Loss Function
Loss(Cost)
Learning 이라는 것은 “Loss”를 “Optimization” 하는 것.
model의 output이랑 target(label)이 최대한 비슷할 때 이 값이 작아지는 방향으로 보통 define함.
확률 분포 간 차이로 볼 수도 있다.
- classification task에서는 마지막 layer가 분류할 target class 개수랑 dim이 같은데, 이를 softmax하면 확률 분포가 model의 최종 output이라고 볼 수 잇다.
- 따라서 learning은 output probability distribution과 target probability distribution을 최대한 비슷하게 해주는 방향으로 진행되어야 한다.
- 확률 분포 차이를 나타내는 지표로 KL-divergence라는 지표를 쓸 수 있고, metric 조건을 정확히 만족하진 못하지만, 대략 distance 개념 정도로 이해할 수 있다.
- d > 0, d(x, x)=0 → x=0, triangular-ineq
How to design a good loss function?
Abstract
- A loss function can be any differentiable function that we wish to optimize
- Deriving the cost function from the Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) principle removes the burden of manually designing the cost function for each model.
- Consider the output of the neural network as parameters of a distribution over
(: log-likelihoood 로 변환)Regression Loss
Regression - estimation target
regression이란, 결국
즉, output은 real-value 한 개.
- regression을 수행하는 모델이 예측하는 에러 Gaussian distribution으로 보자!
- target 값은 gaussian의 mean value.
