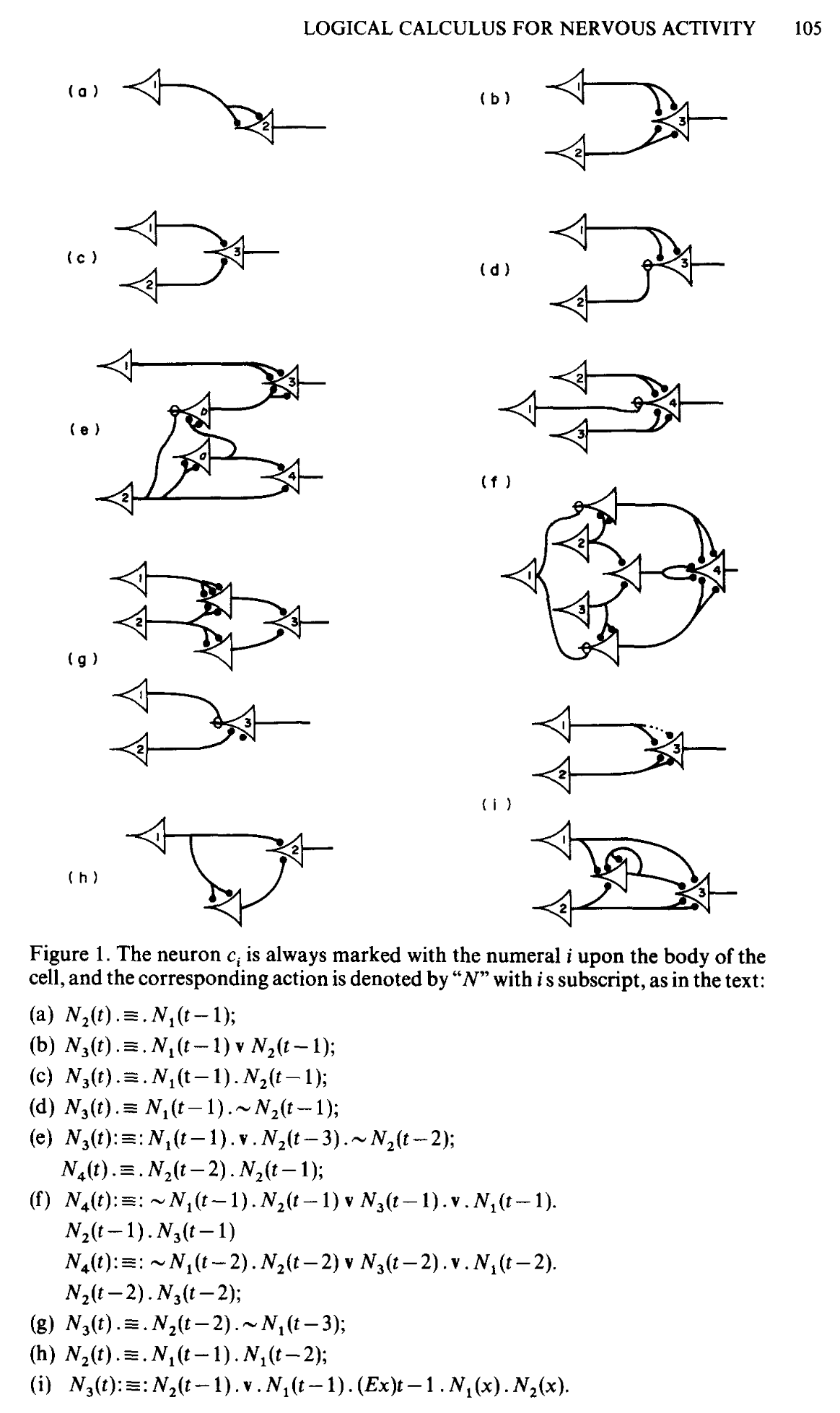
Neuron Model - A logical calculus of the ideas immanet in nervous activity
Abstract
Abstract
Because of the “all-or-none” character of nervous activity, neural events and the relations among them can be treated by means of propositional logic. It is found that the behavior of every net can be described in these terms, with the addition of more complicated logical means for nets containing circles; and that for any logical expression satisfying certain conditions, one can find a net behaving in the fashion it describes. It is shown that many particular choices among possible neurophysiological assumptions are equivalent, in the sense that for every net behaving under one assumption, there exists another net which behaves under the other and gives the same results, although perhaps not in the same time. Various applications of the calculus are discussed.
원본 링크
- 뉴런의 실무율(0 or 1) 특성을 논리 회로로 볼 수 있지 않을까? 에서 출발하여 이를 구조화 함.
- 다른 학문들(심리, 신경과학, 뇌 등)에서 다뤄지는 촉진, 억제 등의 활동이 근본적으로 equivalent 하다는 것을 주장.
Computing Machinery and Intelligence
Can Machine thinks?
원본 링크
이 질문에 대한 답으로 Turing 은 Turing Test(Imitation Game)을 제안. → 사람과 기계를 구분할 수 없다면 지능이다!
구체적으로 방을 나눠 사람1, 기계, 심판 이렇게 구성하고 심판이 사람과 기계의 identity를 구분하는 방법으로 실험이 진행되는데, 서로 간의 대화 수단이 자연어만 포함되다 보니, natural-language dialogue만을 통해 구분해야한다.
→현대의 multi-modal을 잘 반영하지는 못하는 정의네.
Dartmouth Conference
원본 링크AI
“An attempt will be made to find how to make machines use language, form abstractions and concepts, solve kinds of problems now reserved for humans, and improve themselves. We think that a significant advance can be made if we work on it together for a summer.”
Bold proposal: “Build a system that could capture every aspect of intelligence.”
The perceptron, a perceiving and recognizing automaton (Project Para)
Perceptron was inspired by..
- The organization of behavior.(Hebb, 1949, A neuropsychological theory.)
The Universal model
- Originally assumed could represent any boolean circuit and perform any logic
- Also provided a learning algorithm
But… XOR 를 해결할 수 없었다… → AI Winter
원본 링크
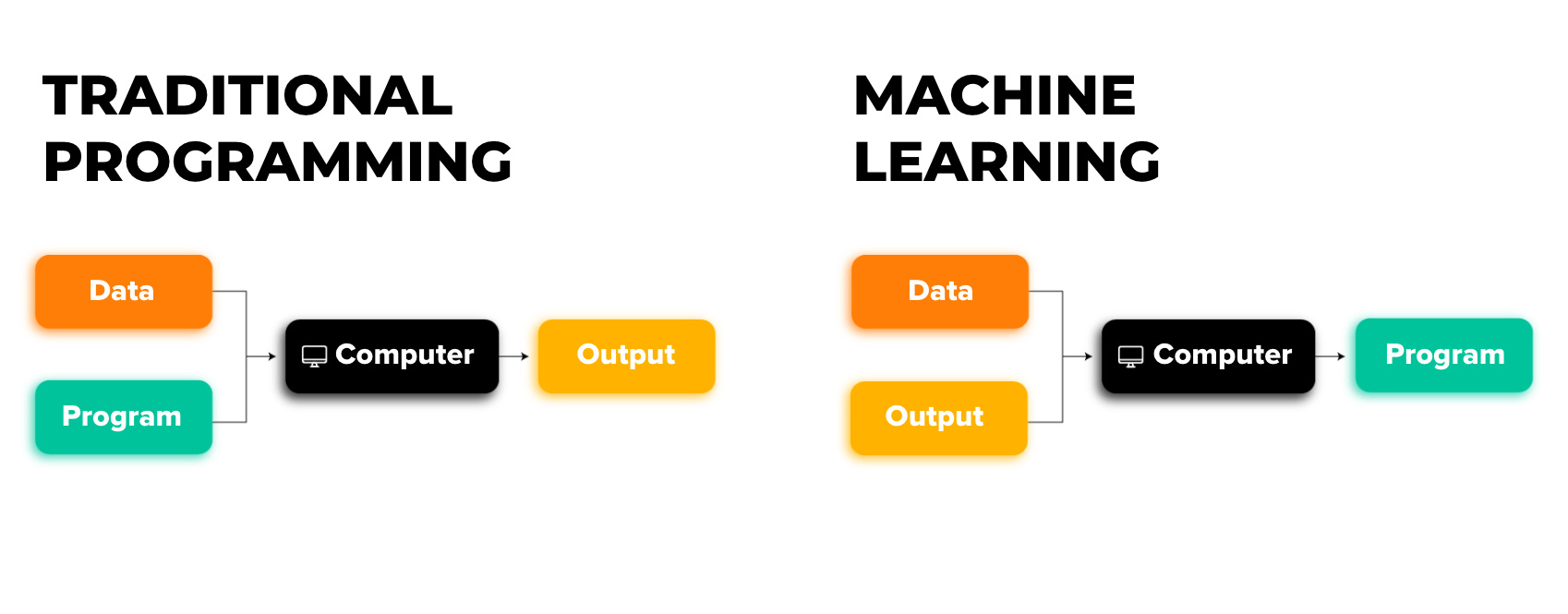
Paradigm Shift with ML
ML
Machine Learning is the field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed - Arthur Samuel(1959)
원본 링크
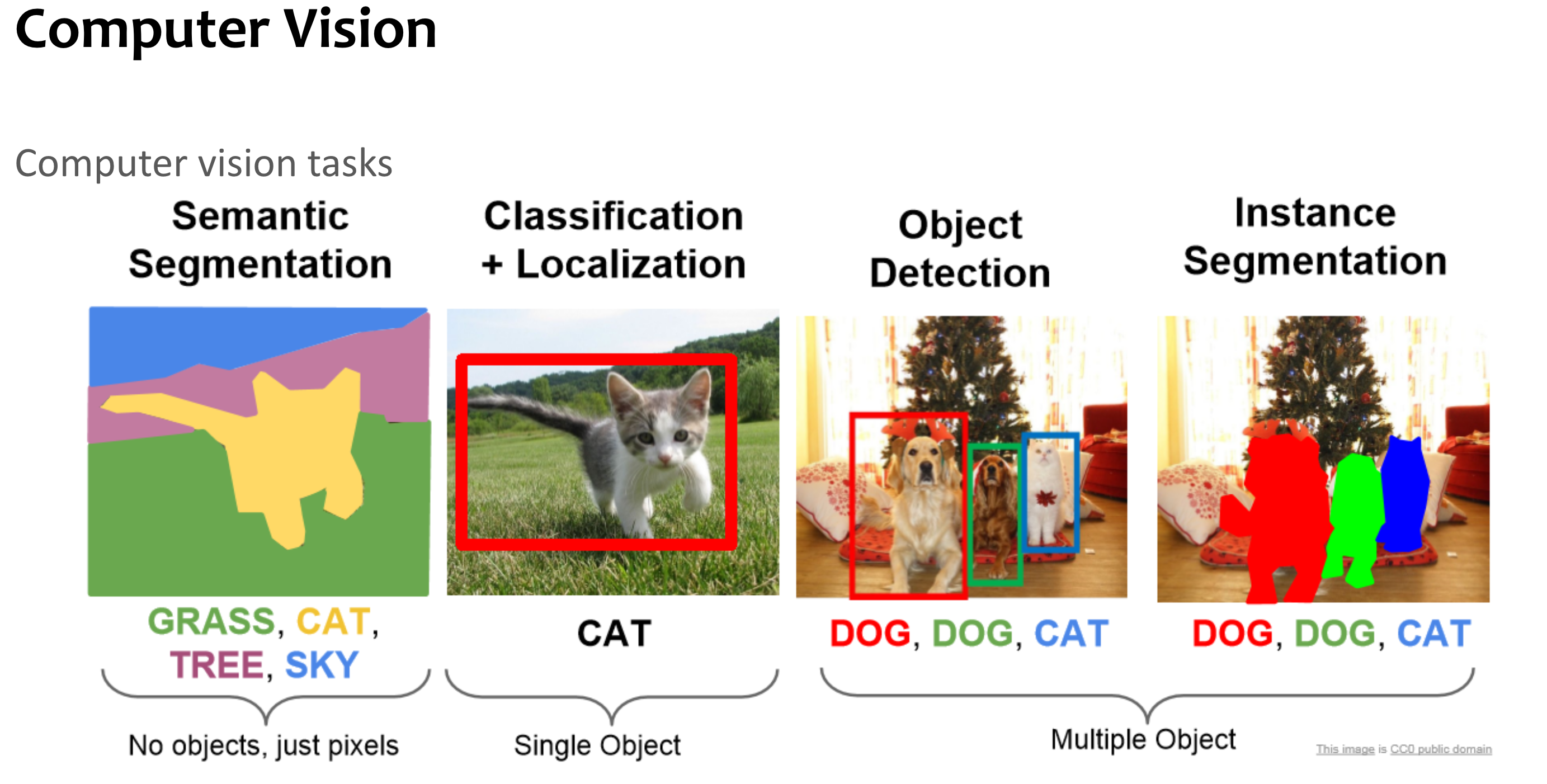
Computer Vision
Summary
Computer를 활용해서 img를 processing.
