Summary
LLM을 다루는 전반적인 지식을 아주 얕고 넓게 아우르는 book.
Chap 1. Introduction
1.3 Evolution from Traditional NLP Models to State-of-the-Art LLMs
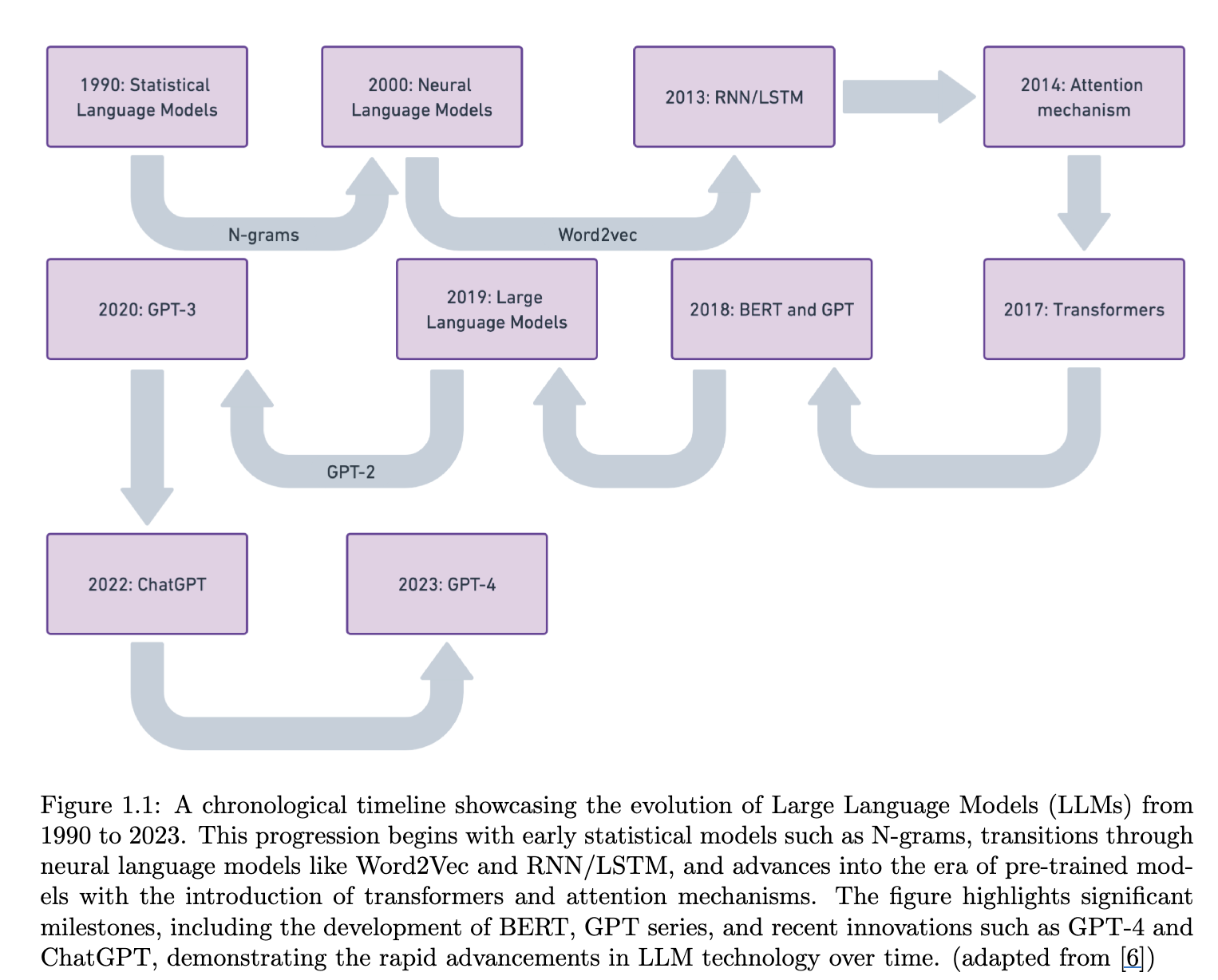
1.3.1 Statistical Language Models (SLMs)
- 통계 데이터를 기반으로 Maximum Likelihood Estimation 기법으로 모델을 fit하곤 함.
- n-gram 등이 있음.
- 가정으로는 Markov Assumption(n-step)
- Task는 NTP.
Attention
Sparsity problem : 특히나 n-gram의 경우, n 값이 커지면 쉽지 않지.
Long-term dependencies : 일반적으로 4,5-gram까지가 한계이니, context가 매우 작지.위 두 문제가 trade-off라 해결치 못함.
1.3.2 Neural Language Models (NLMs)
Important
Word 를 Vector로 보자!
Semantic를 latent space로 projection하자.
1.3.3 Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs)
- Pre-train & Fine-Tuning Paradigm이 Improving Language Understandingby Generative Pre-Training, GPT 논문을 통해 LM 모델들이 따르는 표준 학습 패러다임으로 자리잡음.
- 대표적으로 GPT, BERT가 있음.
1.3.4 Large Language Models (LLMs)
- 방대한 양의 데이터로 학습되는 모델들.
- 대표적으로 GPT, Llama, PaLM 등이 있음.
- 최근 방법들은 pretrain → human-alignment, 2-step 흐름.
1.4 Overview of Current Leading LLMs
현재 업계 대표 모델들로는
- OpenAI의 GPT3, GPT4 등
- Google의 PaLM 등
- Meta의 Llama 등 이 존재.
학습 패러다임은 일반적으로
- Pre-train
- Human-Alignment로 이루어짐.
또한, Multi-modal 쪽도 주시할 필요 있음.
