Image Captioning
Summary
Tip
Warning
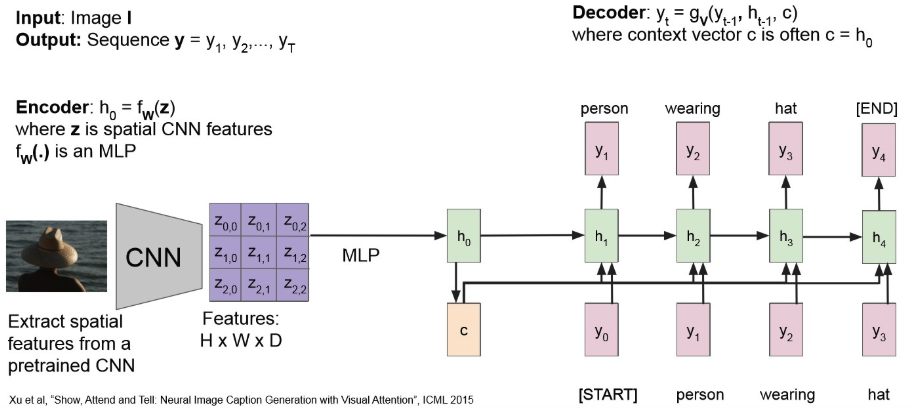
마찬가지로, bottle-neck 문제가 있다.
(Many-to-One) architecture를 따르다보니, input 정보를 하나의 context vector로 압축하는게 쉬운 일은 아니다.또한, 기존 RNN 문제인 long-term dependency 문제 역시 존재.
→ Attention을 적용해보자!Check
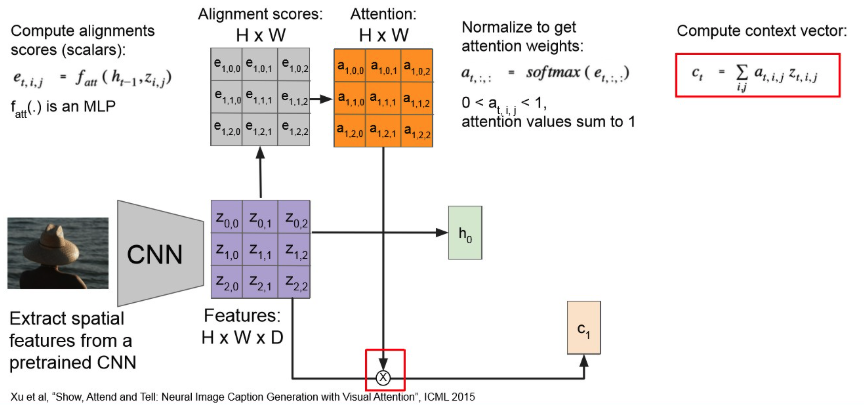
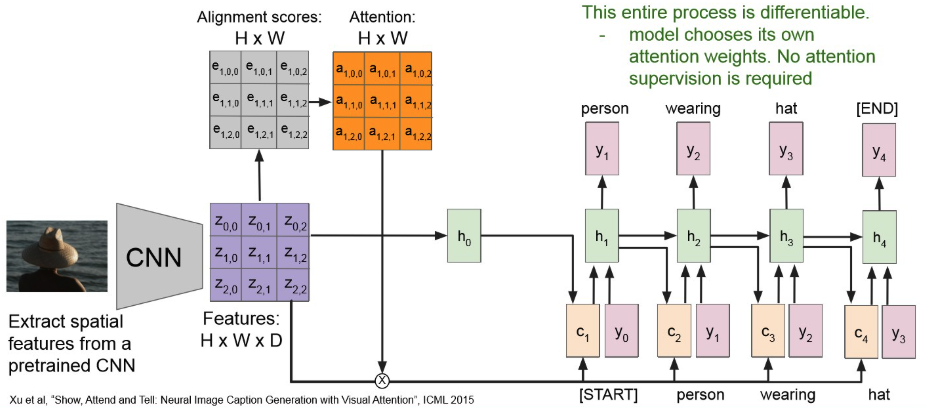
Attention : 모든 time step 마다 context vector를 생성.
→ 각 time-step 마다 context vector에 기여하는 img-region이 다르다!
- attention 수행하여 attention map 만들고,
- 이를 기존 Feature map이랑 element-wise mul 해준뒤,
- MLP 통과 시켜 context-vector 얻는다.