Tasks
원본 링크
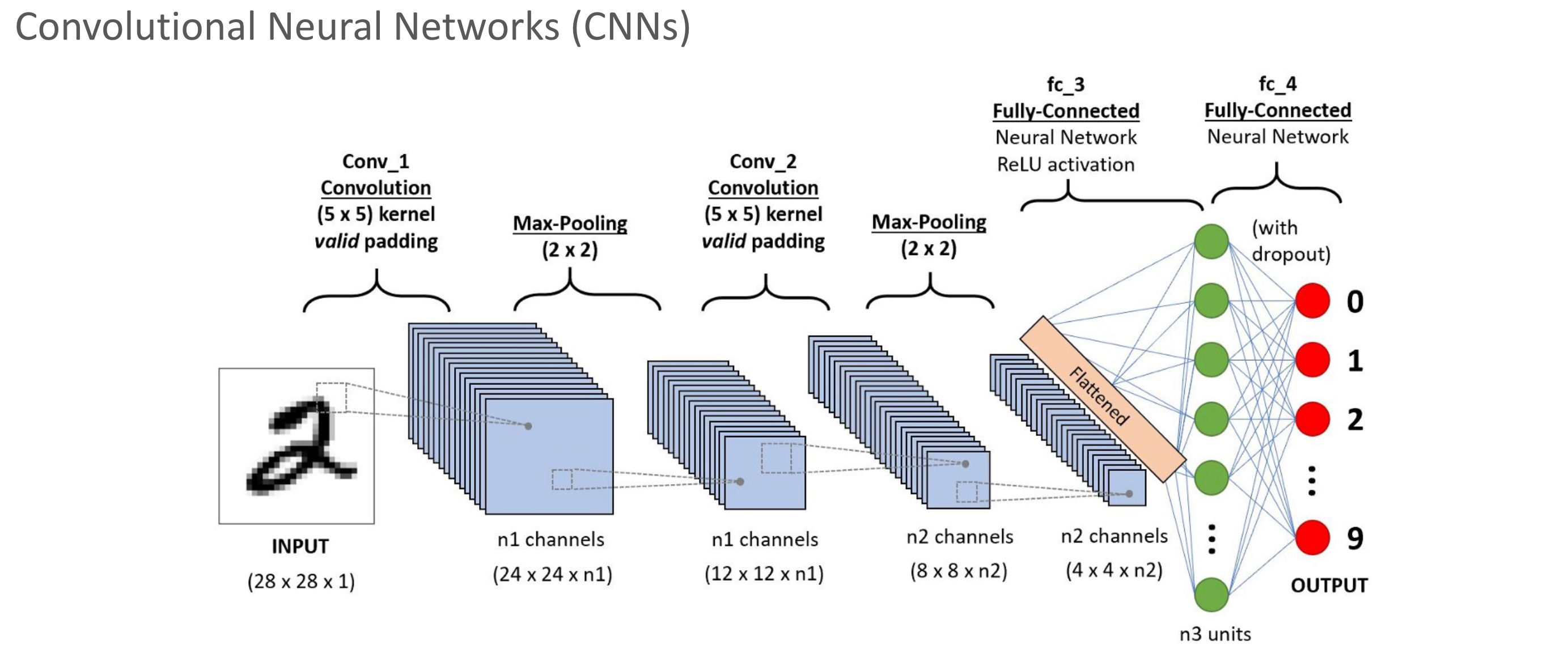
CNN
Summary
Vision 계열 대표 base 모델이자 architecture.
2012년 IMAGENET Challenge에서 AlexNet이 SOTA 달성하며 알림.
가장 핵심은 convolution(정확히는 cross-correlation) 연산을 수행하는 filter.
key: “feature를 filter로 추출하자.”
Convolution vs Cross-Correlation
일반적인 DL context에서 사용되는 연산은 모두 cross-correlation이다.
filter를 target matrix에 적용할 때에, entry 순서 맞춰서 적용하는 것이 cross-correlation.
convolution은 순서를 바꿔야 함.→ 이로 인해 convolution의 경우, associative property 지님.
Multi column
Cross Correlation
Convolution
Before the CNN
FC layers
NOTE