- Mean Square Error(MSE)
- Mean Absolute Error(MAE)
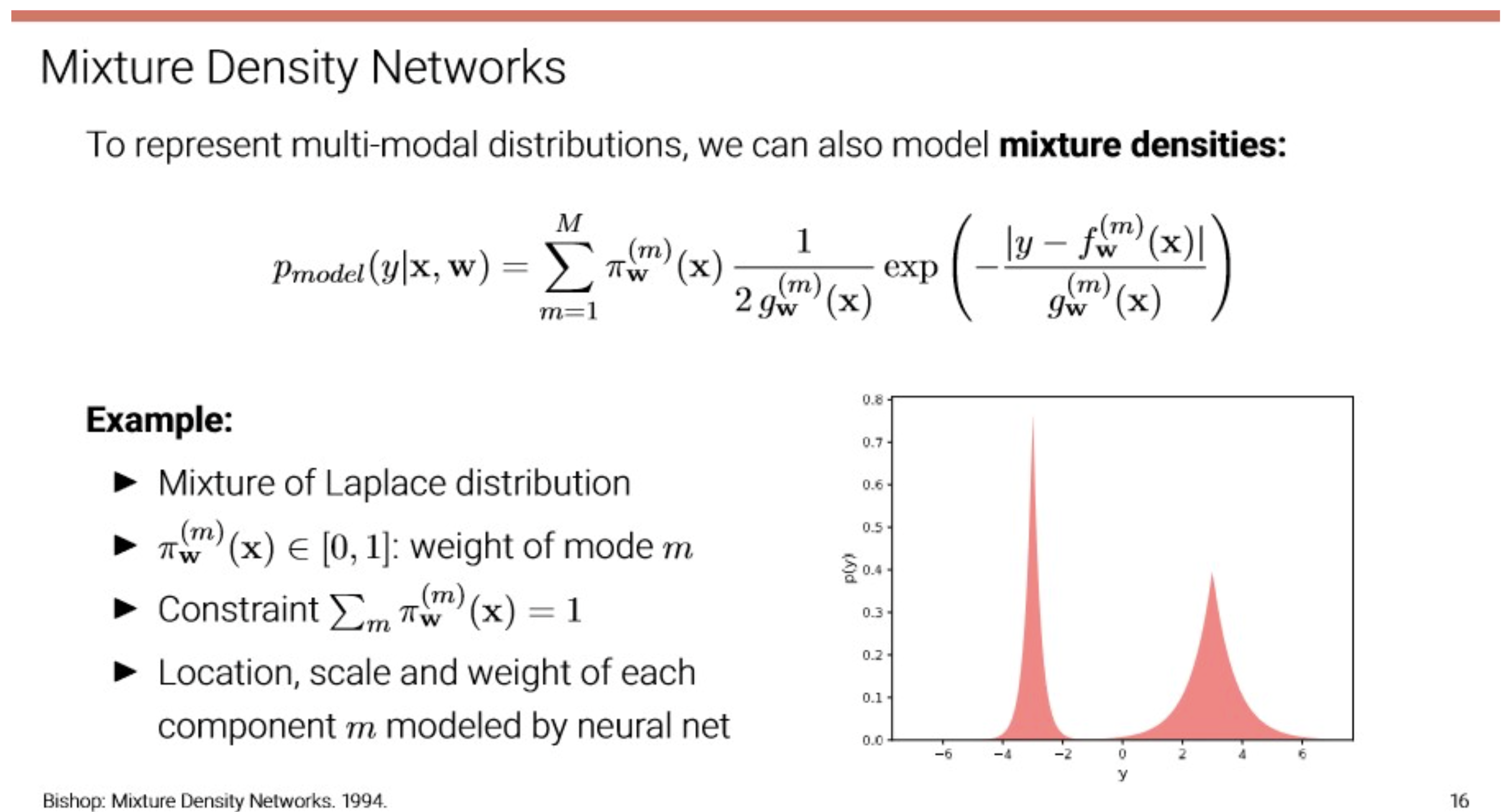
- 여러 분포가 섞인?
Classification Loss
Classification - estimation target
classification이란, 결국
즉, output은 real-value vector.
- classification을 수행하는 모델이 예측하는 것은
- 2 classes: regression with sigmoid로 확률을 바로 뽑던지, 아니면 softmax를 사용.
- BCE(Binary Cross-Entropy) Loss
- more than 2: 일반적으로 softmax
- CE(Cross-Entropy) Loss
Softmax - Logistic regression
Logistic regression
원본 링크Logistic regression
logistic regression의 경우, linear regression의 output을 확률값 범위로 고정해주는 activation function(tanh)을 적용한 걸로 볼 수도 있는데, classification task에 수행할 수 있다는 점을 잘 기억하자!
h(\mathrm{x}) & \text{if}\; y = 1 \\ 1 - h(\mathrm{x}) & \text{if}\; y = 0 \end{cases}$$ 이걸 좀 compact 하게 한 줄로 써보면, $$P(y|\mathrm{x}) = a^y(1-a)^{(1-y)}$$
→ ouput 값이 확률 값의 범위에 무조건 떨어지니까.
수식으로는 아래와 같이 model 을 define하고,
model의 output을 posterior 해석.Expand to BCE
위의 식에서 여러 개의 데이터가 i.i.d. 가정을 통해 뽑혔다고 한다면,
여기서, MLE
where
실제 compute 할 때에는 log 씌우는 게 값이 stable하여 log를 씌운 이후 계산한다고 하는데 정확히 어떠한 말일까..?
또한, 값을 maximizing 하는 것 보다는 minimizing 하는게 편하기 때문에(??) negative log-likelihood를 minimizing 한다.