- 이를 RNN에 넣어서 seq generattion
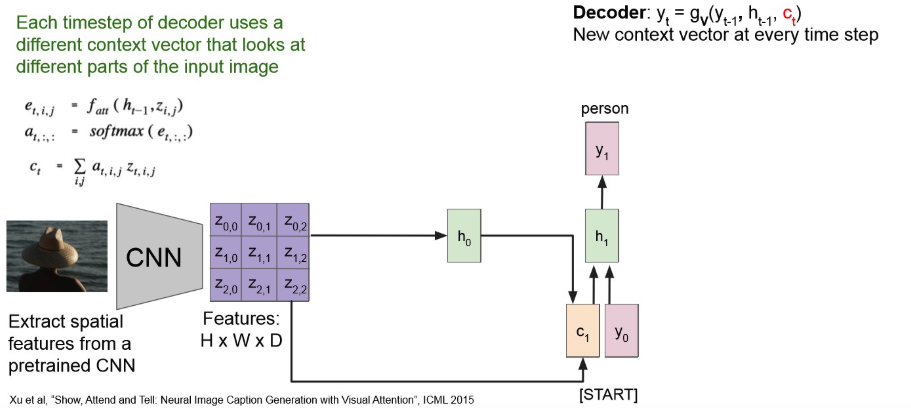
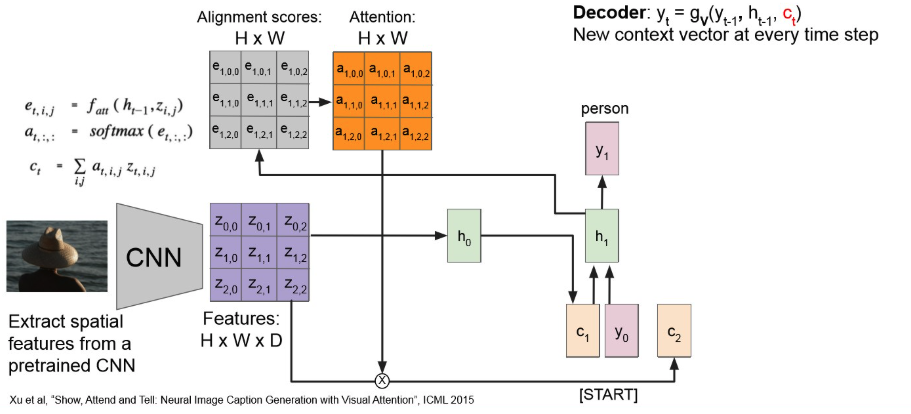
그러면 첫 output은 다음과 같이 나오고,
이를 반복해서 다음 context vector는 아래처럼 만들어진다.
계속 반복해보면,
원본 링크Note
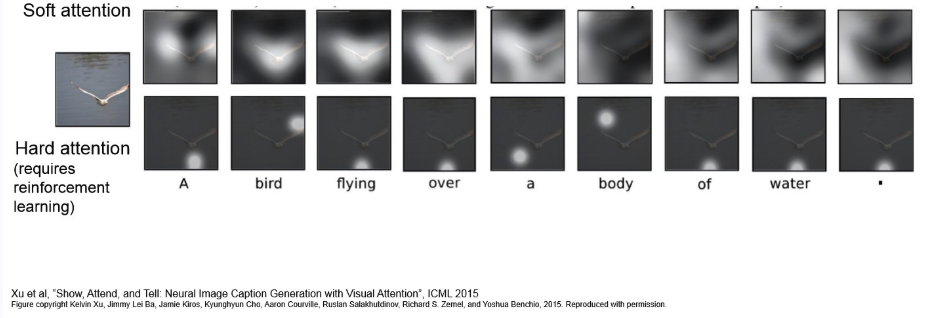
- Soft-Attention : input의 모든 부분에 대해 Weighted-Sum을 구하는 방식.
- 모든 input region에 대해 0~1 사이 확률 값(attention score)를 부여하고, 이를 합쳐 context vector를 생성.
- Differentiable하여 기존 Backpropagation을 통해 learnable.
- input이 클 경우, cost-expensive
- Hard-Attention: input 중 특정 영역을 sampling.
- 확률 분오에 따라 특정 region을 하나 선택. 선택되지 않은 곳은 0으로 치환.
- Non-differentiable.