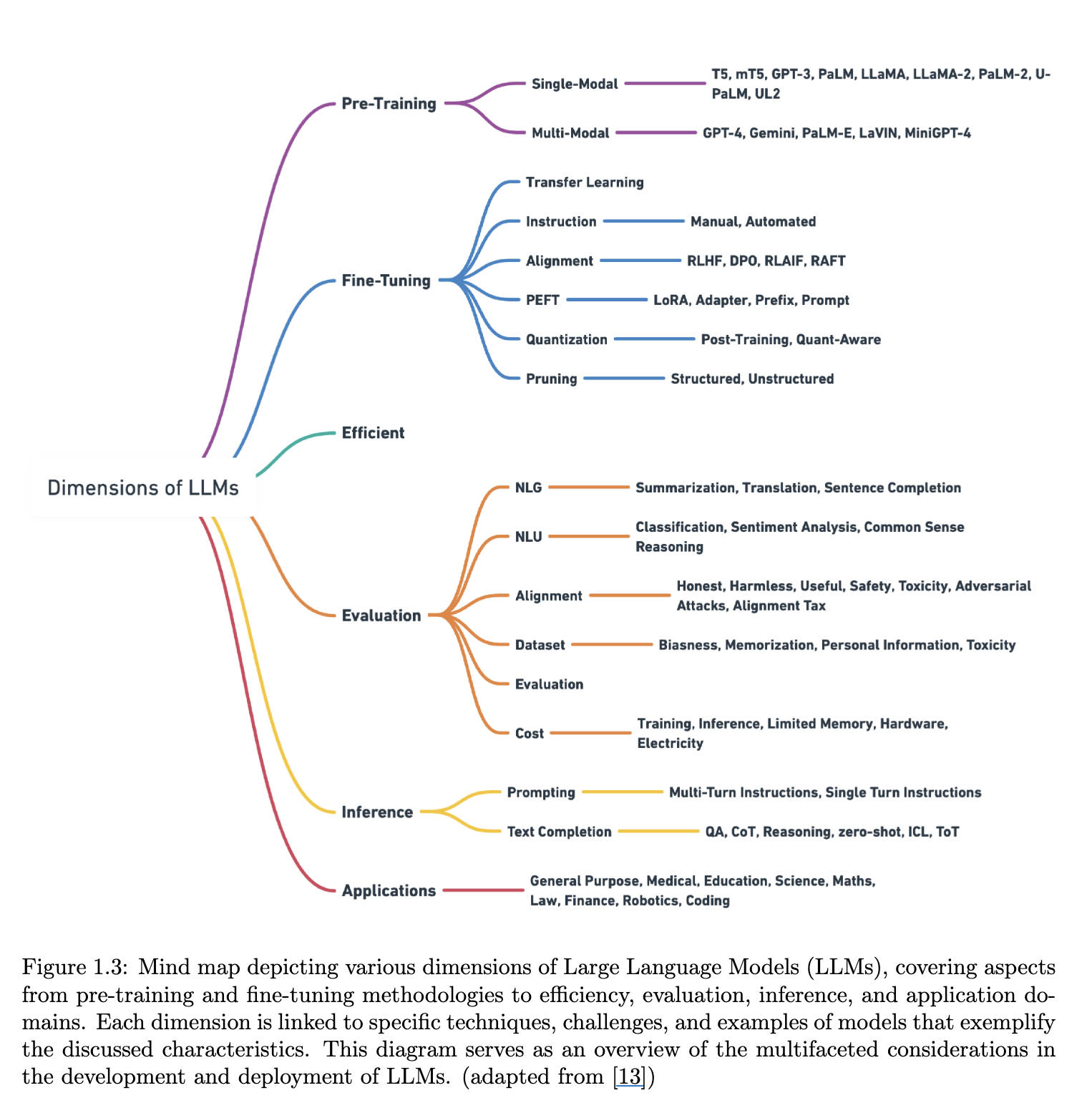
1.5 What is Fine-Tuning?
Summary
잘 학습된 pre-trained model에 task/domain specific 한 데이터로 downstream task 성능을 올리는 기법.
pre-train된 knowledge-representation을 downstream-task에 맞춰 transfer한다고 표현할 수 있을 듯.Benefits:
- Time / Computing Efficiency
- 일반적으로 바닥(randomly initialized weights)부터하는 학습보다 성능이 보장된다는 것이 정설.
결국 근본적으로 효율을 위해 고안된 방법이니, 효율이 중요하고, 그로 인해 전체 weight를 업데이트 하는 것(Full-Fine Tuning)이 아닌, PEFT(Parameter Efficient Fine Tuning), HFT(Half Fine-Tuning) 같은 기법들이 나오고 있음.
1.6 Types of LLM Fine-Tuning
1.6.1 Unsupervised Fine-Tuning
- label을 요구치 않는 Fine-Tuning
- 사실상, pre-train의 연장선.(만약 pre-train을 Self-supervised learning했다면)
- 도메인이 다른 셋들에 대해서 사용하긴 함.
1.6.2 Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)
- 일반적으로 pre-train을 self-supervised learning 했다면 사용.
- 대부분의 LLM이 이걸 함.
1.6.3 Instruction Fine-Tuning via Prompt Engineering
- 보통 형태의 셋을 사용하여 학습
- 특정 산업이나 목적에 맞춰진 specialized assistant 개발에 많이 사용됨.
- 또는 human-alignement
- 프롬프트에 고의존적이고, 학습을 위한 프롬프팅에 정교한 설계가 필요.
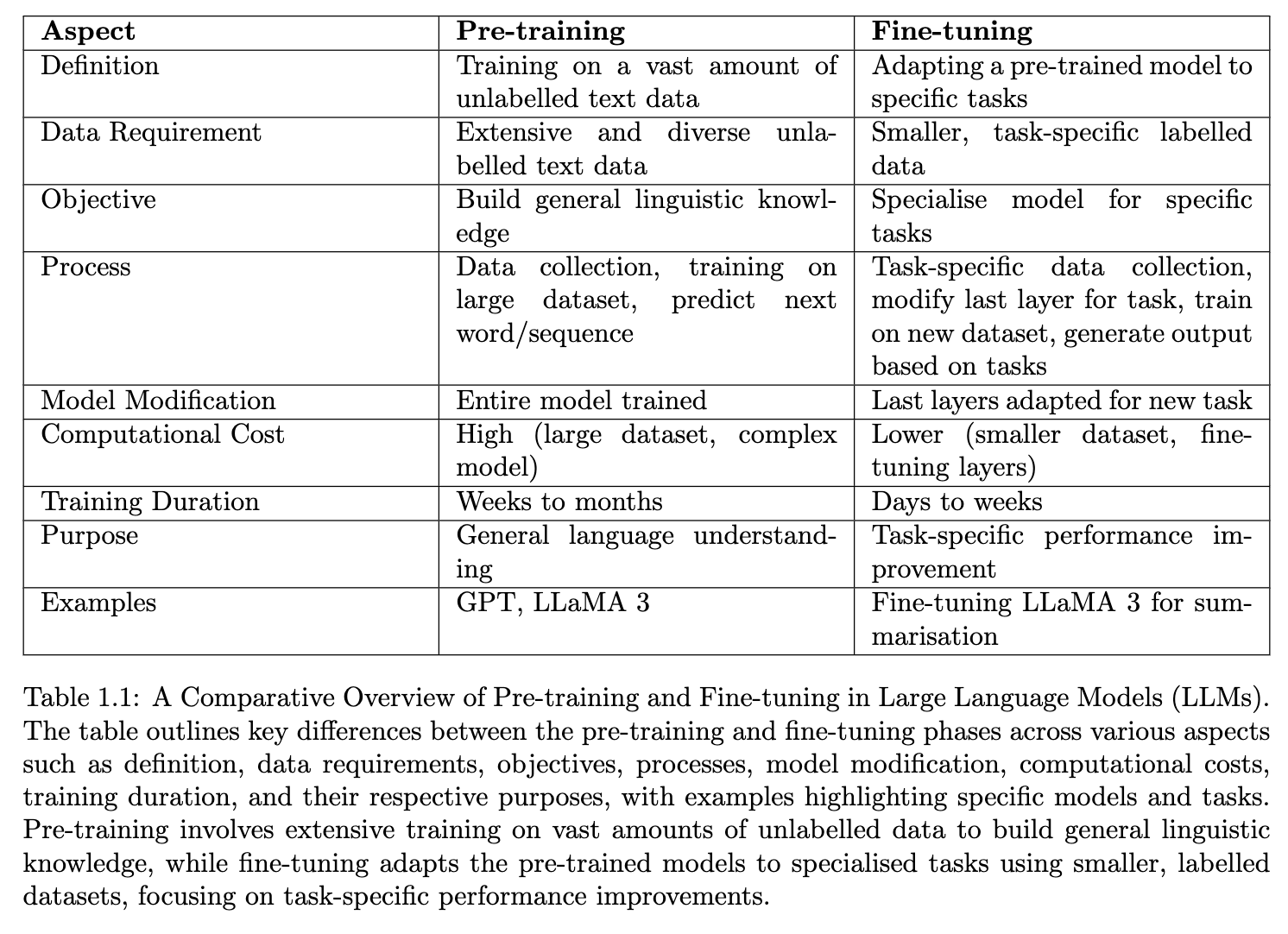
1.7 Pre-training vs Fine-tuning
1.8 Importance of Fine-Tuning LLMs
Summary
- Transfer Learning : Time-Cost-Data Efficiency
- Improved Generalization(in specific domain)
- Fast Convergence
1.9 Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
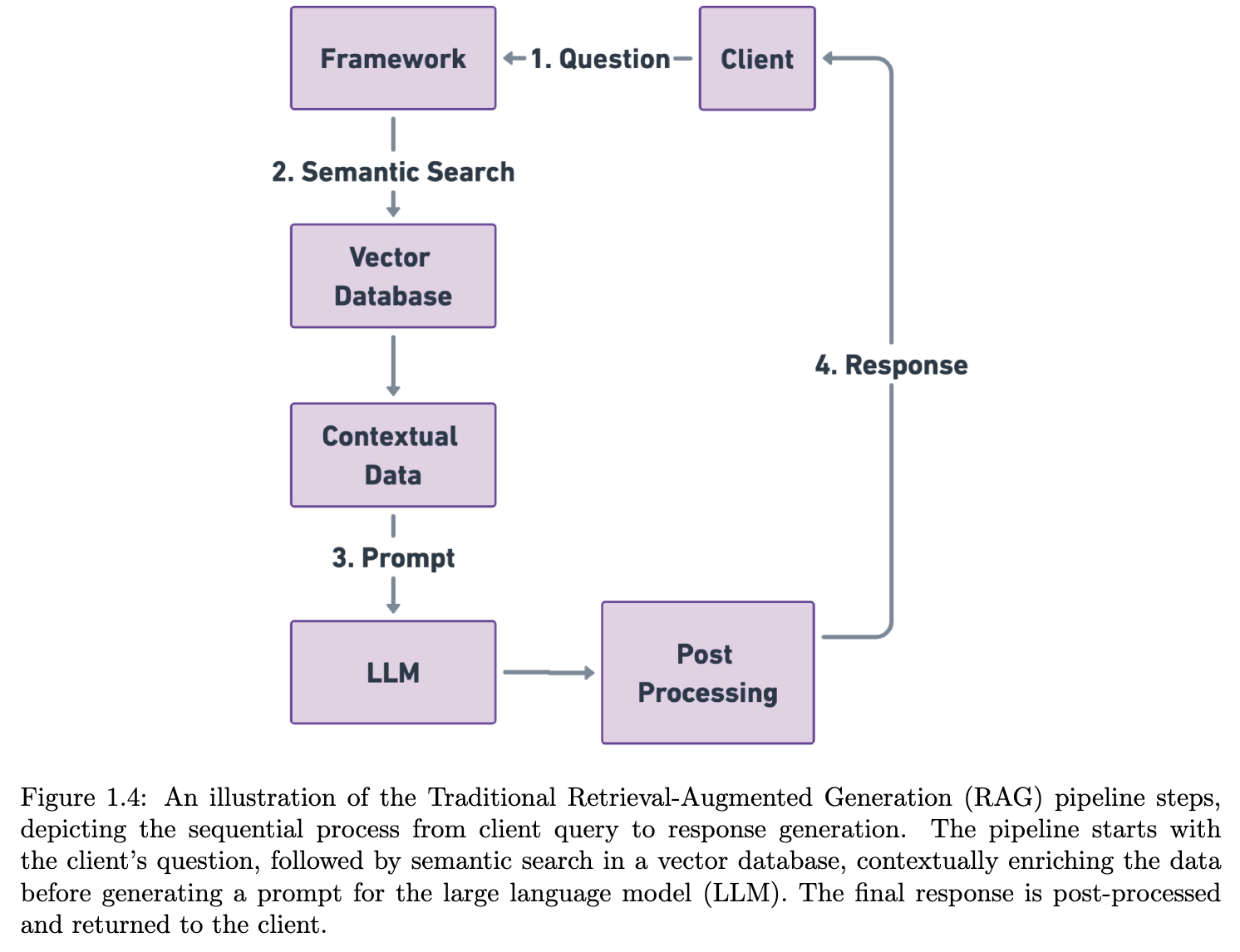
- External memory bank