형태인 fc layer는 output으로 score를 뱉어냄.
pixel space에서 projection한 걸로 볼 수도.
이걸 visualization 해보면, 클래스 별 template을 가질 수도 있고 그럼.
Feature Representation
- 직접 hand tuning하여 feature를 정의하고 detect.
- DL 이전에 꽤 많이 사용됨.
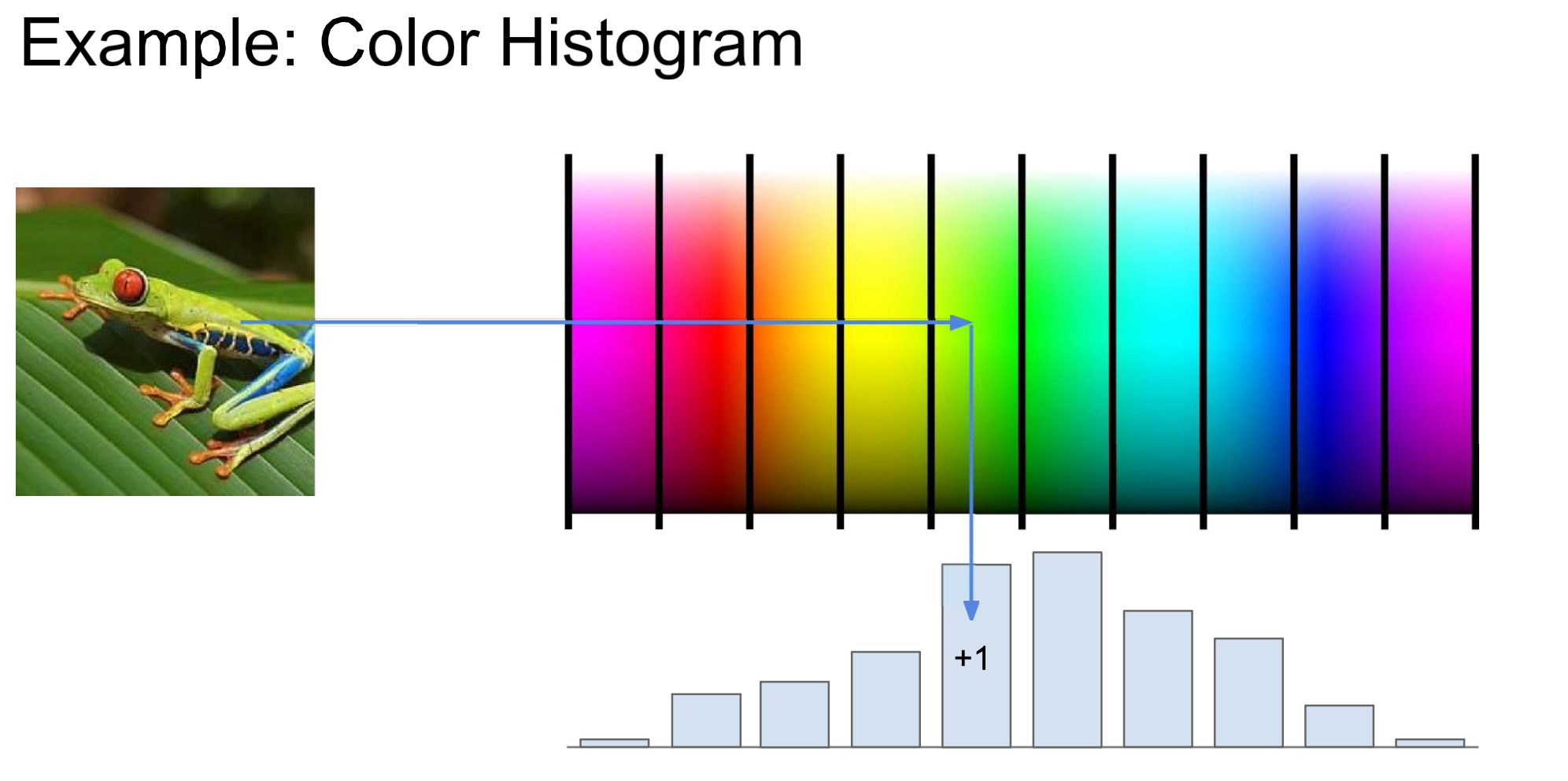
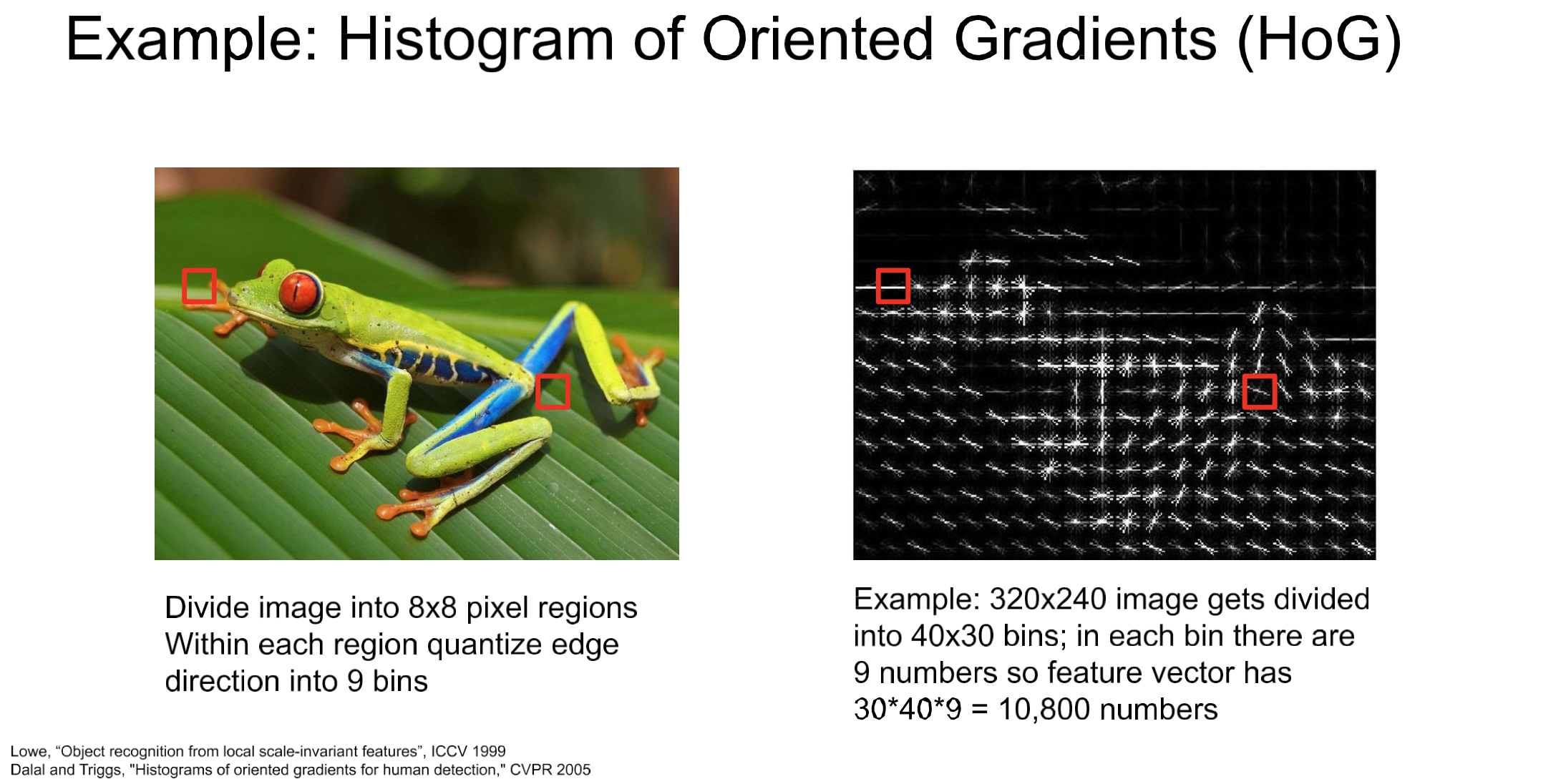
Color Histogram → HoG
NOTE
이렇게 frog의 feature인 color를 다룬다던지
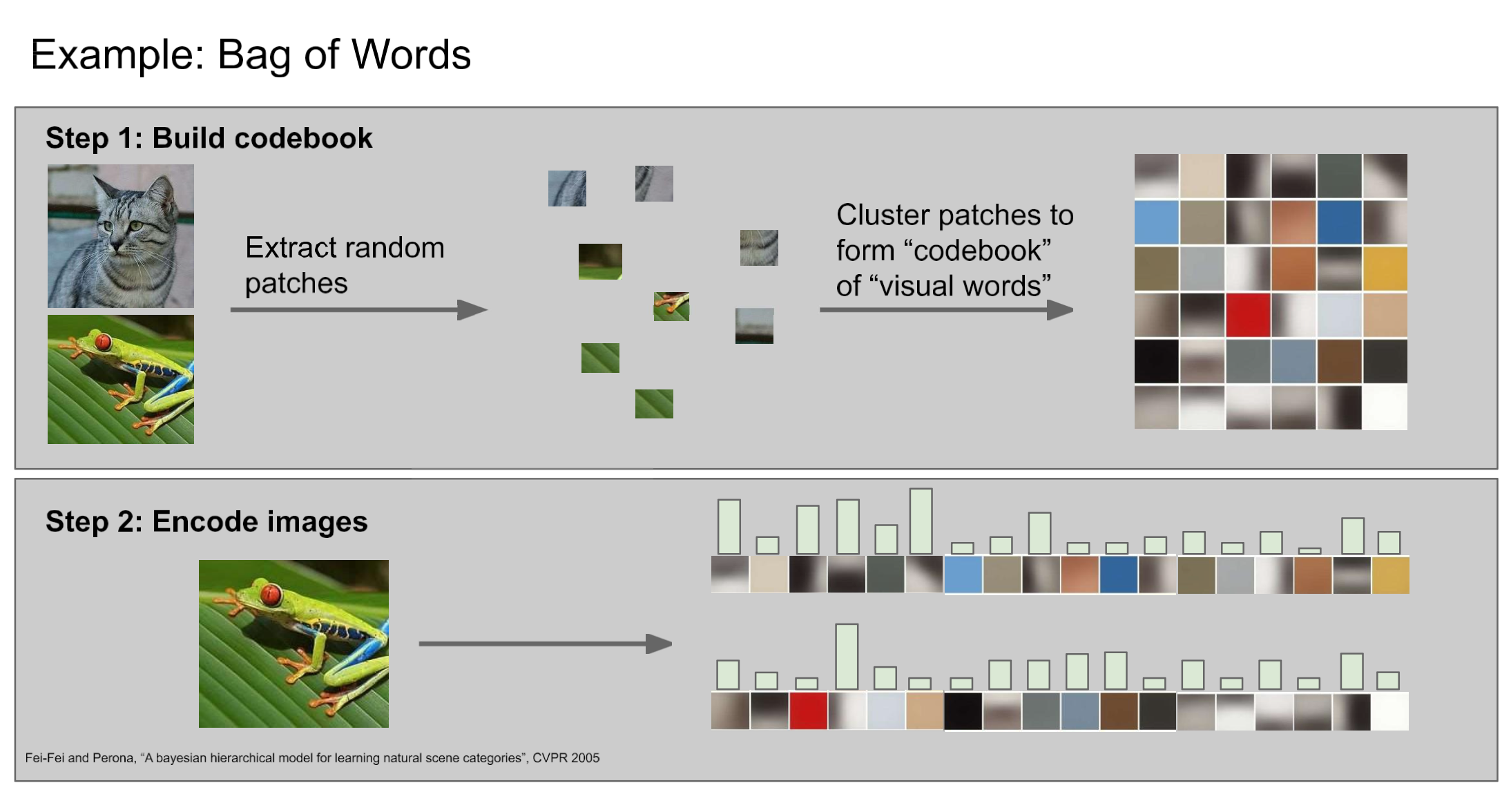
color gradient 즉, 색이 급변하는 것을 detect해서 edge로 인식하게 coding.BoW(Bag of Words)
NOTE
- NLP에서도 과거 자주 사용되던 방법.
step1. dictionary 정의
- 사전(codebook)을 만들기 위해 사진에서 random하게 patch 만들고 원본의 label을 붙여서 만듦.