- 일반적 Backpropagation을 사용할 수 없어서, 강화학습의 REINFORCE(? 공부하자.) 같은 걸 사용한다.
- inference 시, 연산 비용은 적을 수 있으나, 학습 과정이 까다롭고 variance가 클 수 있다고 한다.
Transformer
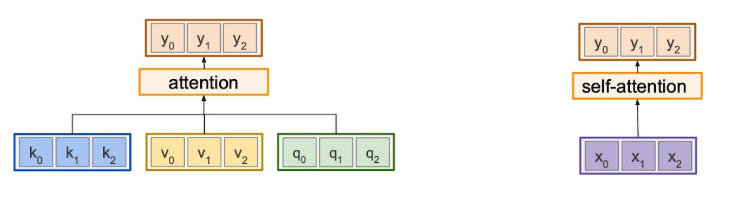
Attention
Attention
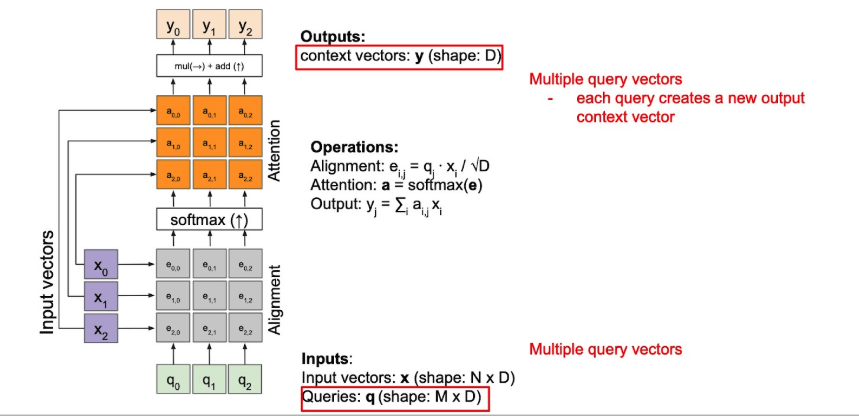
General Attention(Cross-Attention)
General Attention(scaled-dot attention)
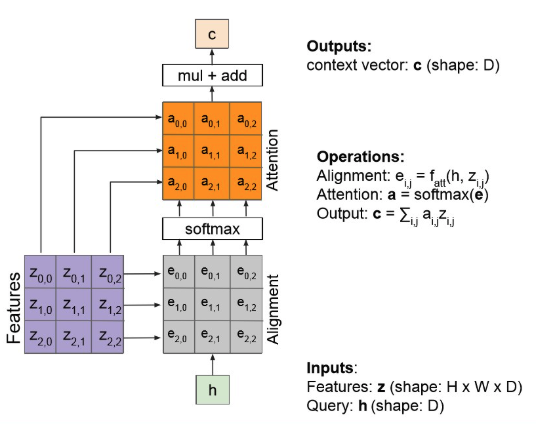
Attention block in Image Captioning
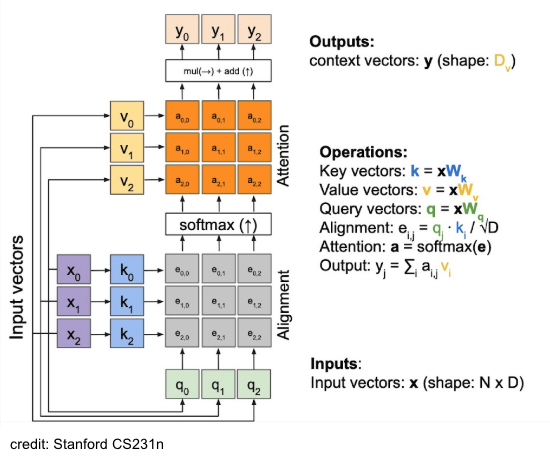
- alignment layer를 통과한 후, softmax를 통과시켜서 attention-map을 획득.
- attention map이 그 부분에 얼마나 attention을 가할 지 말하는 거니, 이를 원본에다 element-wise mul하고, sum.
- 이의 output이 context vector.