- Knowledge Database
- 모델 내부의 지식에 의존하지 않고, 질문과 관련된 데이터를 실시간으로 찾아내서 모델에게 참고자료로 제공.
1.9.1 Traditional RAG Pipeline and Steps
총 5단계로,
- Data Indexing: RAG에서 데이터 검색을 위한 전처리 단계.
- 데이터 처리, chunking, VectorDB에 저장.
- Input Query Processing: User의 query를 DB검색이 수월하도록 processing.
- 질문을 단순화, vector-encoding
- Searching and Ranking: 변환된 query를 기반으로 indexing된 데이터 중 연관성이 높은 걸 select.
- TF-IDF, BM25, 더 나아간 최신은 BERT encoding도 사용한다고 함.
- Prompt Augmentation : 기존 user query에 VectorDB를 참조한 데이터 보강
- 즉, context를 더 enrich하게 만듦.
- Response Generation : 보강된 prompt 기반 NTP/Generation.
Question
Hallucination을 줄이는데 일부 기여한다고 함. 정말?
Engineering 단에서는 잘 이해가 되질 않네. Context-window가 늘어나는 것도 아니잖아.Hallucination은 일반적으로 OOD에 대해 잘 일어난다고 함.
→ 이 떄, RAG가 정보만 적절히 잘 물어오면, 거기에 attention줘서 잘 처리하는 듯.
→ 또한, 덤으로 source도 알 수 있고.
1.9.2 Benefits of Using RAG
Summary
- Up-to-Date and Accurate Responses: VectorDB에 정보만 추가하면 되니, 최신 정보 유지를 위한 품이 적게 듦.
- Reducing Inaccurate Responses: 약간의 Hallucination 극복.
- Domain-Specific Responses: 마찬가지의 맥락으로 VectorDB에 domain-specific한 데이터 넣어서 특정한 domain을 위한 약간의 fine-tuning효과를 내기도.
- Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: Fine-Tuning 대비 cheap. Scalability도 좋고.
1.9.3 Challenges and Considerations in Serving RAG
Summary
- Latency
- 별도의 VectorDB 운영을 위한 비용. API당
- Accuracy: Knowledge Base에도 적당한 정보가 없거나, 틀린 정보가 있다면, 좋지 못함.
- Recency : 최신 정보 업데이트 지속적 필요.