step2. image encode
- dictionary 활용해서 이미지들을 encoding
Summary
Feature 접근이랑 비교해보면, feature extracting을 모델이 직접하게 한 데에 의의가 있다.(ConvNet)
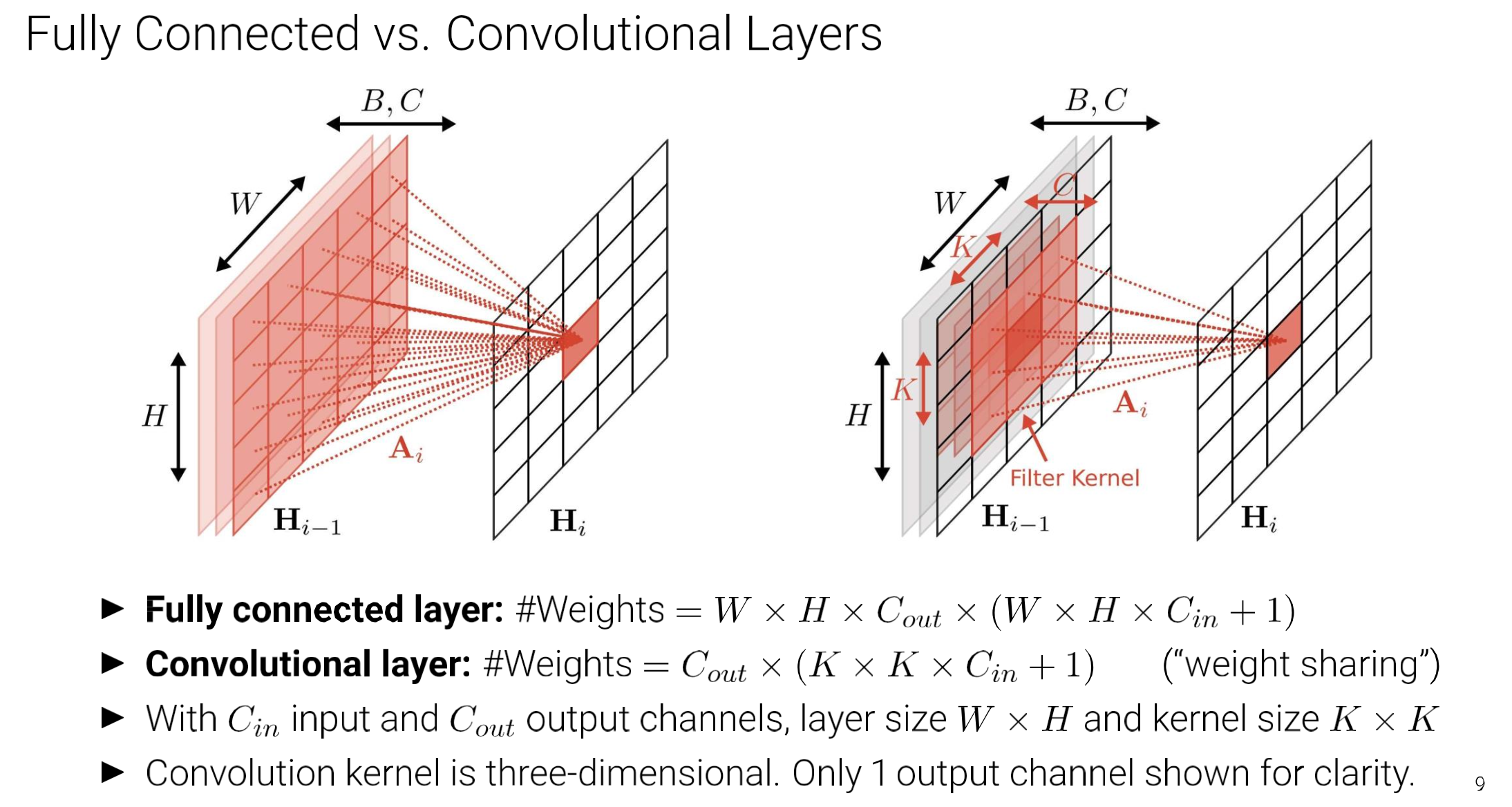
FC layers vs Convolution layers
Note
- “weight sharing”
- 1 : bias
Main Concepts of CNN
Important
- Sparse-connectivity: FC는 말 그대로 하나의 output value가 이전 layer output의 weighted-sum 형태로 들어가니, 하나의 activation에 관여하는 값들이 너무 많음. 반면, CNN은 sparse하게 locality를 잘 살린 architecture하고 볼 수 있음.
- Parameter-sharing: filter가 translation하면서 convolution 연산하니, parameter를 공유하는 효과
- Many layers: 여러 filter를 한 번에 사용하여 pattern인식에 수월.
Question
filter끼리 안 비슷해질라나?
Question
Is CNN only for img? → Nope. Also can be performed in audio area.
CNN in audio detection(ex)
Todo
- task: 위 spectrum을 가지고 ‘welcome’ 발화 부분 segmentation
by using MLP...
이렃게 trivial 하게 전 영역을 MLP하면 되겠지만, 문제는
이렇게 데이터가 주어진다면,
- 위 사진의 데이터로만 학습하면 target이 다른 위치에 있는 즉, 아래 사진의 경우를 예측하기 힘들다.
- 또한, NN의 size도 크고, 연산량이 너무 많이 필요할 뿐더러, 다른 위치에 target이 등장하는 데이터가 발생하면 재학습해야 한다.
Important
결국 우리가 원하는 건, translation에 무관하게 잘 예측하는 분류기!
→ translation에 무관하게 : Shift InvarianceScan
원본 링크Summary
작은 MLP를 window크기 만큼 움직이며, scan.
이후 max 통과 시키면 있었는지 여부는 확인할 수 있겠지.
아님 task에 따라 max 대신, softmax, MLP 등을 붙일수도 있겠지Example
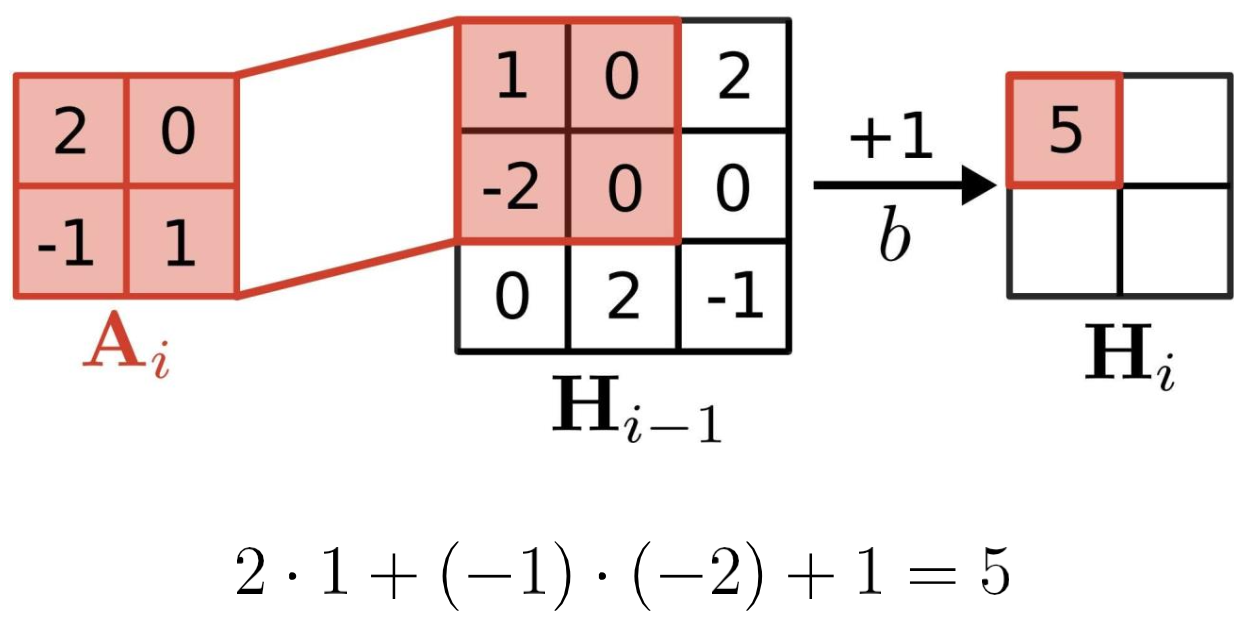
- bias 잊지 말 것.
- element-wise 연산
- Low-rank~ 는 구현 파트에서 다룸.
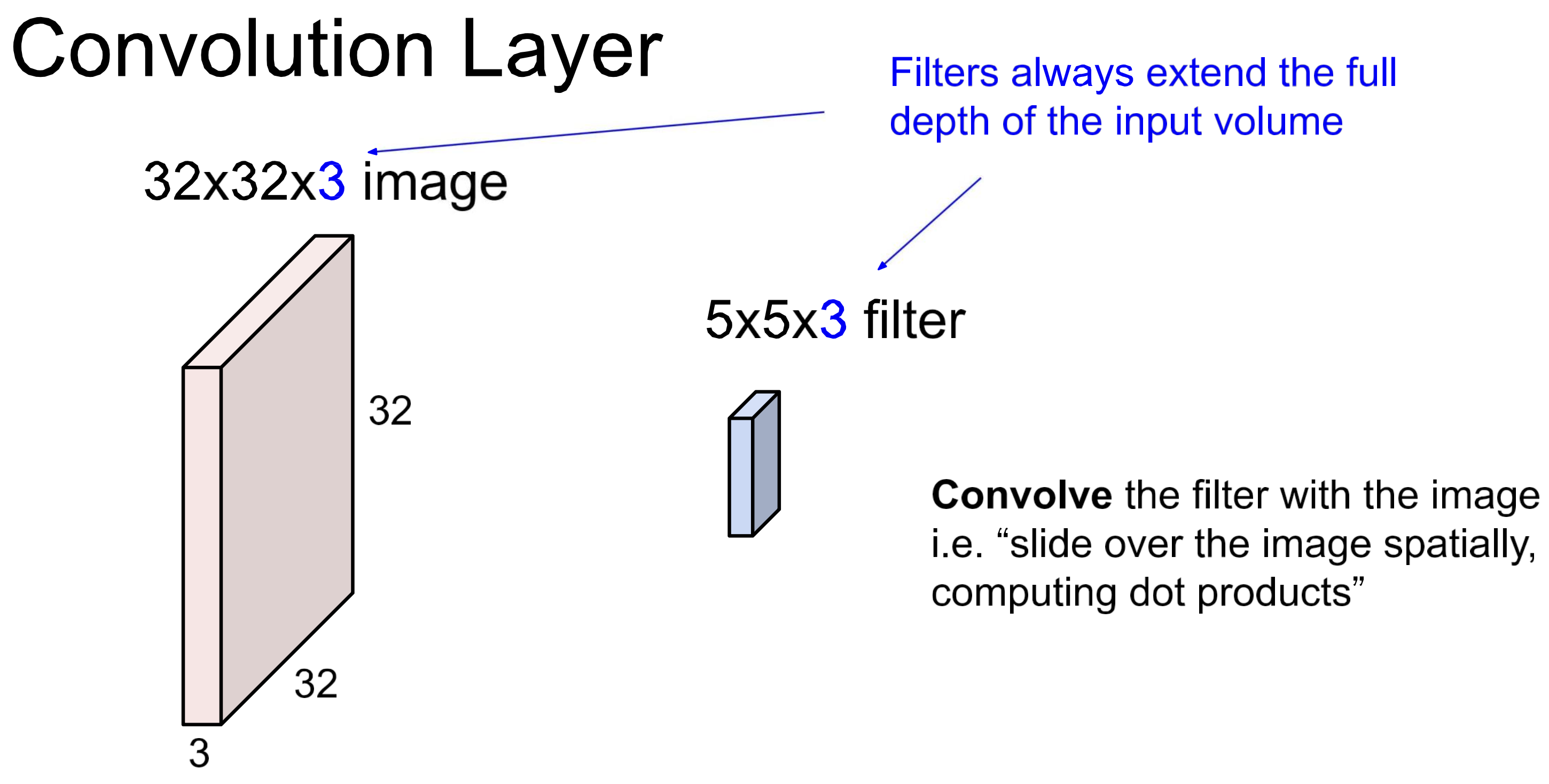
Conv-Layer
Filter size
Conv layer에서는 마지막 차원을 일치시켜야 함. (filter_depth)
Activations
결국 한 번의 convolution 연산 output은 scalar 하니이고 이걸 이동하며(sliding) 모아서 output 전체를 구성.