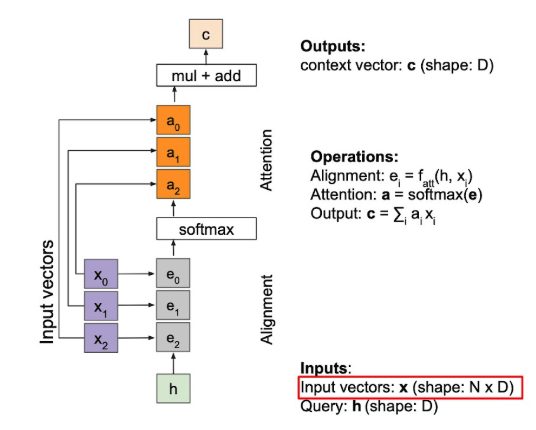
이를 일반화해서 아래처럼 그릴 수 있다.
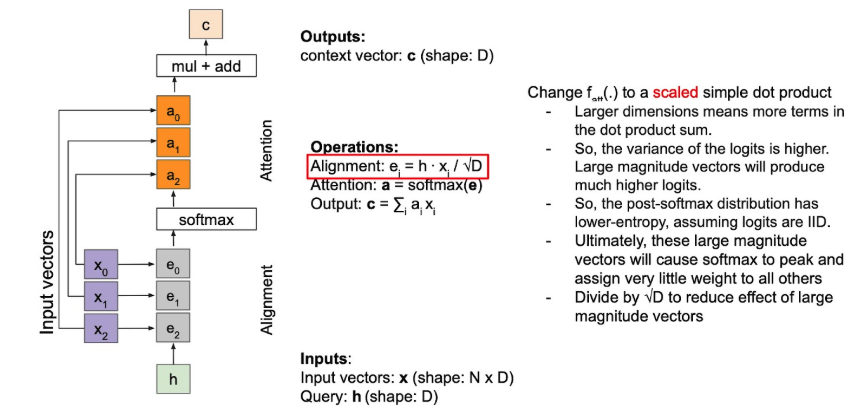
- 는 simple하게 dot-product 사용할 수도 있다.
- 이때, dot-attention에 scaling(smoothing)을 걸어주면, scaled-dot attention
- 를 dot-product하고, 로 나눠주는 것.
- benefits:
- prob-dist에서 한 값만 극단적으로 커지는 걸 완화하고,
- numerical stability 확보 가능(softmax에서 )
General Attention(to the QKV attention)
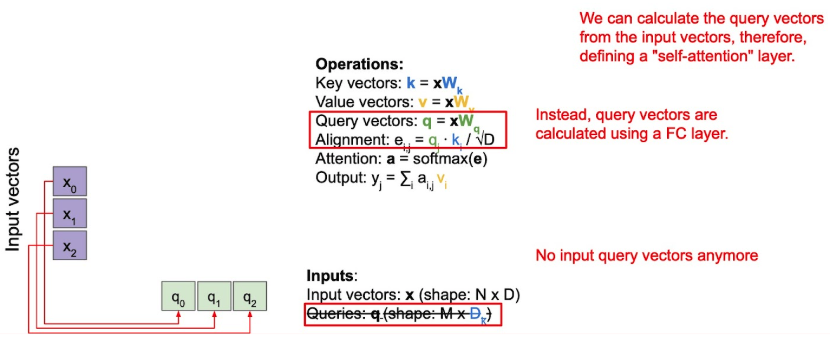
- Query expansion
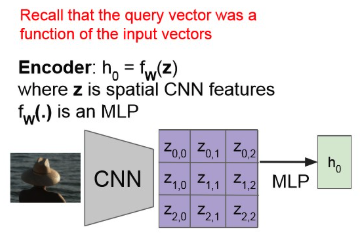
input vector가 attention 계산과 alignment 시 동일하게 사용되는데, 굳이 같아야 할까?
→ K, V matrix로 decompose.