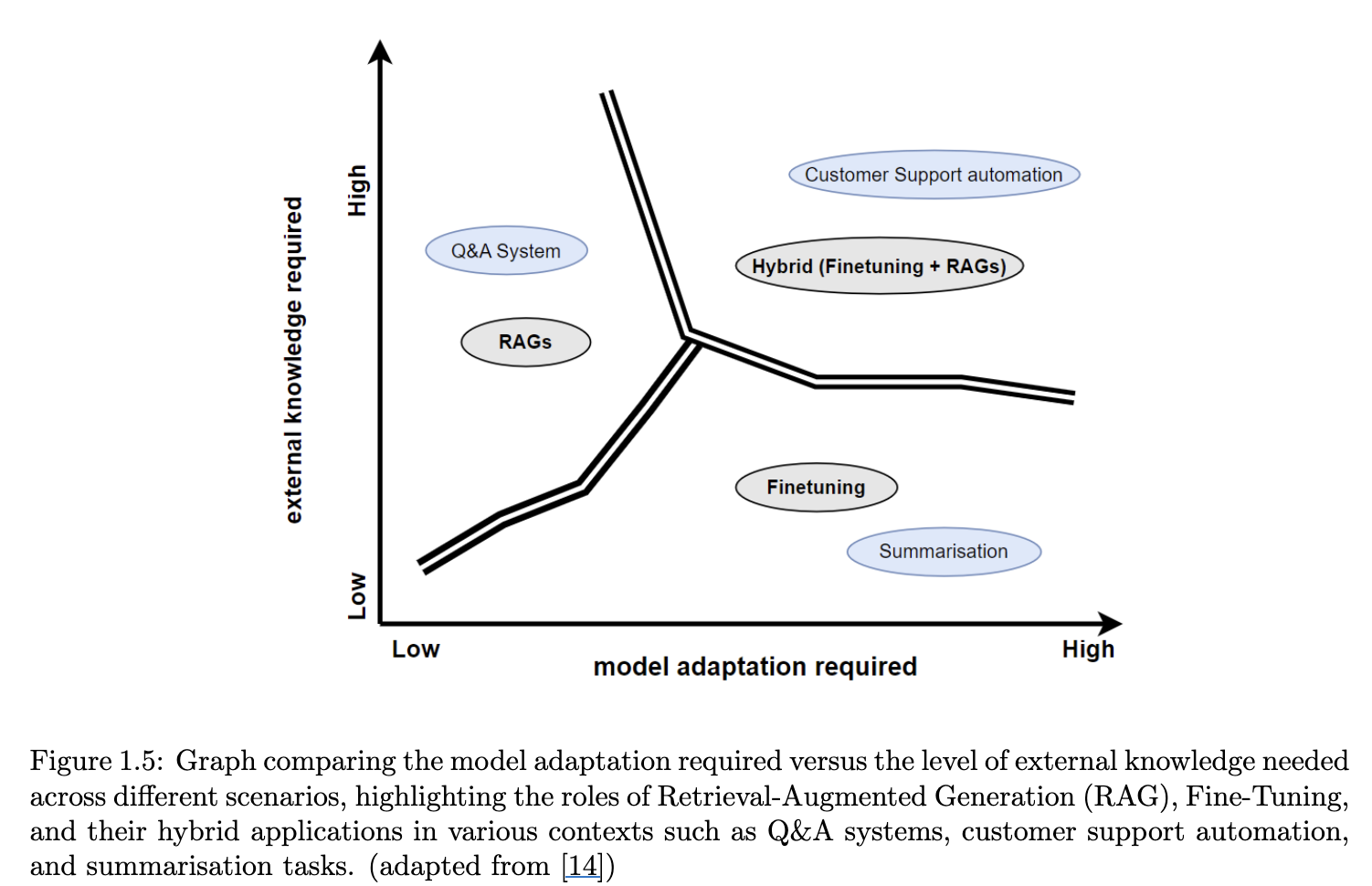
1.9.5 Considerations for Choosing Between RAG and Fine-Tuning
Chap 2. Seven Stage Fine-Tuning Pipeline for LLM
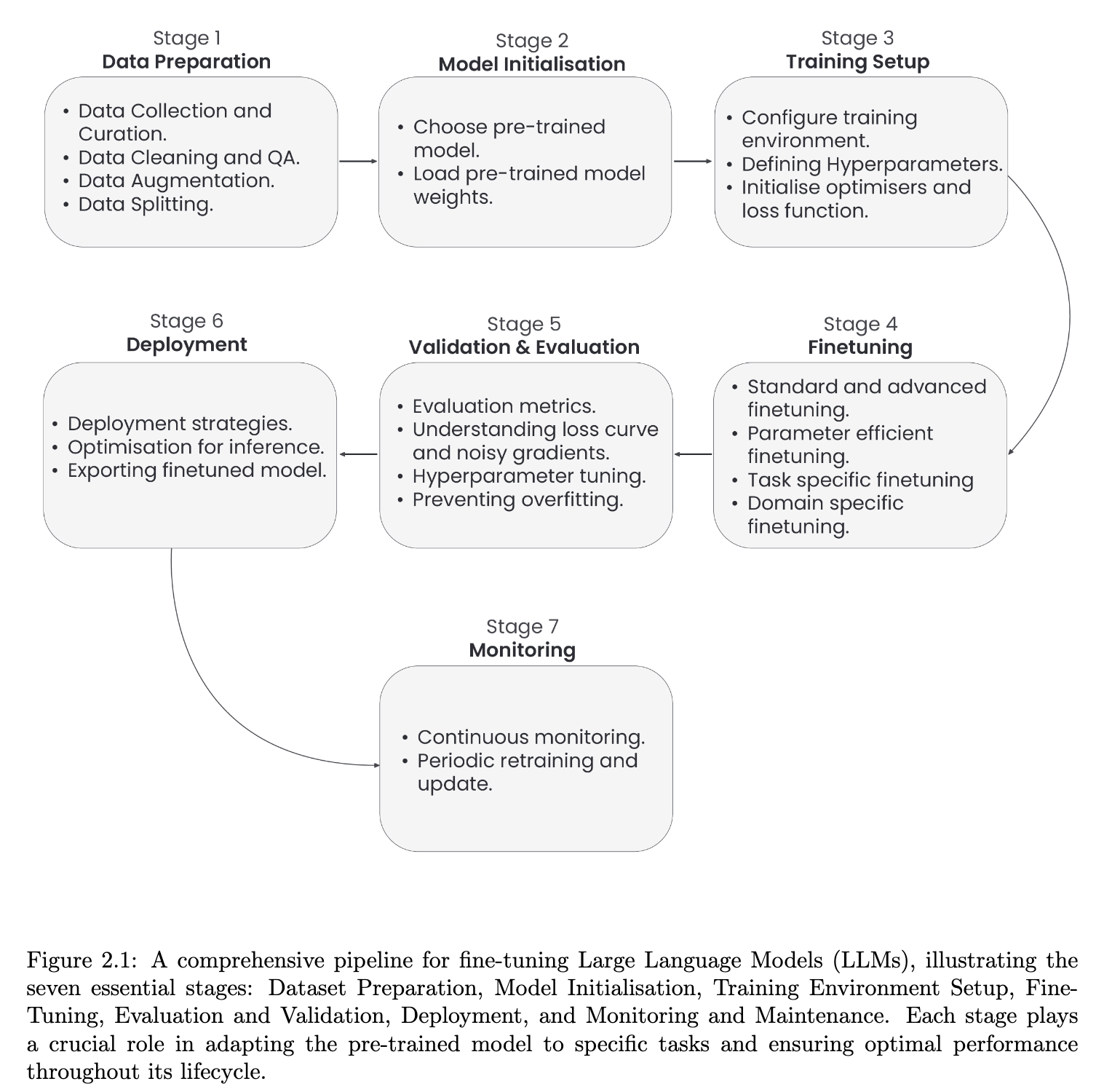
- 일반적인 DL-workflow 중간에 Fine-Tuning 들어간 정도.
3 Stage 1: Data Preparation
3.1 Steps Involved in Data Preparation
3.1.1 Data Collection
3.1.2 Data Preprocessing and Formatting
- 유용한 전처리 함수들을 가지고 있는 lib들로는
- spaCy, NLTK, HuggingFace, KNIME 등.
3.1.3 Handling Data Imbalance
- 실무에서 많이 겪는 대표적 문제 중 하나로,
- 예를 들어보자면, 분류 문제에 대해 특정 클래스의 데이터 불균형 등이 있음.
- 이에 대한 solution으로는,
- Over-sampling | Under-sampling
- SMOTE: imbalanced class label 문제에 초점을 둔 Data Augmentation.
- 소수의 클래스 내 interpolation으로 새로운 데이터 생성.
- python lib: imbalanced-learn
- SMOTE: imbalanced class label 문제에 초점을 둔 Data Augmentation.
- Adjusting Loss Function
- 대표적으로 Focal Loss, Cost-Sensitive Learning : Loss 단 수정을 통해 취약한 클래스에 대한 손실을 강화.