- output을 feature map이라고 함.
- 한 번의 convolution 연산에 사용되는 input 영역을 receptive field라 함.
- weight sharing
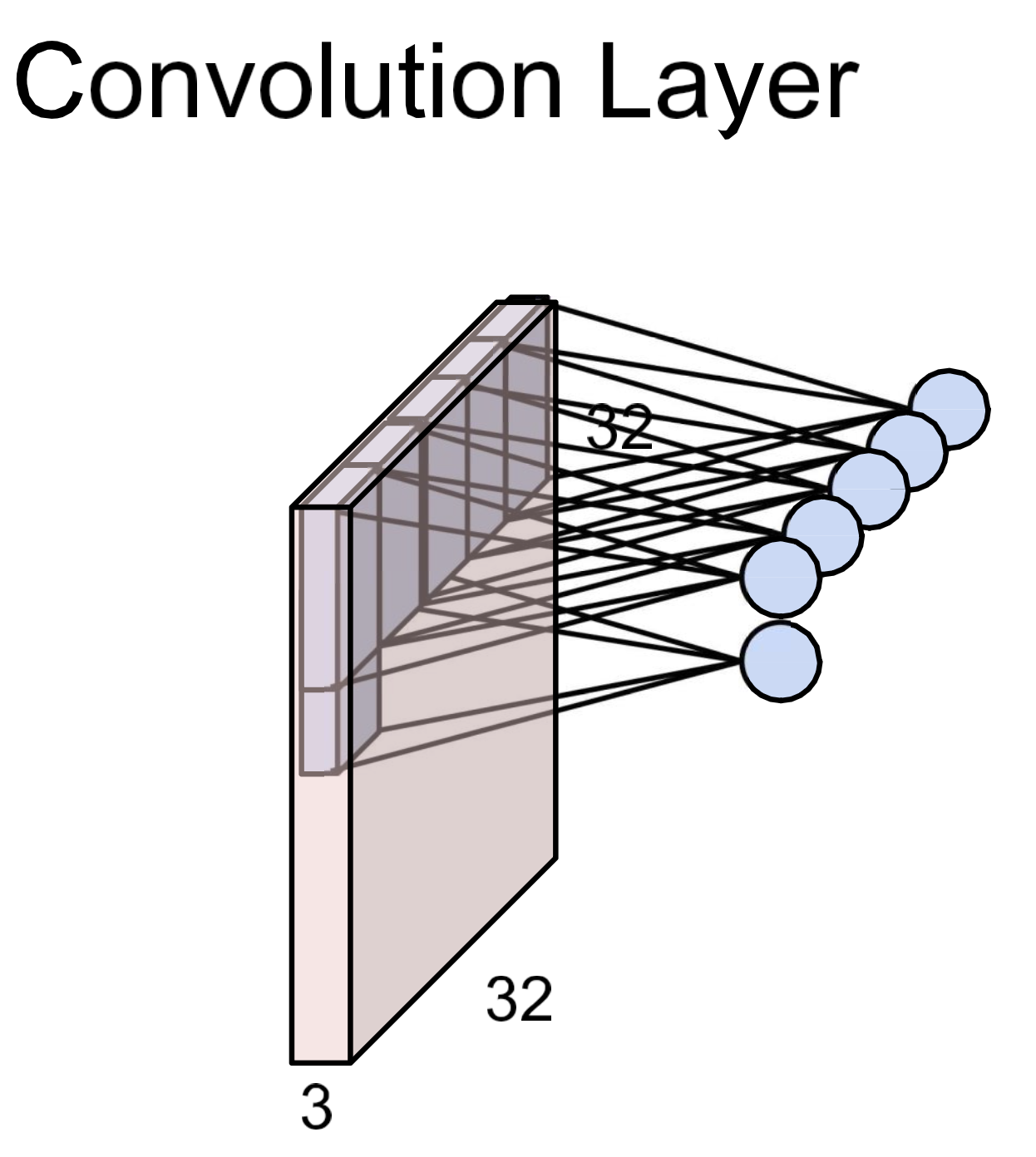
Layer overview
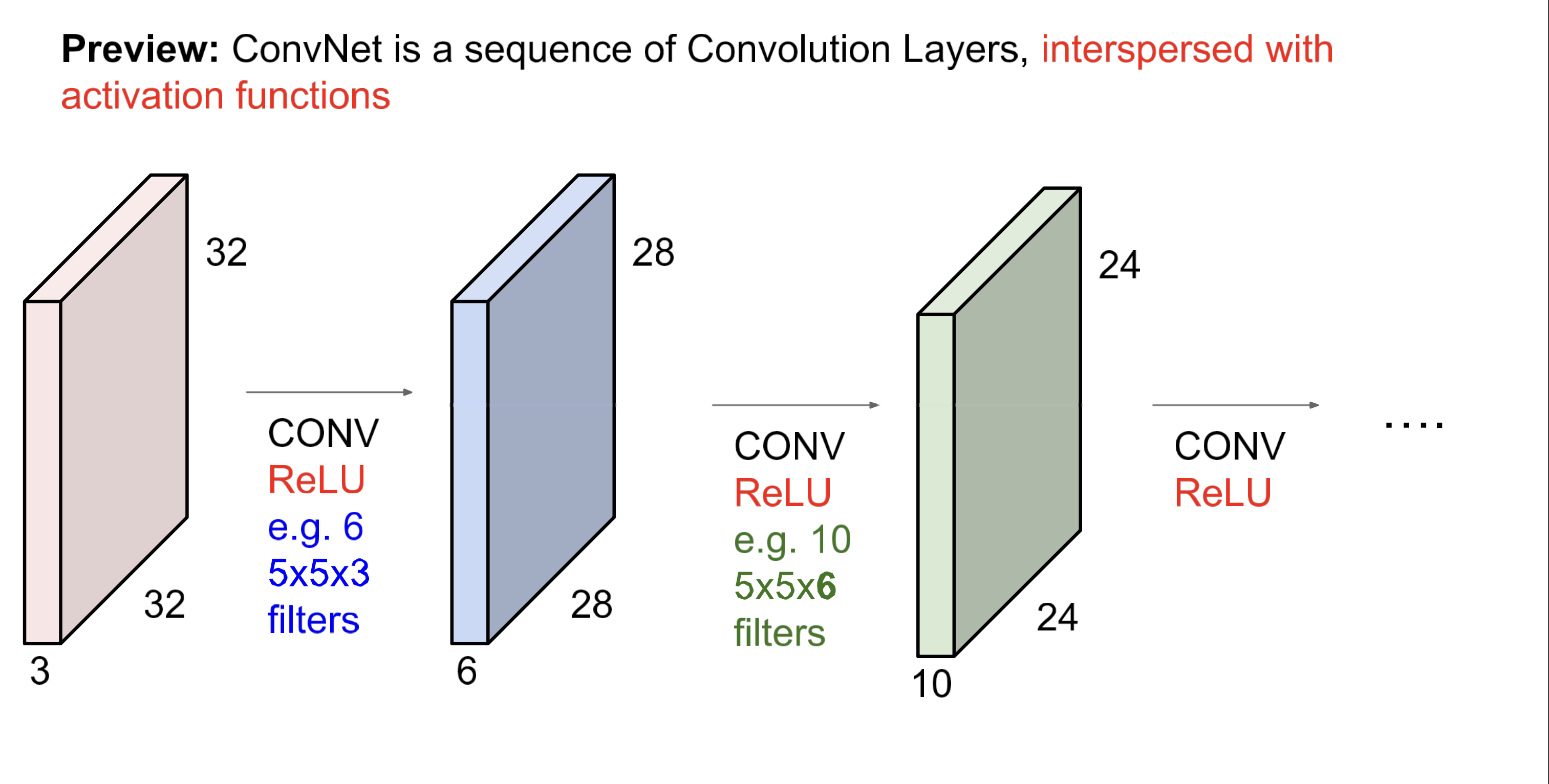
filter(kernel)이 여러 개이면, 위 그림과 같은 구조.