Expand to Multiple Classes
Categorical distribution을 다음과 같이 정의
따라서 probability distribution은
로 표현될 수 있고,
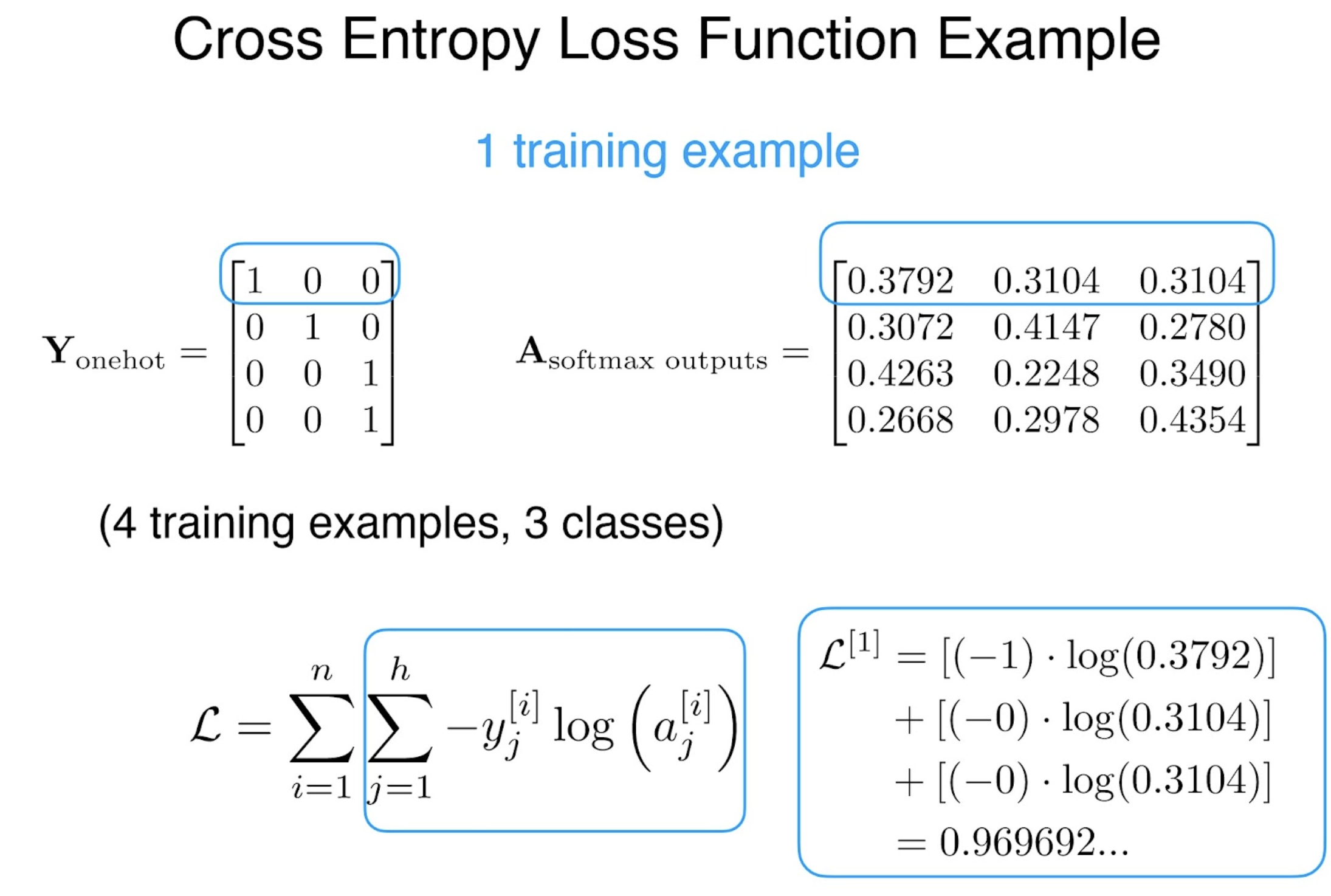
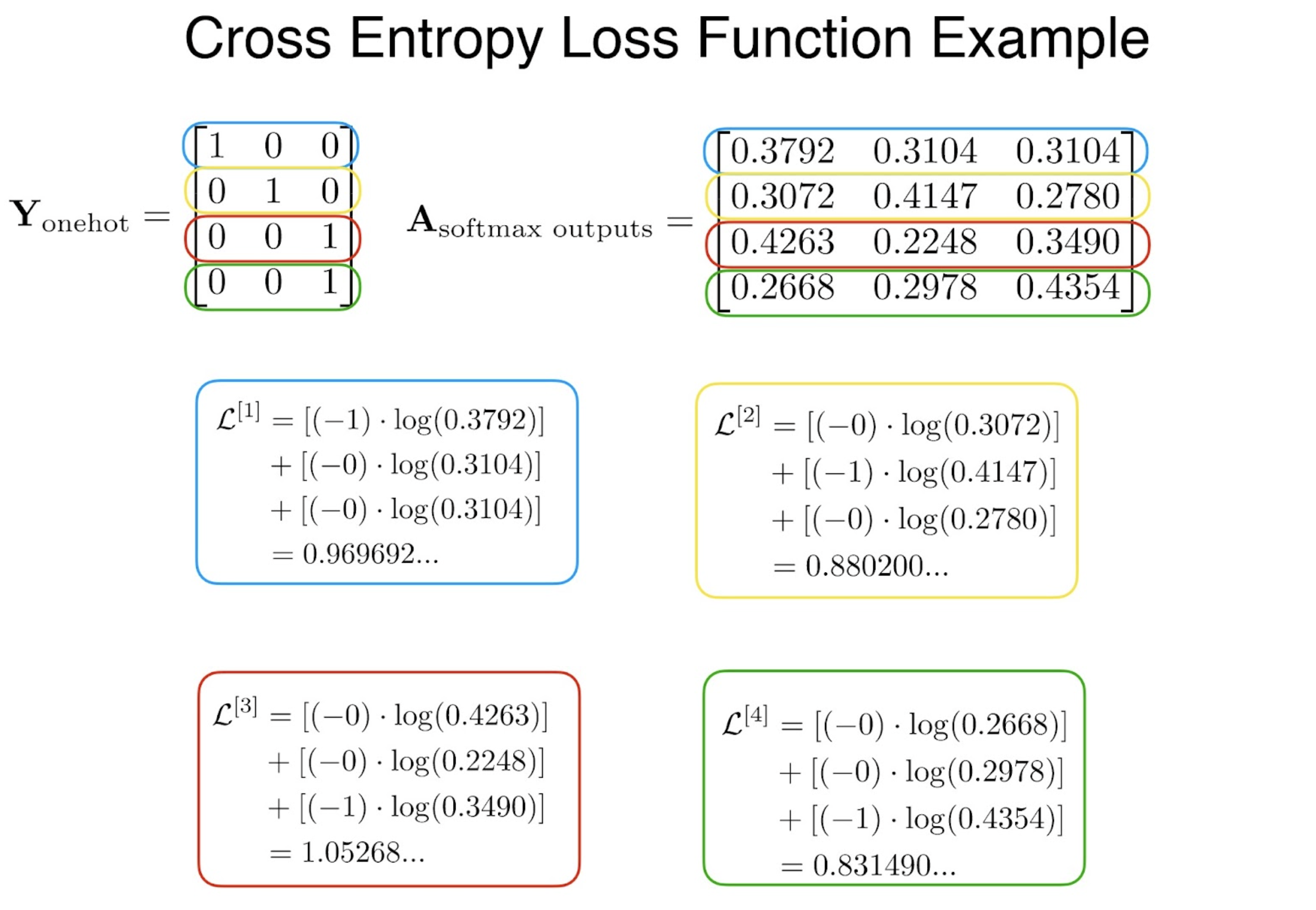
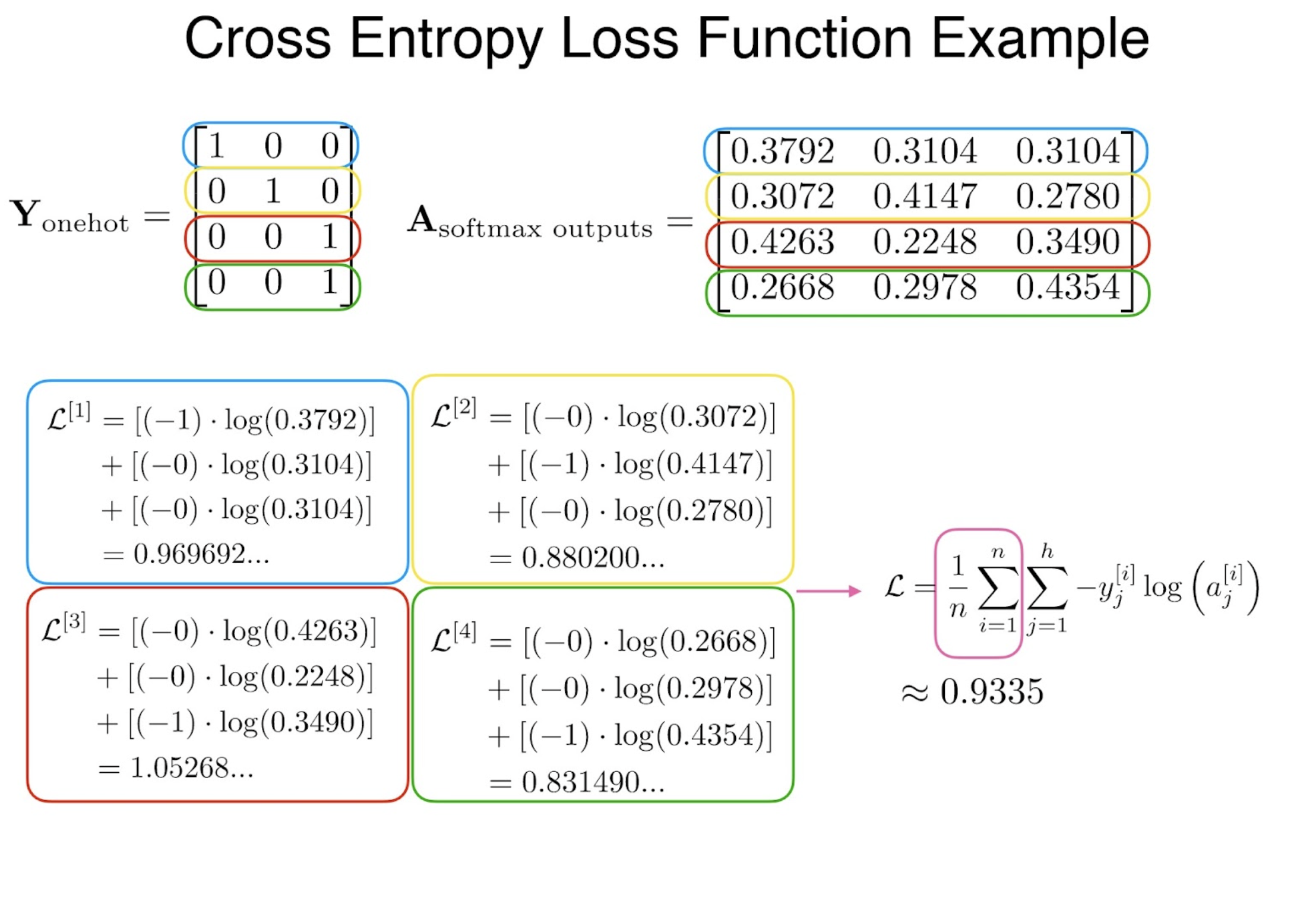
: One-hot vector로CE(Cross-Entropy) Loss?
Let
then we obtain,
In other words, we minimize the cross-entropy loss(CE loss).