- python lib: focal_loss
- Ensemble
- 대표적으로 bagging,boosting 사용하는 모델들을 활용함.
- python lib: sklearn.ensemble
- Stratified Sampling
- 한 batch 내부에 클래스별 비율을 맞춰주자는 접근.
- python lib: sklearn.model_selection.StratifiedShuffleSplit
- Data Cleaning
- 이건, 기본.
- Approximate Metrics
- Acc 보다는 F1-macro 같은 클래스별로 고려되는 지표를 사용하자.
- python lib: sklearn.metrics
3.1.4 Splitting Dataset
배치를 어떻게 구성하냐도 학습 시 중요 사항.
일반적으로 사용하는 전략은
- Random Sampling(Shuffle)
- Stratified Sampling
- K-Fold Cross Validation
- LOOCV(Leave One Out Cross Validation): 배치 뽑은 것에서 하나만 eval, 나머지를 train으로 사용.
3.2 Existing and Potential Research Methodologies
3.2.1 Data Annotation
3.2.2 Data Augmentation
데이터가 모자란 상황에서 사용.
- Word Embedding : 유사한 embedding vector를 가진 단어들로 대체
- Back Translation : 원본 → 타 언어 → 원본 언어 로 번역을 하면 paraphrasing한 효과 획득
- Adversarial Attacks : Hard negative sample을 제공하는 것과 유사하게, 어려운 문제를 제공함으로써, 더 좋은 decision boundary 만드는데 보탬.
- NLP-AUG lib: 문장, 단어, 문자 등 텍스트 증강 및 오디오나 스펙트럼까지 증강해주는 lib.
3.2.3 Synthetic Data Generation using LLMs
3.3 Challenges in Data Preparation for Fine-Tuning LLMs
3.4 Available LLM Fine-Tuning Datasets
데이터셋 참고 링크 : LLMXplorer
4 Stage 2: Model Initialisation
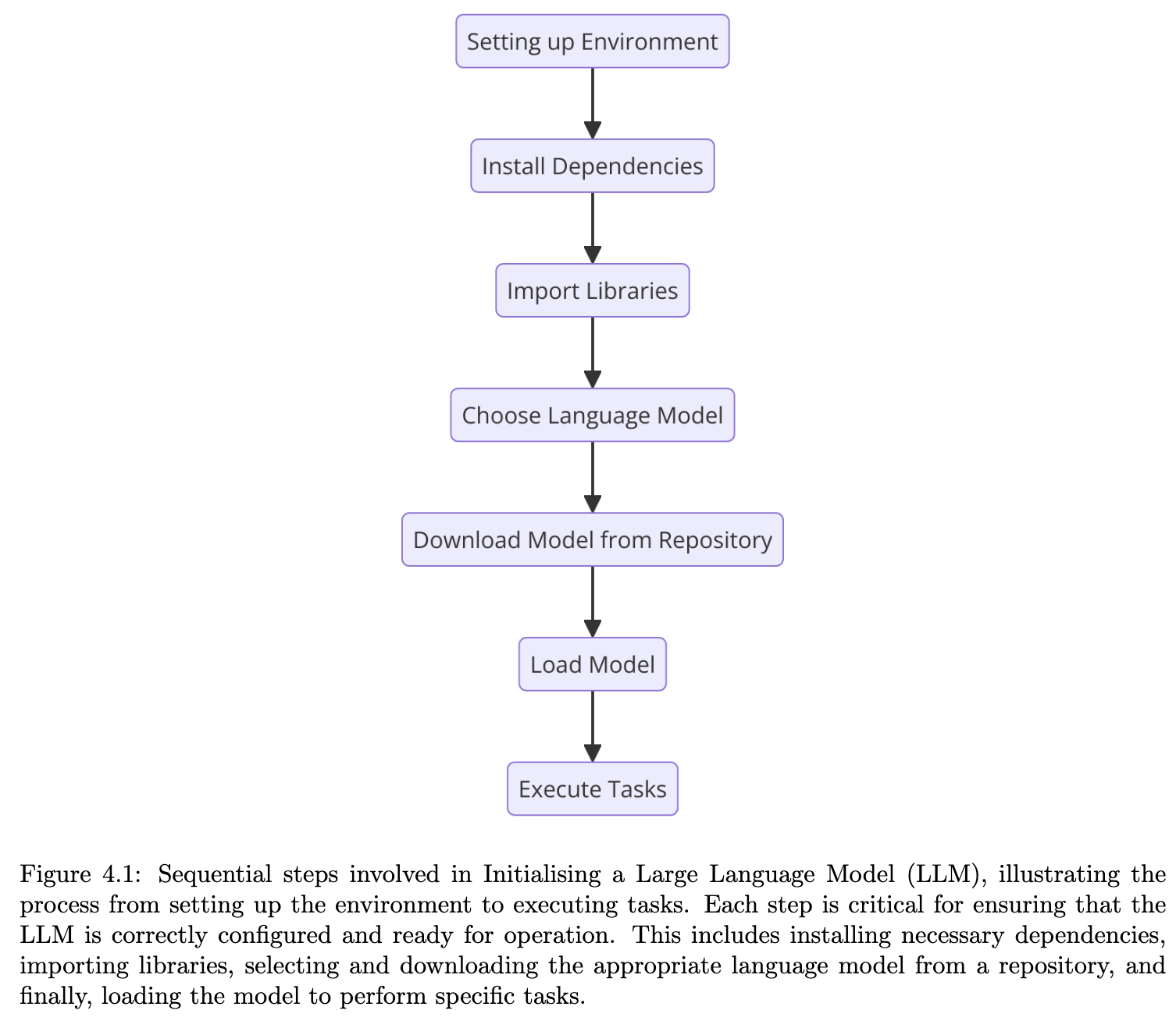
- 이러한 전체적인 step.