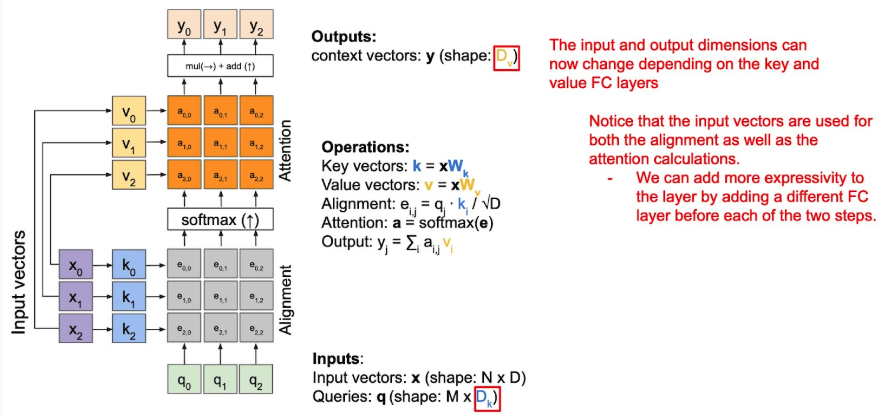
- Key-Value expansion
- context 계산과 alignment(attention-map을 구하는) 계산 시 사용하는 input-vector를 중간에 MLP 통과시켜서 압축도 해주고, 서로 다르게 해줘서 expressivity를 증가.
Self-Attention
Self-Attention
Q도 input에서 direct하게 뽑자!
- 이러한 self-attention도 permutation invariant.
Warning
문제는 이러한 순서에 무관한 게, NLP에서는 좋지 않을수도.
일반적으로 말의 순서가 바뀌면 의미도 바뀌니까.
→ Positional Encoding 도입.Masked Attention
NOTE
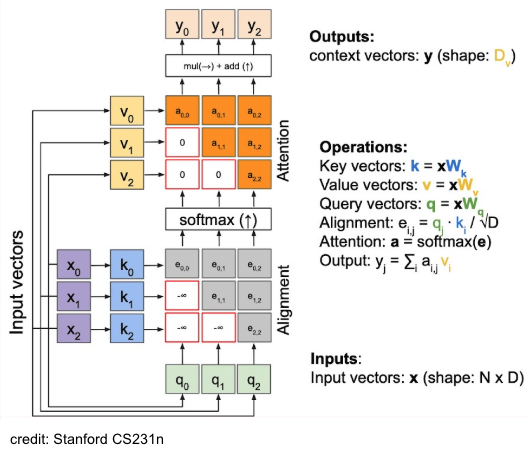
Language Model 학습 시 attentionㅇ 할 때, 현재 time-step 기준으로 이전의 query에 대한 참조를 막고 싶은 때가 있다.
- 예를 들어 GPT 처럼 NTP 과제를 수행해야 하는 모델을 학습 시킬 때, 다음 token을 예측하기 위해 현재 토큰 이전만 참고하여 attention을 수행해야 하지, 그 이후의 token까지 미리 보고 결과를 예측하는 건 사람이 정보 처리하는 것과는 조금 다르다.
- 이때 attention에 masking을 적절히 하여, attention하는 것이 masked-attention
- future token 위치에 를 넣어서 attention map에서 해당 위히에 0이 부여되도록 함.
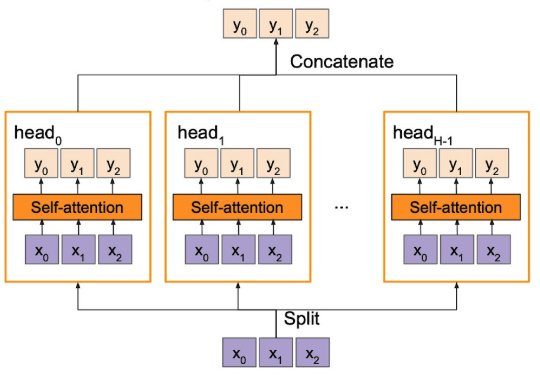
Multi-head self-Attention
NOTE
- One-to-many 같은 task 시 유리한 점도 있다.
- 일단 기본적으로 expressivity도 증가하겠지.
Comparison between self-attention & general-attention
Summary
- self-attention은 input으로 부터 Q, K, V 생성하고, general은 그게 아닐 수도 있다.
Transformer에서
- encoder-decorder attention이 general attention의 한 예시
- Q: Decoder oriented
- K, V : Encoder oriented
- encdoer 내부의 attention은 완벽한 self-attention
- Q, K, V: 모두 encoder input으로 들어오거나 encoder 내부의 이전 layer로부터 오는 Q, K, V 사용해서 attention 진행.
Examples
원본 링크Example
Positional Encoding
Positional Encoding
Summary
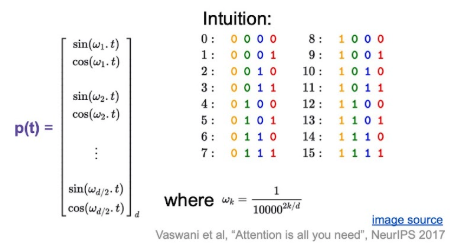
input seq에 대한 순서 정보를 encoding 하는 게 목적.
transformer에서는 아래와 같이 sine-cosine을 사용해서 fixed encoding 함.
