer가 깊어질수록, chain-rule에 의해 곱해지는 term들이 많아질텐데, 그러면 앞 쪽에 있는 layer 들일수록 learning되지 않을 수 있지.
- Outputs are not zero-centered → introduces bias after the layer
- sigmoid와 그 gradient는 항상 positive이기 때문에 model wight의 bias
- 라 할 때, =
- 모든 gradient는 동일한 부호를 가짐.
다음과 같이 구현.
원본 링크Sigmoid
def sigmoid(x: float) -> float: return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))원본 링크tanh
tanh(hyperbolic tangent)
- activation 중 하나로 대표적으로 많이 사용됨.
- range:
- anti-symmetric
- zero-centered
Problems
- Saturation “kills” gradient : 입력 값의 절댓값이 커질수록 기울기 소실
- 특히나 layer가 깊어질수록, chain-rule에 의해 곱해지는 term들이 많아질텐데, 그러면 앞 쪽에 있는 layer 들일수록 learning되지 않을 수 있지.
다음과 같이 구현.
원본 링크tanh
def tanh(x: float) -> float: return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))