각 kernel 별 bias 가 하나씩. 즉, bias의 개수 = kernel의 개수
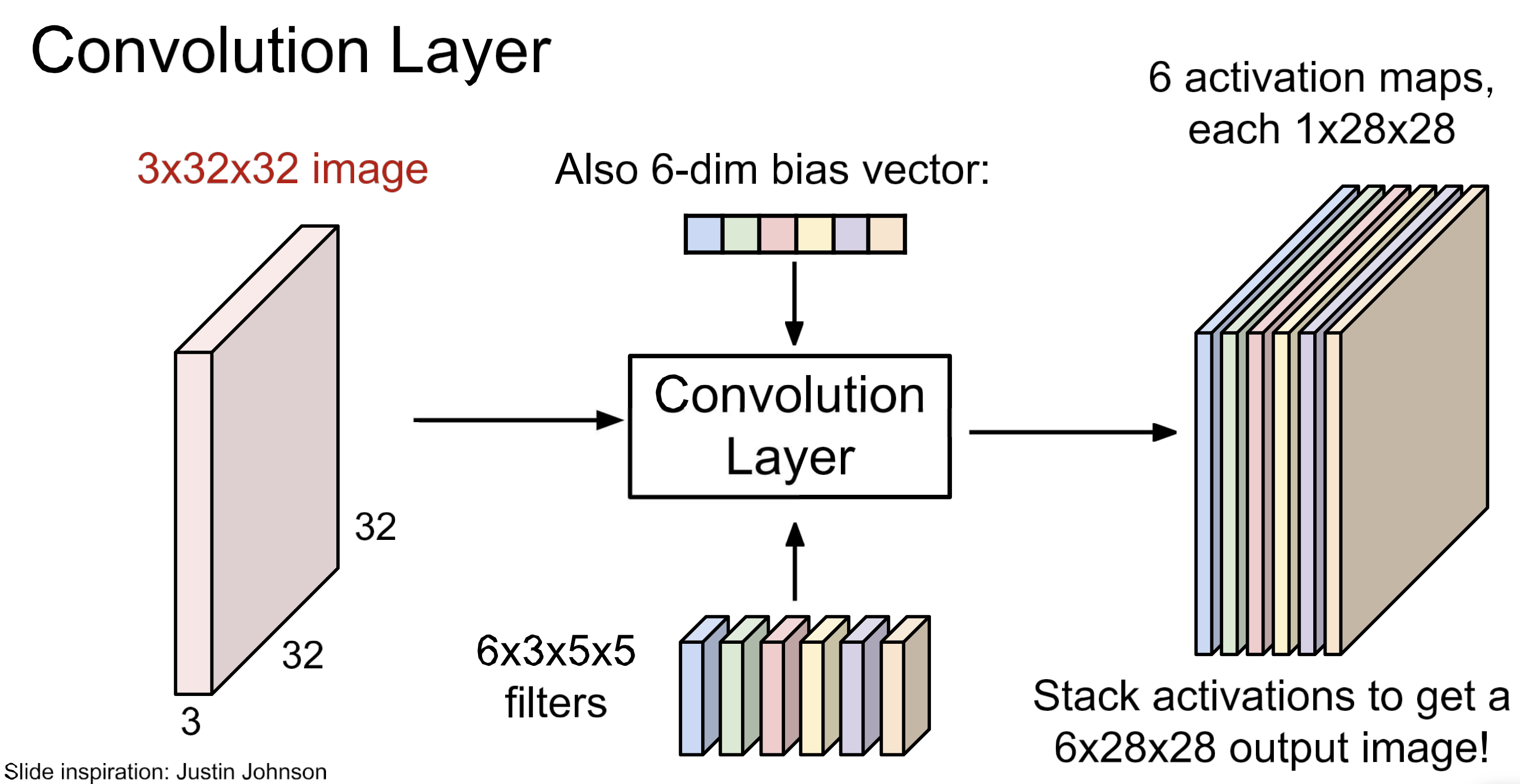
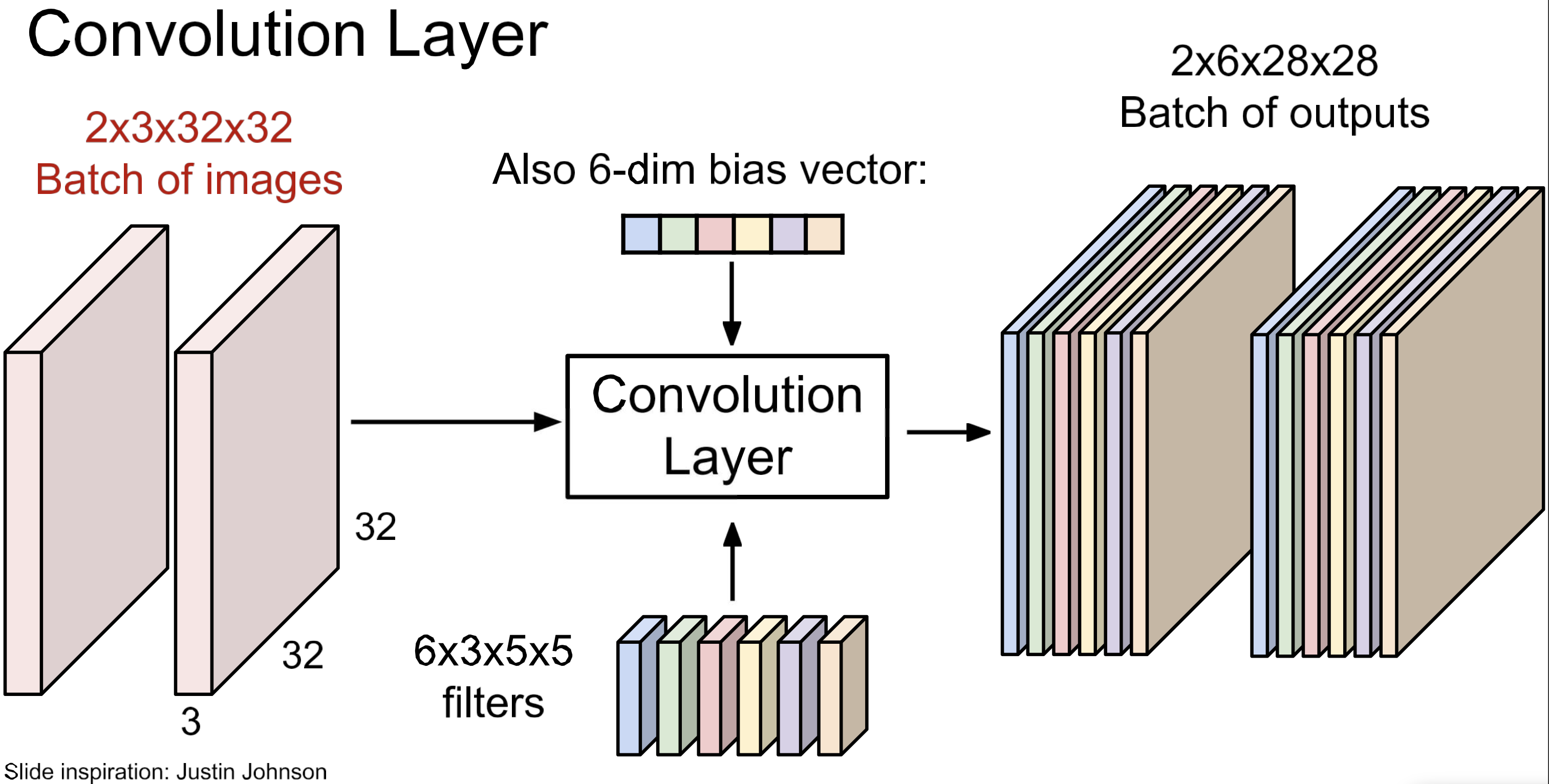
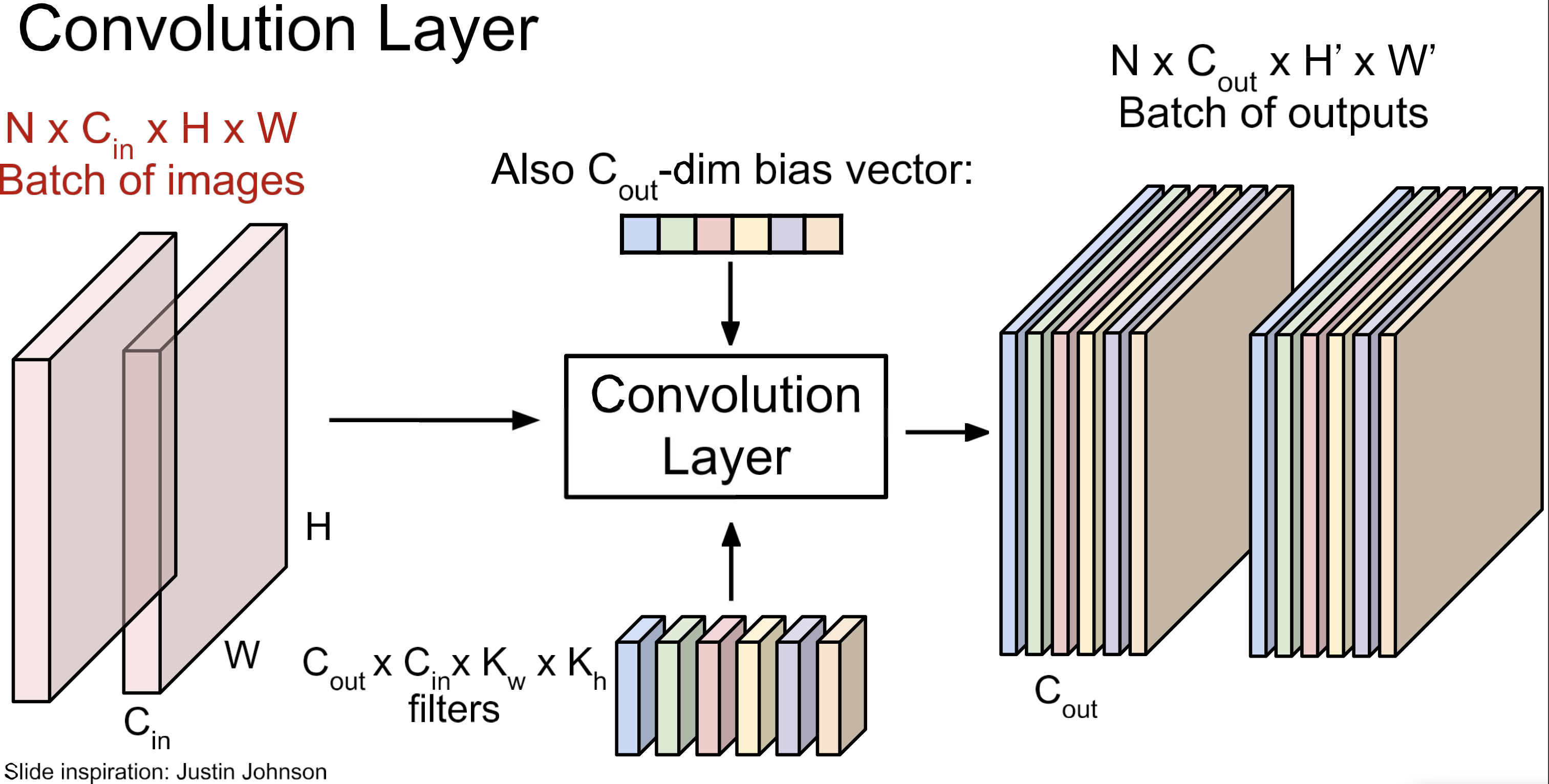
batch 처리까지해서 본 view.
문자화해서보면 위 처럼. 이게 Conv Layer. 이제 이 layer를 여러개 쌓고 중간에 activation function을 넣어주면,
ConvNetWhat do Filters learn?