원본 링크Question
Why sine | cosine?
- 덧셈 정리 같은 걸 사용하면, 특정 offset 위치를 선형함수로 표현할 수 잇으니, 모델 입장헤서 학습하기 쉬워, 상대적 거리를 학습할 수 잇을 것이라 기대 가능.
- Extrapolation : train-set보다 더 긴 문장이 들어와도, 주기 함수를 사용하면, fixed된 rule에 따라 이에 해당하는 positional vector를 만들어낼 수 있어, 유연하게 대처할 수 있을 것이라 기대.
# Comparison between RNN
Summary
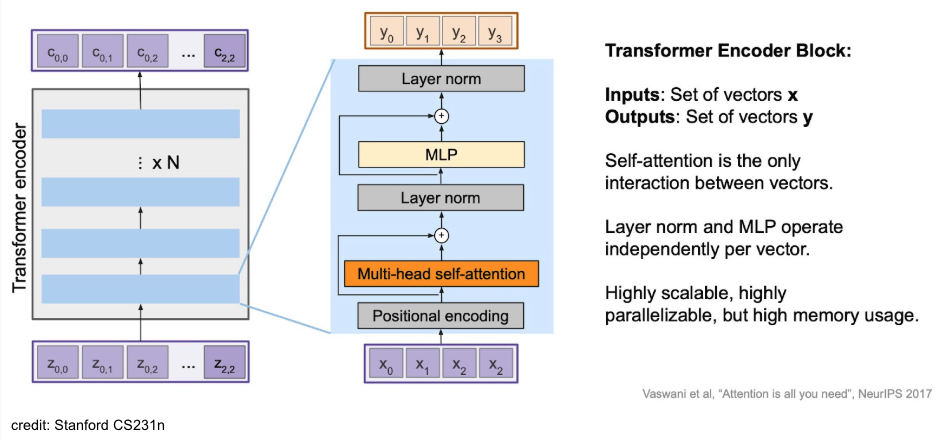
Tranformer Architecture
Encoder
Summary
original transformer information
- (numer of head)
- (dimension of query)
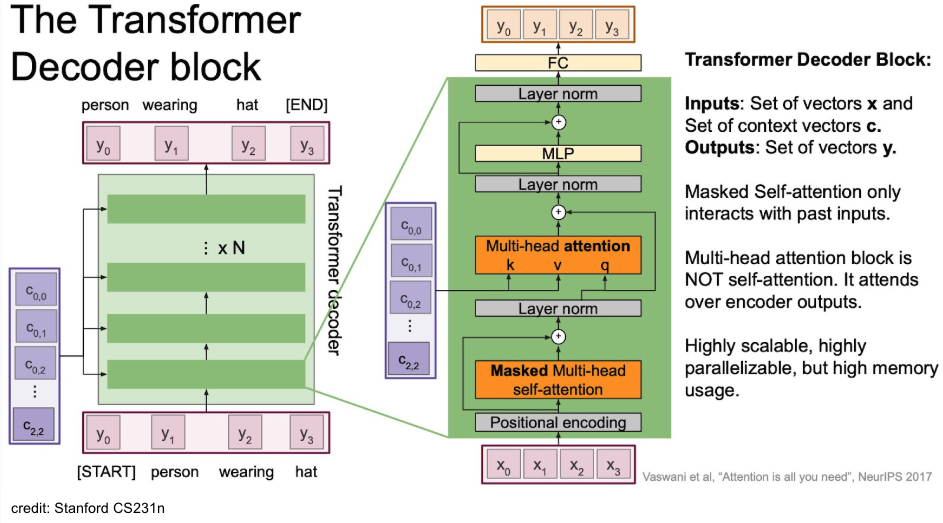
Decoder
Summary
original transformer information
- (numer of head)
- (dimension of query)
Tip
대부분은 encoder와 비슷한데 중간에 encoder-decoder attention이 들어가 있음. 이 때, K, V의 source는 encoder라는 점이 point!