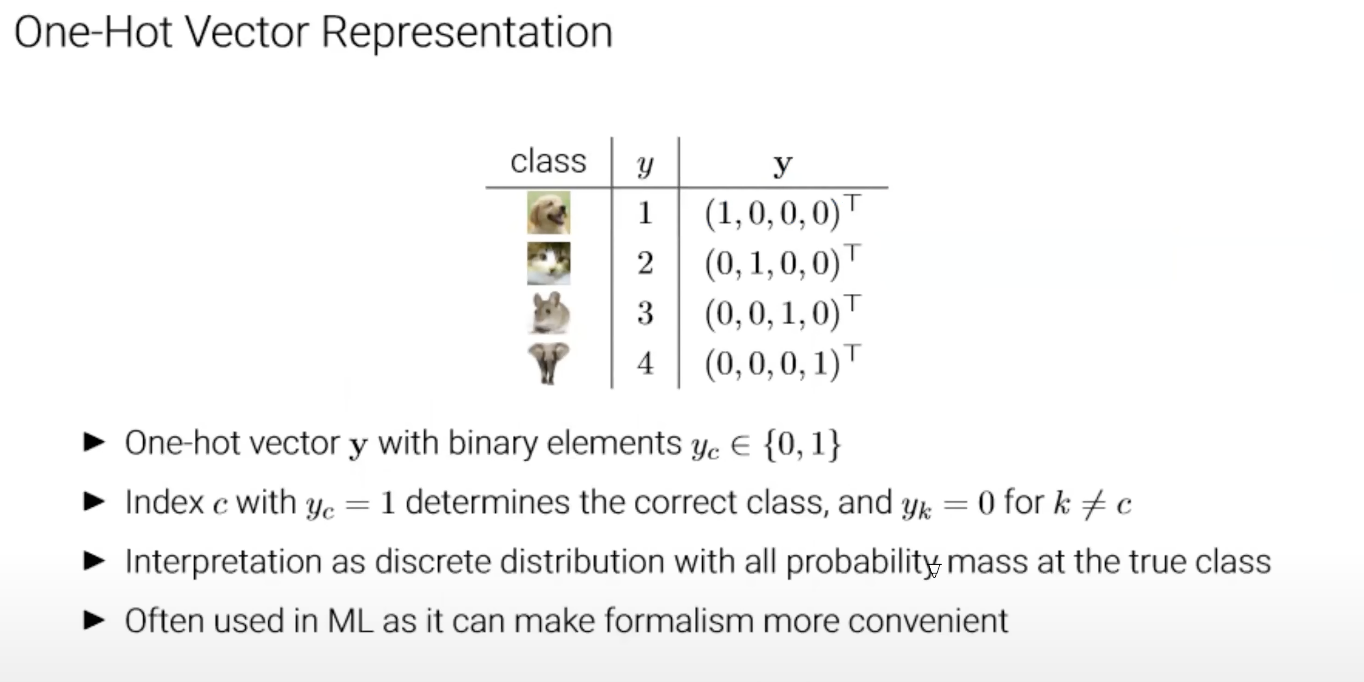
The target is a One-hot vector with its c’th element.원본 링크CE-Loss
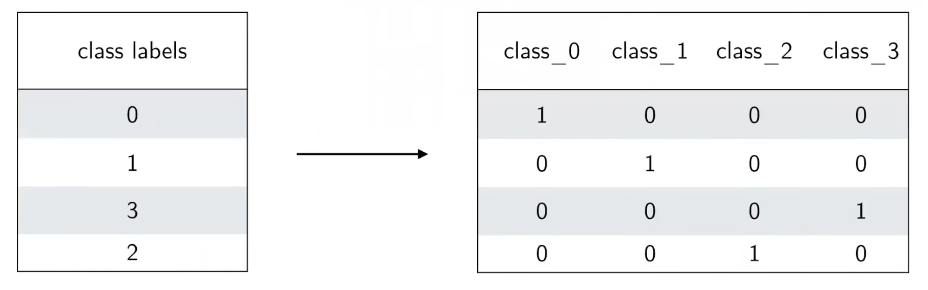
One-hot vector
one-hot vector : one-hot encoding
one-hot vector: true class만 1, 나머지 category에 대해서는 0
원본 링크
Regularization
Regularization
Let
만일 우리가 를 만족하는 파라미터 를 찾았다고 한다면, 그게 unique할까?
→ Nope. 도 동일하게
Regularization: prevent the model from doing too well on training data. overfitting을 피하려는 전략 중 하나. 수식으로 보자면,
앞의 term이 Data Loss, 뒤의 term 이 penalty, regularization term.
model complexity가 커지면, generalization 관점에서 모델이 너무 train set에만 익숙해져 이를 피하려고 regularization을 사용.Occam's Razor
“Simple is the best.”
Among the multiple competing hypotheses, the simplest is the best.Examples
L2-Regularization
L1-Regularization
Elastic-Net(L1 + L2)
Why Regularization?