4.3 Challenges in Model Initialisation
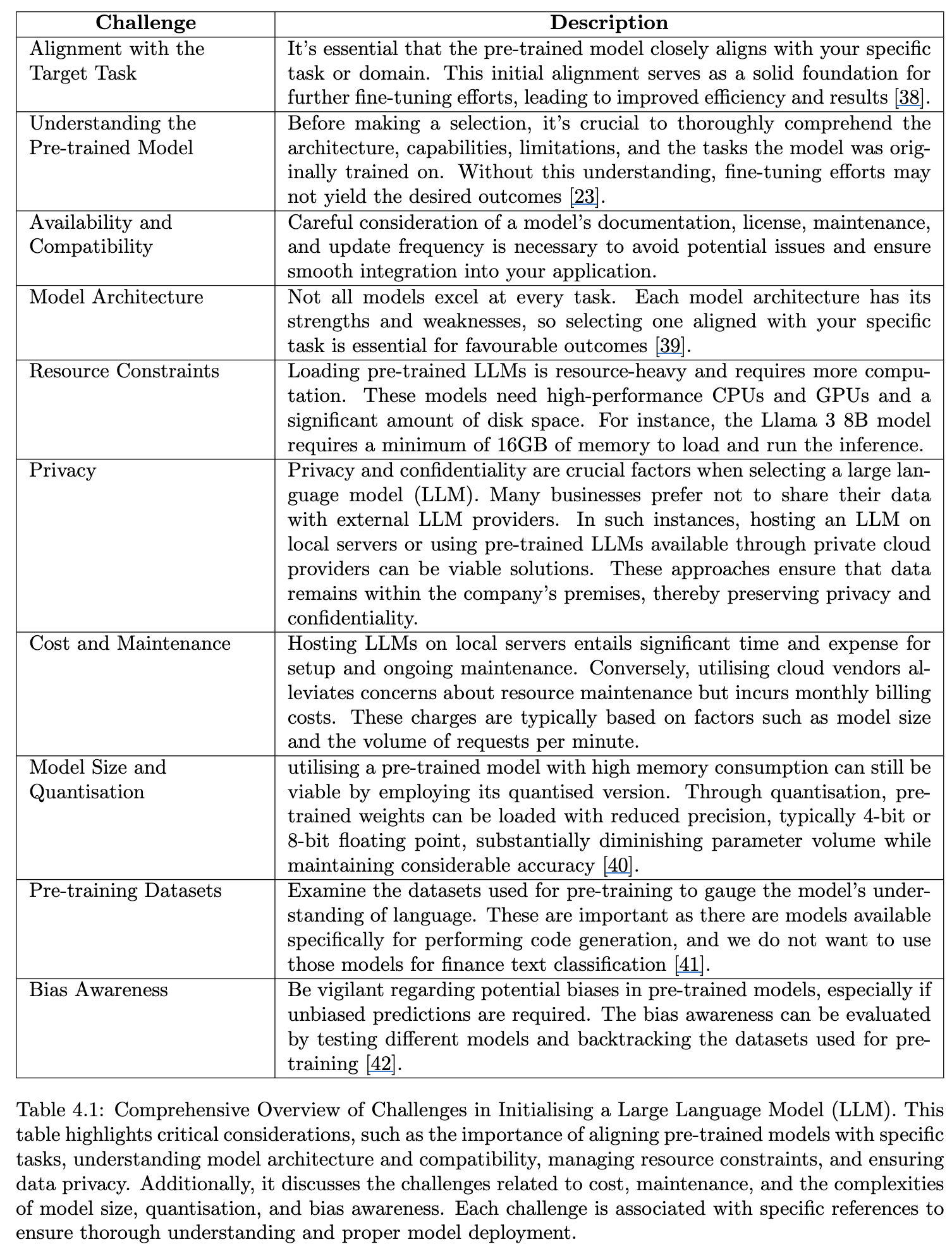
- 결국 자원 및 효율을 고려해야 함.
4.4 Tutorials
Llama3 Summarisation
HuggingFace tutorial for LLM hands-on
PyTorch for fine-tuning models
5 Stage 3: Training Setup
5.1 Steps Involved in Training Setup
준비할 건 크게 3가지로,
- training env
- Hardwares: GPU/TPU
- lib : Torch, Tensorflow / CUDA, cuDNN, …
- Hyperparameter
- batch size, lr, epochs, …
- Optimizer, Loss
- 어떤 optimizer에 어떠한 hyper-parameter 줄건지(weight-decay,…)
- Loss는 어떻게 define 할 건지.
5.2 Setting up Training Environment
5.3 Defining Hyperparameters
가장 중요 즉, 학습에 영향을 많이 미치는 hyper-parameter들은
- batch size
- learning rate
- epochs
5.3.1 Methods for Hyperparameter Tuning
Question
그러면 어떻게 ‘좋은’ hyper-parameter를 찾을 것인가?
- Random Search
- 정해진 범위 내에서 랜덤 조합하여 선책하고 평가.
- 빠르고, 간단. 단, global optima를 찾는다는 보장을 할 순 없음.
- Grid Search
- 격자 형태로 가능한 파라미터 조합짜서 다 해보고 고르기.
- 느리지만, 해당 범위 내에서는 global optima를 보장.
- Bayesian Optimisation
- 과거의 평가를 바탕으로 확률 모델 구축하여, 다음 탐색 포인트를 대강 예측하여 시도.
- Grid보다 적은 시도로 global optima를 찾을 수 있지만, 구현이 복잡.
- Automated hyperparameter Tuning
- 동시에 여러 파라미터 조합으로 학습시키고 최적해 찾기.
5.4 Initialising Optimisers and Loss Function
5.4.1 Gradient Descent(GD)
5.4.2~.3 Stochastic Gradient Descent(SGD) & Mini-batch GD
5.4.4 AdaGrad
5.4.5 RMSProp
5.4.6 AdaDelta
- default lr setting이 필요없다는 게 특징.
- RMSProp이나 AdaGrad보다 구현이 복잡하고, 수렴시키려면 더 많은 iteration이 필요하다.
5.4.7 Adam
5.4.8 AdamW
6 Stage 4: Selection of Fine-Tuning Techniques and Appropriate Model Configurations
6.1 Steps Involved in Fine-Tuning
6.2 Fine-Tuning Strategies for LLMs
6.2.1 Task-Specific Fine-Tuning
6.2.2 Domain-Specific Fine-Tuning
6.3 Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) Techniques
6.3.1 Adapters
Summary
풀 파라미터 튜닝을 하는 게 아니라, 모델 전체에 작은 adapter를 달아서 그 부분만 학습시키자.
- 일반적으로 Attention 바로 뒤, FFN 바로 직전에 linear projection을 하나 추가.
- 구체적으로는 down-projection이랑 up-projection 으로 이루어져 있어, 구조적으로는 auto-encoder와 동형.
- LoRA와 구분해보자면, adapter는 물리적으로 layer를 삽입하는 것. LoRA는 삽입 x
6.3.2 Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)
6.3.3 QLoRA
Summary
LoRA인데 효율을 위해 quantization
6.3.4 Weight-Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation (DoRA)
6.3.5 Fine-Tuning with Multiple Adapters
6.4 Half Fine Tuning
Check
모델 파라미터를 업데이트 하는게 아니라, layer 별 반만 업데이트하자.
6.4.1 Benefits of using Half Fine tuning
6.4.2 Comparison between HFT and LoRA
6.5 Lamini Memory Tuning
6.5.1 Lamini-1 - A model architecture based on Lamini
Lamini-paper(withdraw, 26.01.20기준) : Banishing LLM Hallucinations Requires Rethinking Generalization
Summary
Mixture of Experts(MoE) 의 개념을 memory에 적용하자.
특정 메모리를 특정 소형 LoRA에게 위임하고 필요할 때마다 LoRA 처럼 사용하자.
약간 RAG의 아이디어도 섞여 있고, indexing 과정에 해당하는 부분을 cross-attention을 사용해서, MoE의 router를 대신함.
6.6 Mixture of Experts(MoE)
6.6.1 Mixtral 8x7B Architecture and Performance
6.7 Mixture of Agents
Summary
Mixture of Experts(MoE) 아이디어를 계승해서 하나의 모델 안에 여러 expert가 아닌, 모델, agent 단위를 묶어서 사용하자는 개념.
6.7.1 Methodology
6.7.2 Analogy with MoE
6.7.3 What makes MoA works well?
6.8 Proximal Policy Optimization(PPO)
6.8.1 Benefits of PPO
6.8.2 Limitations of PPO
6.8.3 Tutorial for training models using PPO technique
6.9 Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)
6.9.1 Benefits of DPO
6.9.2 Best Practices for DPO
6.9.3 Tutorial for training models using DPO technique
6.9.4 Is DPO Superior to PPO for LLM Alignment?
6.10 Odds-Ratio Preference Optimization(ORPO)
6.11 Pruning LLMs
6.11.1 When to Prune AI Models?
6.11.2 Benefits of Pruning
6.11.3 Challenges of Pruning
7 Stage 5: Evaluation and Validation
7.1 Steps Involved in Evaluating and Validating Fine-Tuned Models
7.2 Setting Up Evaluation Metrics
7.2.1 Importance of Cross-Entropy for LLM Training and Evaluation
Summary
정보이론에서 기원해서 전통적으로 ML에서 loss로 많이 사용되고 있다.