Examples
Example
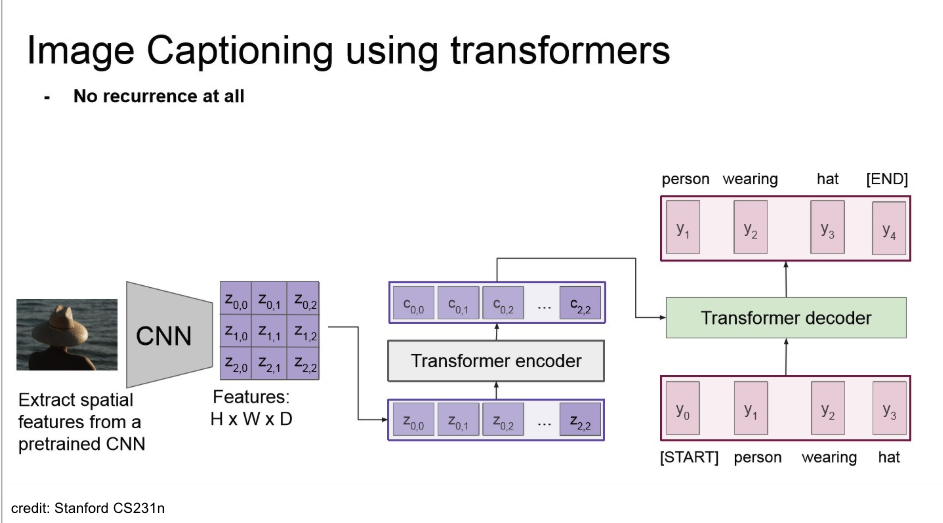
- CNN으로 feature들을 추출하고, 이를 flattening하고 transformer에 넣어서 captioning.
- 학습시에는 recurrence가 없지만,
- inference 때에는 sequencial 하게 단어를 예측해야 하므로, recurrence 존재.
- auto-regressive decoding
- teacher-forcing하니, 이미 다음 레이블을 학습시에는 들고 있음.
- 또한, RNN 계열을 사용하지 않으니, 순환적이지 않음.
Vision Transformer(ViT)
원본 링크Example
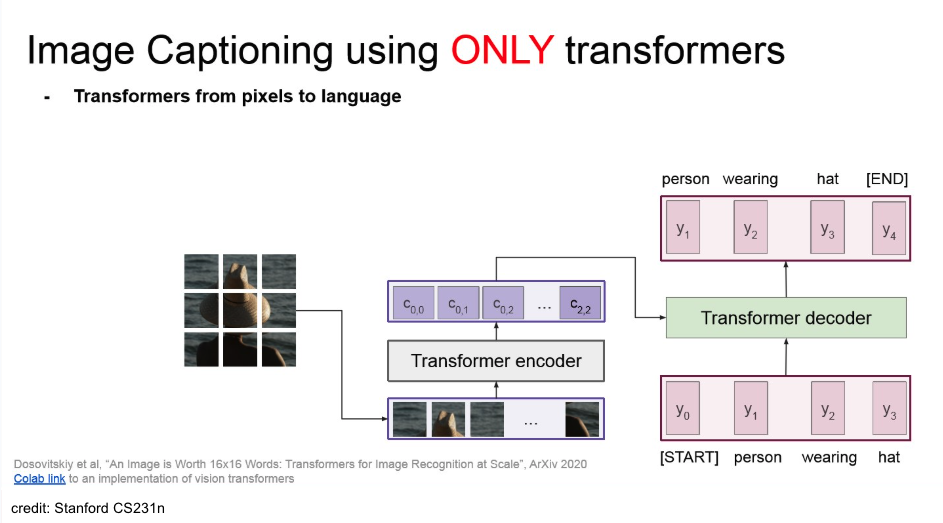
위의 captioning task 에서 CNN을 없애고, img를 patch 단위로 잘라서 바로 transformer에 넣을 수도 있다. → ViT
Vision Transformer
Vision Transformer(ViT)
Summary
transformer model의 attention을 사용해서 만든 vision model.
img를 patch로 분할하고 바로 transformer에 넣음.
Example in Image Captioning
Example
원본 링크Tip


/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Domains/Computer-Vision/assets/ViT.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Transformers/assets/ex-ViT.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Vision-Transformer/assets/ViT-vs-ResNet.png)
/../../../../../AI/Concepts/Architectures/Vision-Transformer/assets/ViT-ex.png)