Multi column
Linear classifier
One template per class
MLP
Bank of whole-image template
AlexNet
First layer conv filter : local image templates(edges, opposing color)
AlexNet: 64 filters(3x11x11)
Feature map size
NOTE
Example
Input size: 32 x 32 x 3
Kernel : 10 per each 5x5 with stride=1, padding=2
output size?
(32-5+2x2)/1+1 = 32 (output size)
32x32x10 (output size per channel)
Number of parameters in this layer?
10 x (5 x 5 x 3 + 1)
760
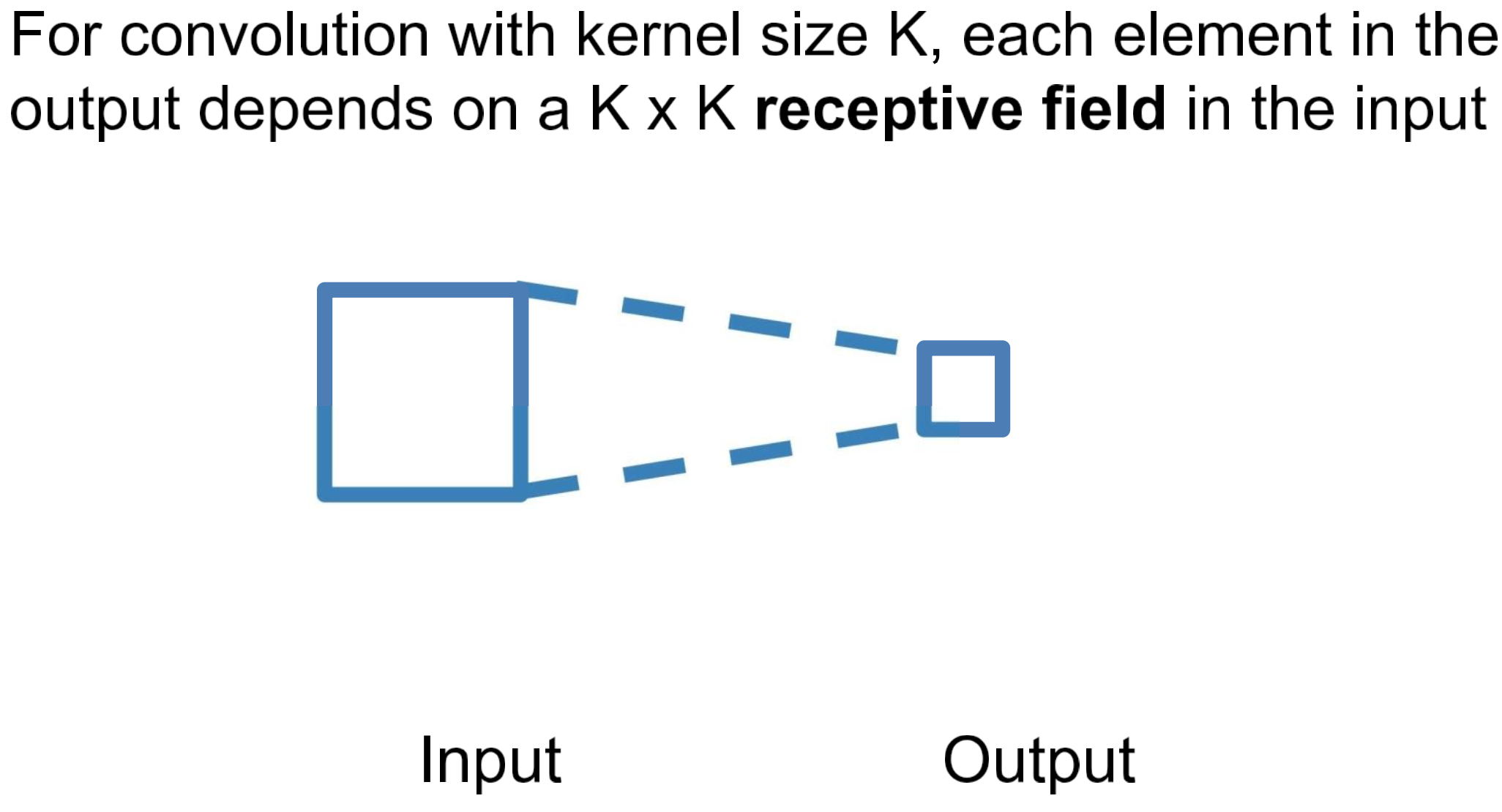
Receptive Fields
NOTE
한 번의 convolution 연산 시 사용되는 Input의 regieon
Warning
“receptive field in the input”
“receptive field in the previous layer”Architecture
Components
Summary
- Conv Layer
- Pooling Layer
- FC Layer
- Normalization Layer
- Activation Function
Case Study
Info
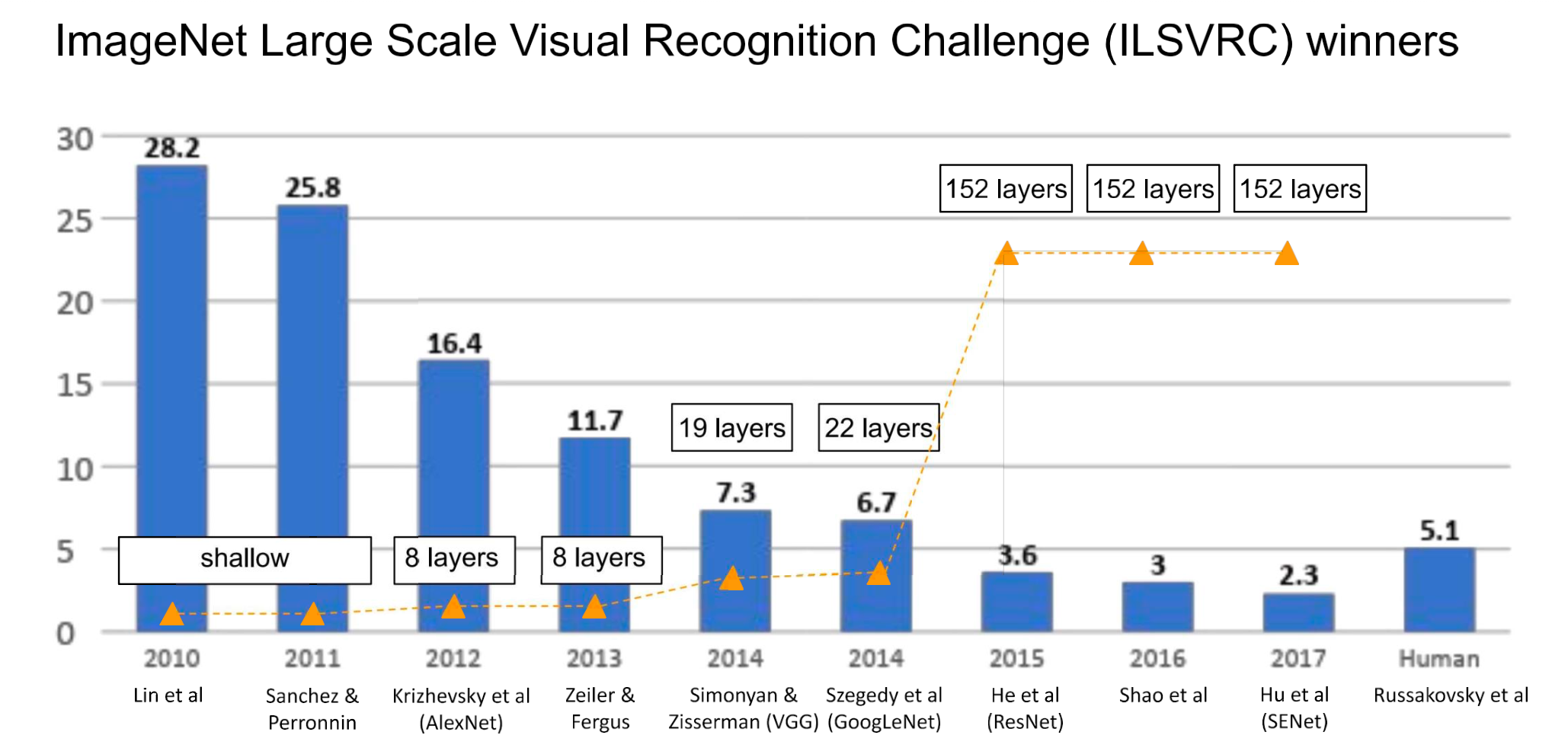
ILSVRC(ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge)
- image classification 대회
- 향후 kaggle로 흡수됨.
원본 링크
- AlexNet
- ZFNet
- VGGNet
- GoogLeNet
- ResNet
- SENet
- DenseNet
- Deep Residual Networks
- Wide Residual Network
- MobileNets
- Neural Architecture Search with Reinforcement Learning(NAS)
- EfficientNet
Vision Transformer(ViT)
Summary
transformer model의 attention을 사용해서 만든 vision model.
img를 patch로 분할하고 바로 transformer에 넣음.
Example in Image Captioning
Example
원본 링크Tip
NLP
Summary
말 그대로 자연어를 처리하는 분야.