확률 분포 간 차이를 나타내는 정량적 지표 중 하나.
7.2.2 Beyond Cross-Entropy: Advanced LLM Evaluation Metrics
Summary
단순 VOCA 확률 분포 간 차이를 보는 걸 넘어서 응답 품질을 평가하기 위한 다양한 eval-metric이 제안됨.
- Perplexity
- Factuality
- LLM Uncertainty
- Context Relevance
- Completeness
- Chunk Attribution and Utilisation
- Data Error Potential
- Safety Metrics
- 대표적으로 bias and fairness, privacy, security 등을 축으로 평가함.
7.3 Understanding the Training Loss Curve
7.3.1 Interpreting Loss Curves
Summary
대표적인 learning curve는 다음과 같은 케이스로 나뉜다.
7.3.2 Avoiding Overfitting
- Regularization
- Early Stopping
- Dropout- A Simple way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting
- Cross Validation
- Batch Normalization
- Larger Datasets and Batch Size
7.3.3 Sources of Noisy Gradients
Summary
Stochastic Gradient Descent(SGD) 나 mini-batch GD같이 인 건 true-gradient랑 batch 단위의 local-gradient의 차이를 허용해주어, loss-landscape 혹은 space에서 약간의 exploration과 같은 효과를 내주어 장점이기도 하지만, 동시에 batch-size가 너무 작고, outlier들만 모여서 만든 이상한 gradient를 만든다면, learning-curve가 그 포인트에서 튀기도 할 것이다. 따라서 이걸 막기 위해,
- Learning Rate Scheduler를 사용하거나,
- Gradient Clipping을 보통 한다.
7.4 Running Validation Loops
7.5 Monitoring and Interpreting Results
7.6 Hyper-parameter Tuning and Other Adjustments
Tip
실무적인 tip으로 다음과 같은 수치 혹은 optim을 추천.
- LR : 2e-4 정도 / 물론 pre-train된 lr보다 작은 범위에서 시작하는 게 좋은 포인트.
- Batch Size: 키우면 gradient가 안정되나(true-gradient랑 비슷), 하지만 memory는 많이 필요.
- Epochs: 충분히 확보해줘야 over, under-fitting 피할 수 있음.
- Optimizer: Paged-Adam 같은 걸로, memory를 아낄 수도 있음.
7.6.1 Data Size and Quality
- 중요하니, 신경써라.
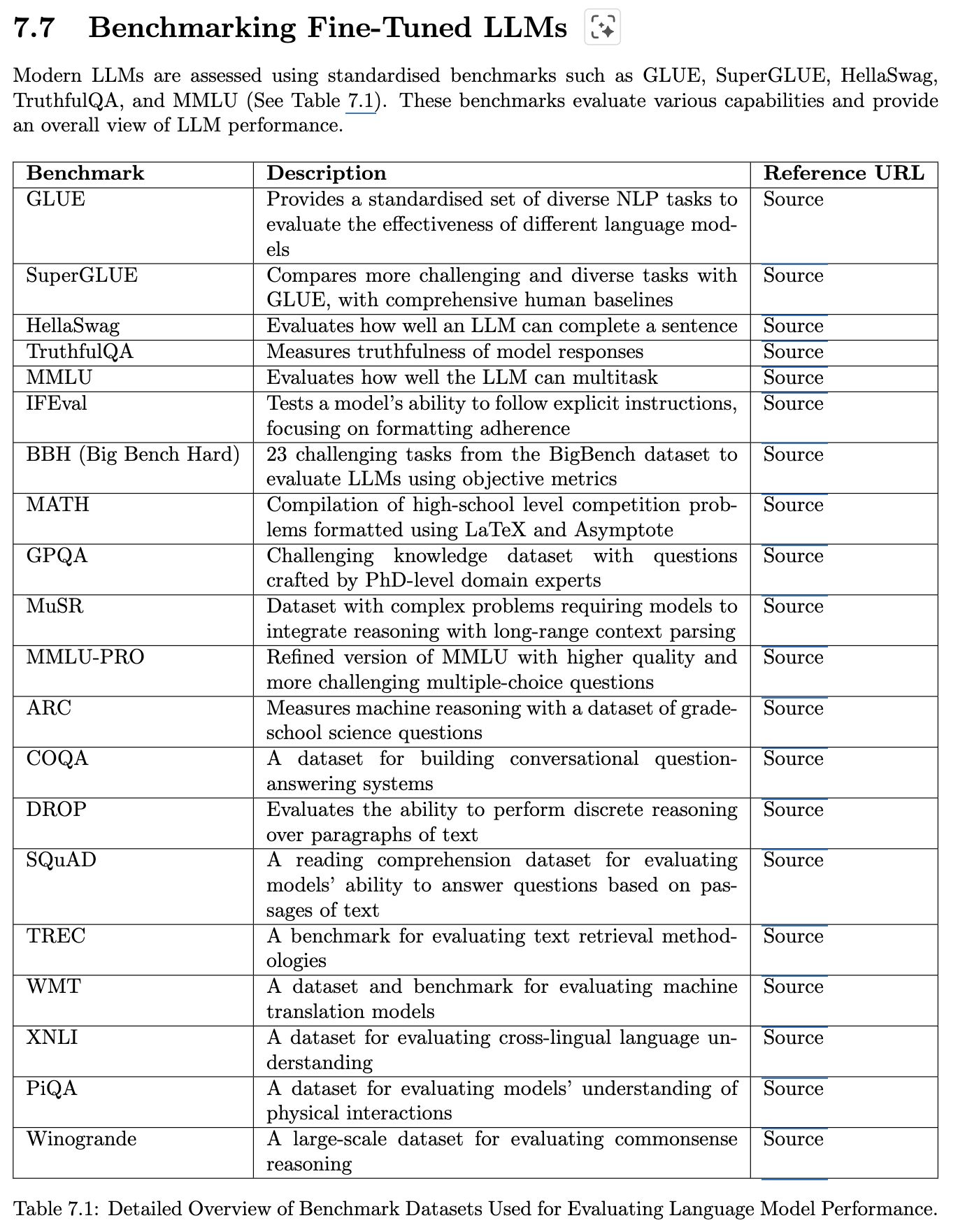
7.7 Benchmarking Fine-Tuned LLMs
7.8 Evaluating Fine-Tuned LLMs on Safety Benchmark
7.9 Evaluating Safety of Fine-Tuned LLM using AI Models
7.9.1 Llama Guard
7.9.2 Shield Gemma
7.9.3 WILDGUARD
8 Stage 6: Deployment
8.1 Steps Involved in Deploying the Fine-Tuned Model
8.2 Cloud-Based Providers for LLM Deployment
Summary
몇가지 cloud-solution을 제공하는 업체들로는 다음들이 유명하다.
- Amazon Web Service(AWS)
- Amazon Bedrock
- Amazon SageMaker
- Microsoft Azure
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Azure Machine Learning
- Google Cloud Platform(GCP)
- Vertex AI
- Cloud AI API
- HuggingFace
- Inference API
- Spaces
- Others:
- OpenLLM
- DeepSpeed
8.3 Techniques for Optimising Model Performance During Inference
8.3.1 Traditional On-Premises GPU-Based Deployments
Question
On-premise(온프레미스):
- 기업이나 개인이 직접 소유한 물리적인 공간(사무실, 데이터 센터 등) 내에 직접 설치하여 운영하는 방식
- cloud랑 반대 개념.
Summary
일반적인 모든 걸 user가 다 관리하는 방법.