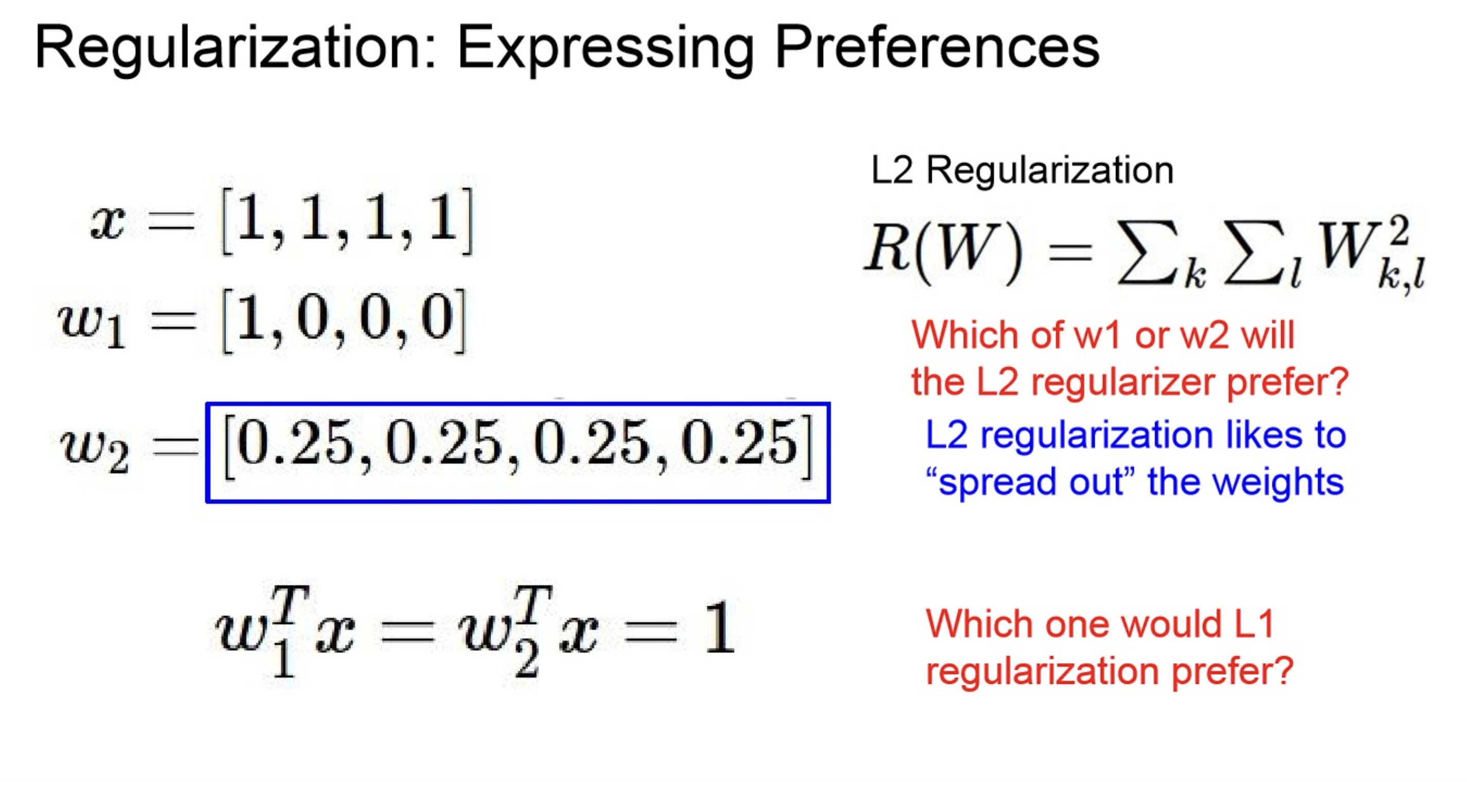
- Express preferences over weights
- Make the model simple so it works on test data
- Improve optimization by adding curvatures
원본 링크Regularization - parameter preference
위 상황에서 는 uniform한 , 은 sparse한 을 더 선호한다.