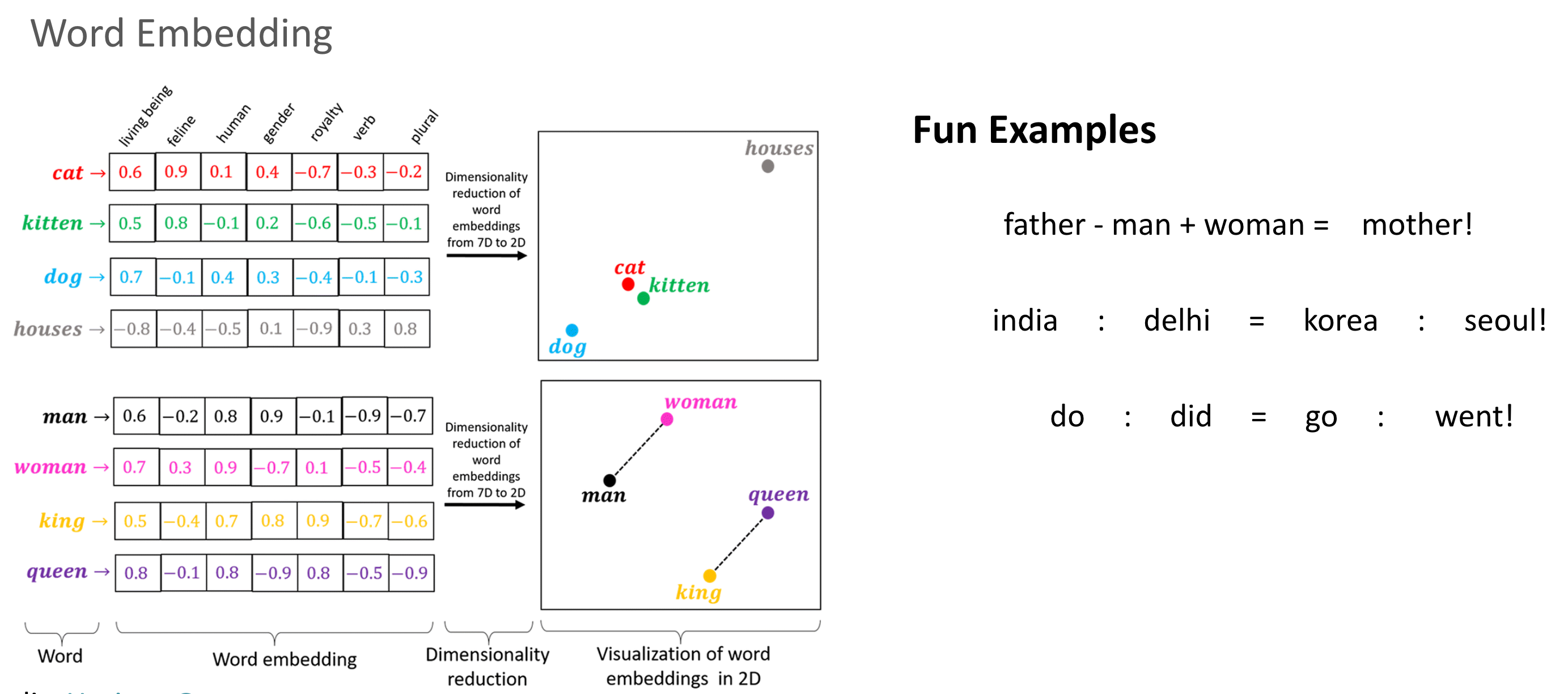
Word Embedding
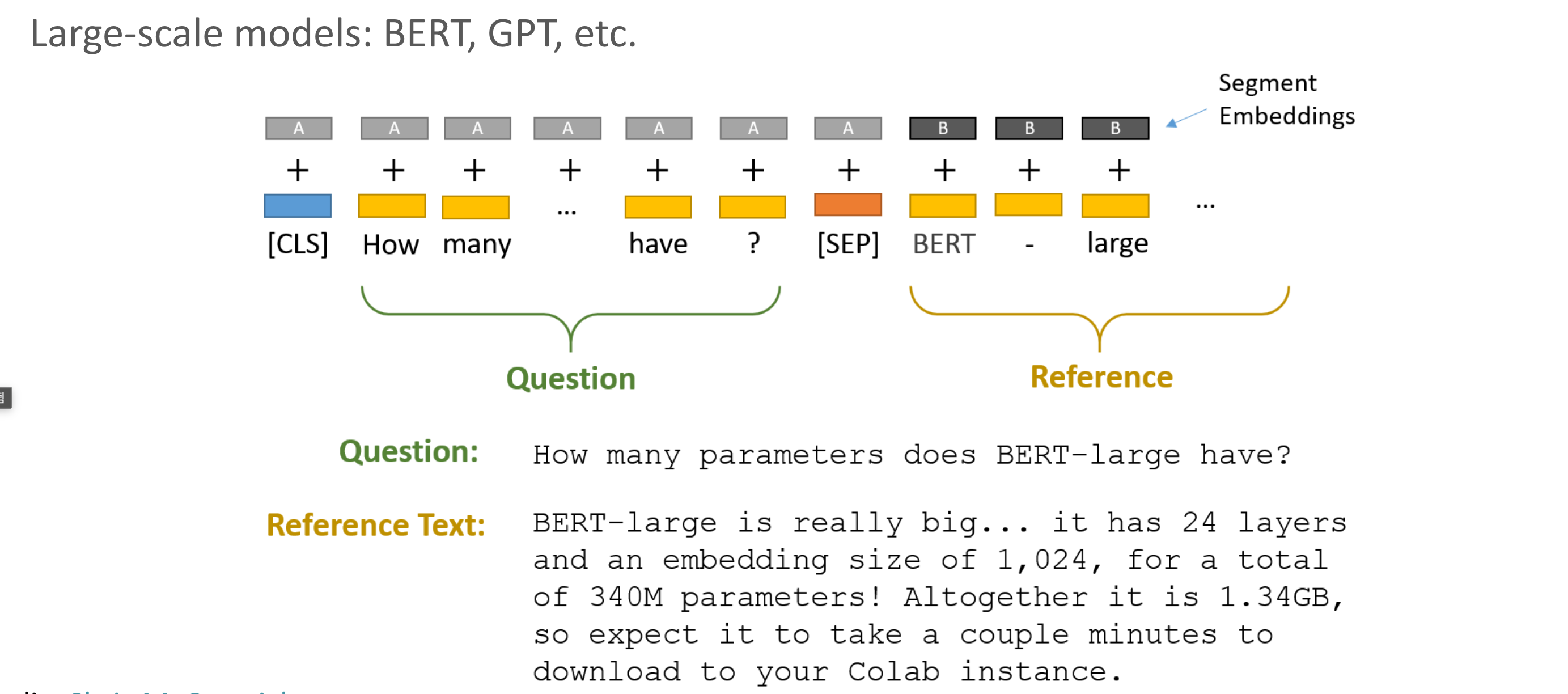
LLMs
원본 링크
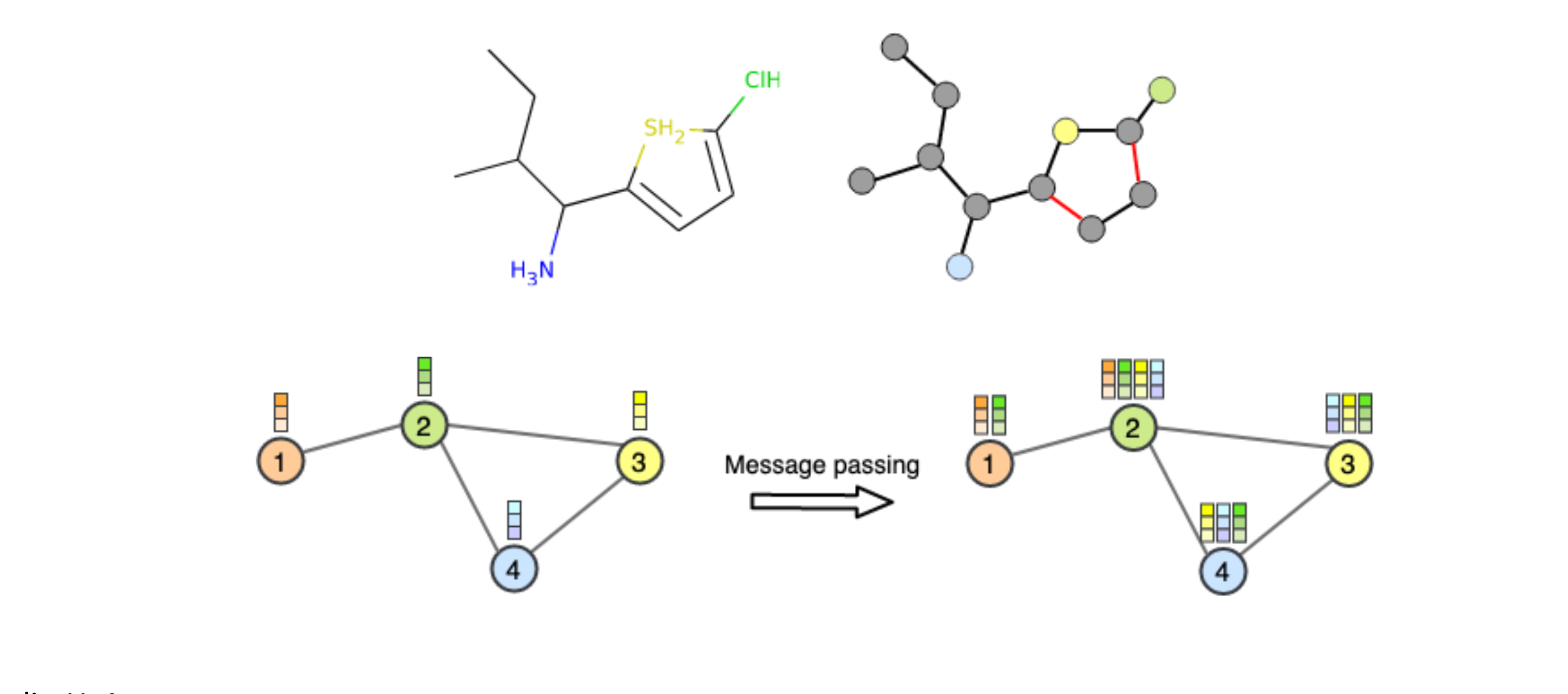
Graph Neural Networks
Summary
그래프 형태의 데이터를 처리하기 위한 신경망
노드와 엣지로 구성된 데이터 처리에 특화됨.원본 링크
Meta Learning
원본 링크Summary
Learning to Learning
- One of the big problem if DL: no adaptation to new tasks or environments.
“다양한 task를 하면서, 새로운 task를 배우는 능력 자체를 학습하는 것.”
GANs(Generative Adversarial Networks)
Summary
서로 경쟁하는 두 개의 신경망을 이용해 현실 같은 데이터를 생성하는 모델(Generative)
- 가짜를 진짜처럼 만들려고 하는 생성자(Generator)와 그걸 잡아내려는 판별자(Discriminator)가 경쟁하며 함께 발전하는 구조
원본 링크
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/CNN/assets/audio-spectrogram.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/CNN/assets/audio-seg-mlp.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/CNN/assets/audio-seg-mlp-prob.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/assets/shift-invariance-soln-scan.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Domains/Computer-Vision/assets/ViT.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Transformers/assets/ex-ViT.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Vision-Transformer/assets/ViT-vs-ResNet.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Vision-Transformer/assets/ViT-ex.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Generative-Adversarial-Networks/assets/GANs-concept-ex.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Generative-Adversarial-Networks/assets/GANs-concept-ex2.png)