8.3.2 Distributed LLM: Torrent-Style Deployment and Parallel Forward Passes
Summary
초거대 모델의 경우, torrent처럼, 분산형으로 모델 파라미터 관리. 각 gpu 노드에 특정 layer만 담당하게 하는 형식처럼도 사용.
주요 lib으로 Petals 등이 있음.
8.3.3 ~ 4 WebGPU-Based Deployment of LLM / LLM on WebGPU using WebLLM
Summary
local에서 모델을 돌리며, web browser단에서 service를 사용할 수 있게 구성한 것.
8.3.5 Quantised LLMs
Summary
학습 완료된 checkpoint를 그대로 사용하지 않고, 모델 파라미터의 dtype을 더 작은 걸 사용해서, 연산량을 줄이는 방법.
모델 자체의 사이즈가 줄어드니, 그만큼 메모리 로드도 줄음.관련 기술 : QLoRA
8.3.6 vLLMs
Summary
Inference serving 속도를 올리고, 메모리 사용을 줄이기 위해 개발된 솔루션.
핵심 기술로, PagedAttention을 사용.
- KV-cache를 연속된 메모리에 저장하는 것이 아닌, 불연속적인 block 단위로 저장함.
- 이를 통해 메모리를 극단적으로 짜내어, throughput을 올림.
- preemptive scheduleing: 요청이 몰리면, 동적으로 순서를 조정.
- continuous batching: 새로운 query가 들어오면, 이전 요청이 끝날때까지 기다리지 않고, 바로 batch에 넣어서 같이 계산.
8.4 Key Considerations for Deployment of LLMs
9 Stage 7: Monitoring and Maintenance
Summary
Bussiness 얘기. App 만들고 배포시에 동적으로 관리를 무러 해야하는 지 다룸.
LLM-level 내용이라기 보단, 시스템을 어떻게 유지/보수하는 지 내용.
9.1 Steps Involved in Monitoring and Maintenance of Deployed Fine-Tuned LLMs
9.2 Continuous Monitoring of Model Performance
9.2.1 Functional Monitoring
9.2.2 Prompt Monitoring
9.2.3 Response Monitoring
9.2.4 Alerting Mechanisms and Thresholds
9.2.5 Monitoring User Interface (UI)
9.3 Updating LLM Knowledge
9.3.1 Retraining Methods
9.3.2 Additional Methods
9.3.3 Key Considerations
9.4 The Future of LLM Updates
Summary
기존 지식에 새로운 지식이 잘 녹아들게 학습할 수 잇는 continuous-learning이 필요할 것이다.
- 그러면서도 catastrophic-forgetting을 피하는 것이 숙제.
knowledge에 유통기한을 부여하는 방법도,,
10 Industrial Fine-Tuning Platforms and Frameworks for LLMs
10.1 Autotrain(HuggingFace)
10.1.1 Steps Involved in Fine-Tuning Using Autotrain
10.1.2 Best Practices of Using Autotrain
10.1.3 Challenges of Using Autotrain
10.1.4 When to Use Autotrain
Summary
깊은 지식이 없고, 빠른 proto-typing에 최적. 리소스 관리가 어려운 사람한테 추천.
10.1.5 Tutorials
10.2 Transformers Library and Trainer API
Summary
추상화를 많이 시켜놔서, 연구자들이 직접 training-loop 단에서 수정한다던가 하는 건 쉽지 않음.
하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝에 대한 자유도를 보장해, 관련 지식을 알아둘 필요가 있음.
마찬가지로 huggingface lib이라 생태계 안에서 효율 극대화.
10.2.1 Limitations of the Transformers Library and Trainer API
10.3 Optimum: Enhancing LLM Deployment Efficiency
Summary
- Quantisation
- Pruning
- Model Distilation 지원.
- onnx 같은 추론 engine을 지원하여 latency 낮추고, throughput을 높임.
10.3.1 Best Practices of Using Optimum
10.3.2 Tutorials
10.4 Amazon SageMaker JumpStart
Summary
Customization에 제약이 있고, AWS 안에 꽤 많이 묶여야 해서 쉽지 않을수도 있다.
10.4.1 Steps Involved in Using JumpStart
10.4.2 Best Practices for Using JumpStart
10.4.3 Limitations of Using JumpStart
10.4.4 Tutorials
10.5 Amazon Bedrock
Summary
이미 잘 만들어진 모델들을 사용해서 애플리케이션을 만드는 툴.
LLM 내부를 막 뜯거나 하는 작업을 위해 만들어진 게 아님.
10.5.1 Steps Involved in Using Amazon Bedrock
10.5.2 Limitations of Using Amazon Bedrock
10.5.3 Tutorials
10.6 OpenAI’s Fine-Tuning API
10.6.1 Steps Involved in Using OpenAI’s Fine-Tuning API
10.6.2 Limitations of OpenAI’s Fine-Tuning API
10.6.3 Tutorials
10.7 NVIDIA NeMo Customizer
Summary
이미 잘 훈련된 pre-trained model을 domain-specific하게 tune하는데 특화됨.
NVIDIA CUDA 생태계랑 호환성 좋음.
다양한 peft 지원.
10.7.1 Key Features of NVIDIA NeMo
10.7.2 Components of NVIDIA NeMo
10.7.3 Customising Large Language Models (LLMs)
10.7.4 Tutorials
11 Multimodal LLMs and their Fine-tuning
11.1 Vision Language Model (VLMs)
11.1.1 Architecture
11.1.2 Contrastive Learning
- CLIP으로 따로 잡고 공부할 예정…
11.2 Fine-tuning of multimodal models
11.2.1 Full-parameter Fine-Tuning
11.2.2 Case study of fine-tuning MLLMs for Medical domain
11.3 Applications of Multimodal models
11.4 Audio or Speech LLMs Or Large Audio Models
11.4.1 Tokenization and Preprocessing
11.4.2 Fine-Tuning Techniques
11.4.3 Fine-Tuning Whisper for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
11.4.4 Case Studies and Applications
12 Open Challenges and Research Directions
12.1 Scalability Issues
12.1.1 Challenges in Scaling Fine-Tuning Processes
Summary
- Computational Resource
- Memory Requirement
- Data Volume
- Throughput and Bottleneck
- Efficient use of Resource
12.1.2 Research Directions for Scalable Solutions
Advanced PEFT
Keyword: Data-Efficient FT
방대한 데이터를 다 쓰는게 아니라, 학습에 실질적으로 성능 기여를 하는 데이터를 잘 선별해서 그런 샘플들만 많이 사용해야 한다.
Influence Score: 각 데이터 샘플이 최종 성능에 미치는 기여도 산출.
12.1.3 Hardware and Algorithm Co-Design
12.2 Ethical Considerations in Fine-Tuning LLMs
12.2.1 Bias and Fairness
12.2.2 Privacy Concerns
12.2.3 Security Risks
12.3 Accountability and Transparency
12.3.1 The Need for Accountability and Transparency
12.3.2 Recent Research and Industry Practices
12.3.3 Promoting Accountability and Transparency
12.3.4 Proposed frameworks/techniques for Ethical Fine-Tuning
12.4 Integration with Emerging Technologies
12.4.1 Opportunities
12.4.2 Challenges
12.5 Future Research Areas
Summary
- Federate Learning and Edge Computing
- 연합, 즉 edge단에서도 학습을 하고, 그걸 central하게 어떻게 묶어서 관리할지.
- Real-Time Decision Support System
- fast-inference를 어떻게 구현할지.
- Ethical Regulatory Implication
- 강화학습 알고리즘
- attention
- Transformer 구현.
- LLM benchmark Survey