Summary
“Count-based의 전역 정보 + Word2Vec의 학습적 효율성을 결합한 모델”
Count-based vs Direct prediction
Multi column
Count based LSA, HAL (Lund & Burgess), COALS, Hellinger-PCA (Rohde et al, Lebret & Collobert)
- Fast training
- Efficient usage of statistics
- Primarily used to capture word similarity
- Disproportionate importance given to large counts
Direct Prediction Skip-gram/CBOW (Mikolov et al) NNLM, HLBL, RNN (Bengio et al; Collobert & Weston; Huang et al; Mnih & Hinton)
- Scales with corpus size
- Inefficient usage of statistics
- Generate improved performance on other tasks
- Can capture complex patterns beyond word similarity
Important
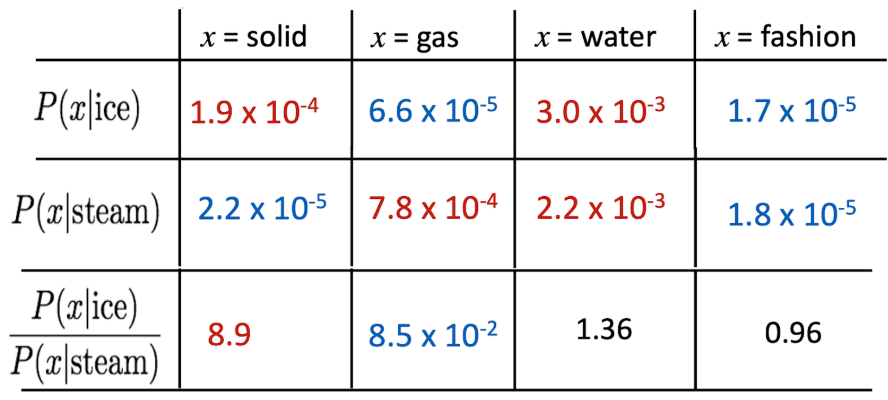
“Crucial insight: Ratios of co-occurrence probabilities can encode meaning components”
- 를 보면, ice랑 더 관련 있음. 이러한 확률 비를 vector space에 모델링 하는 것이 GloVe
위의 걸 어떻게 Design?
Q: How can we capture ratios of co-occurrence probabilities as linear meaning components in a word vector space (i.e., embedding ratios of co-occurrence probabilities)?
A: Log-bilinear model
with vector differencs
GloVe
Summary
count base, direct prediction을 합치니,
- fast training
- scalable to huge copora
- good performance even with small corpus and small vectors