NOTE
- Word2vec(Mikolov et al. 2013)에서 제안됨.
- Large Corpus로부터 학습시킴.
- 모든 단어들은 fixed 된 vector로 표현됨.
- notation:
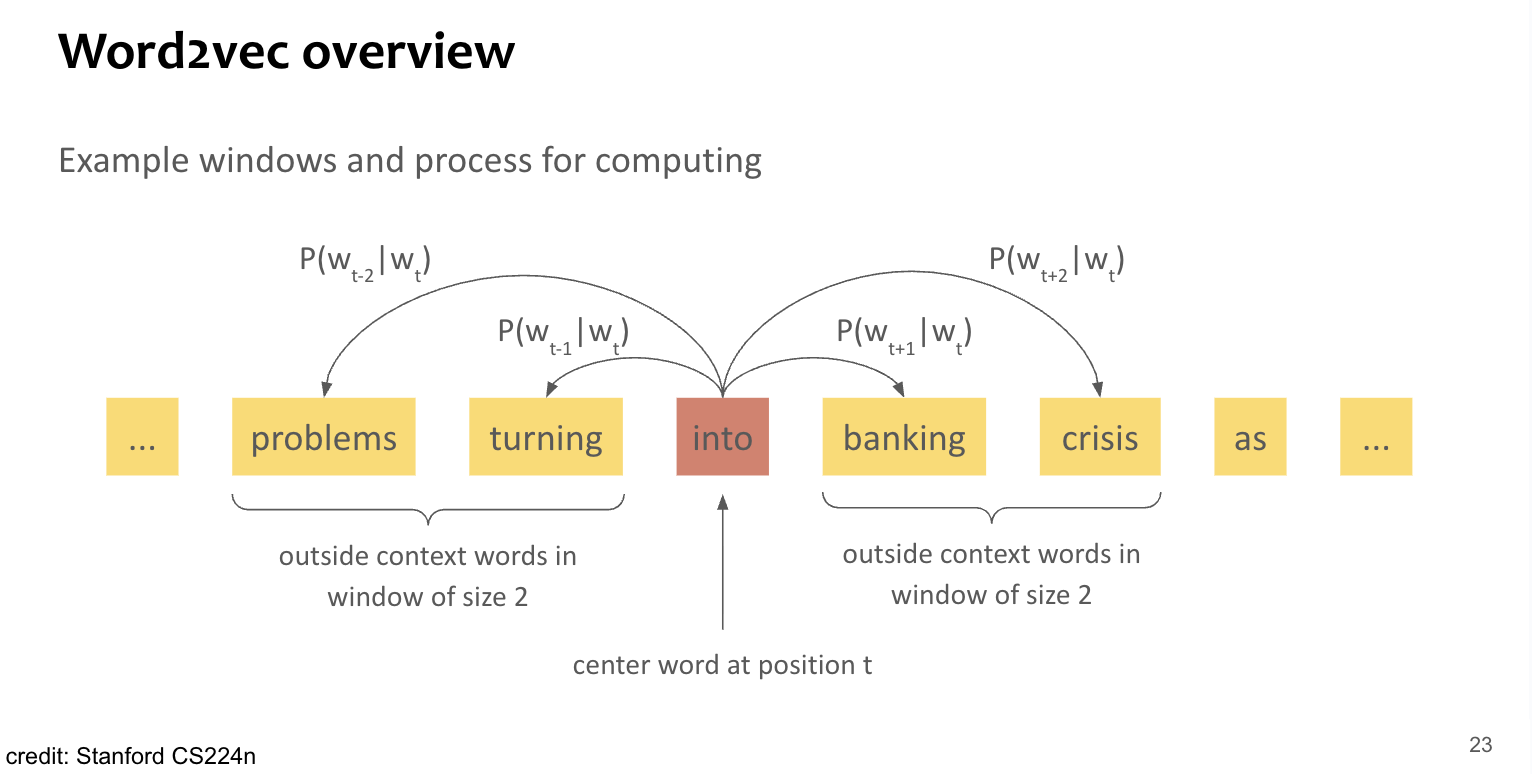
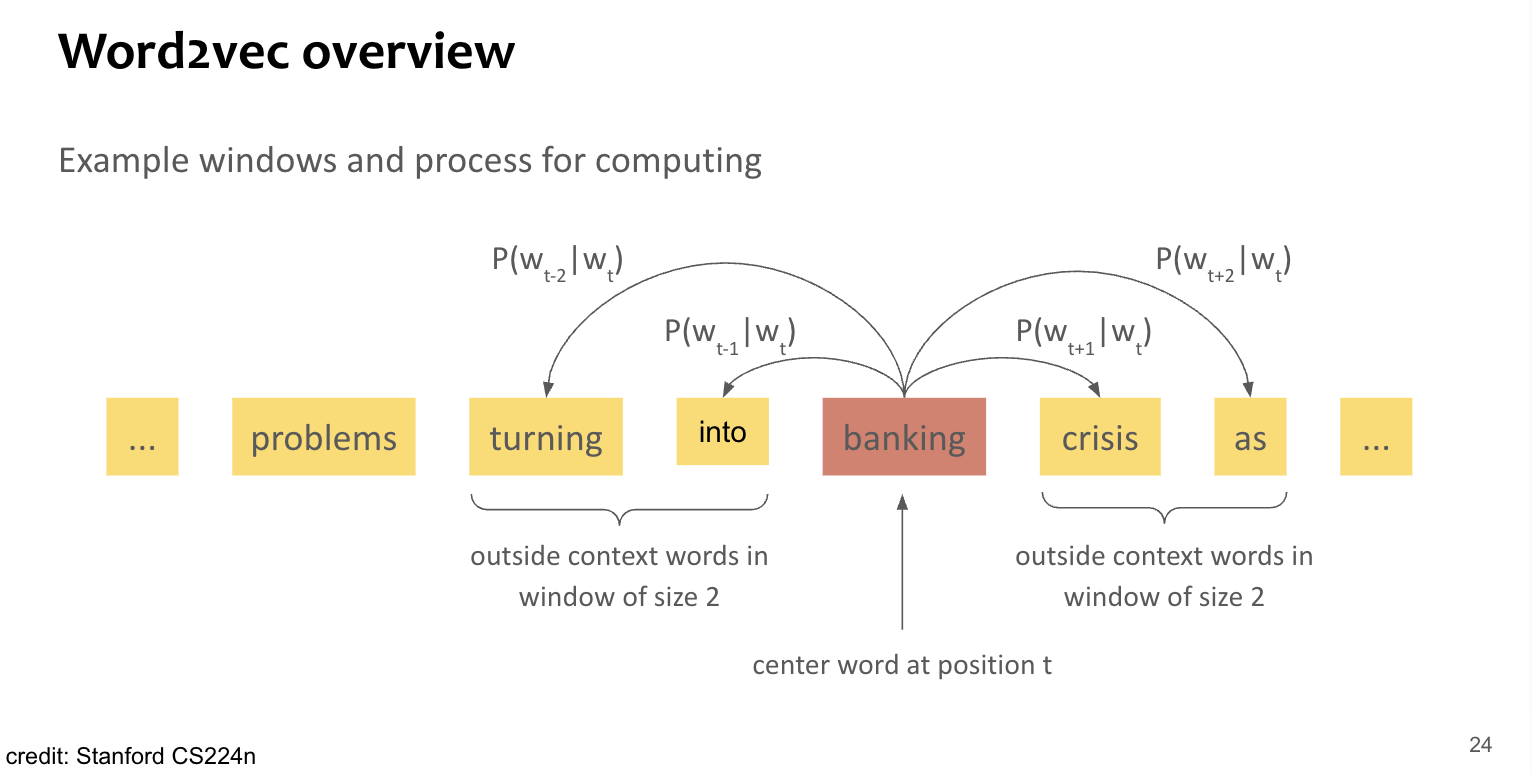
- : center word
- : outside word, i.e. context with fixed window-size
- 단어 벡터 간 유사도를 와 간의 conditional probability를 계산하는데 사용.
- 이 확률을 maximizing 하도록 word-vector 반복 수정.
Leaning
Overview
Example
Loss define
Summary
- 한 word에 대해서도 center로 사용될 때와 context로 사용될 때 다른 vector representation을 가진게 학습을 진행함.
- Softmax와 비슷하게 생김.
- “max” : 큰 값들은 amplified하니
- “soft” : 작은 값들에도 여전히 확률 값을 주기는 하니까.
Training
Summary
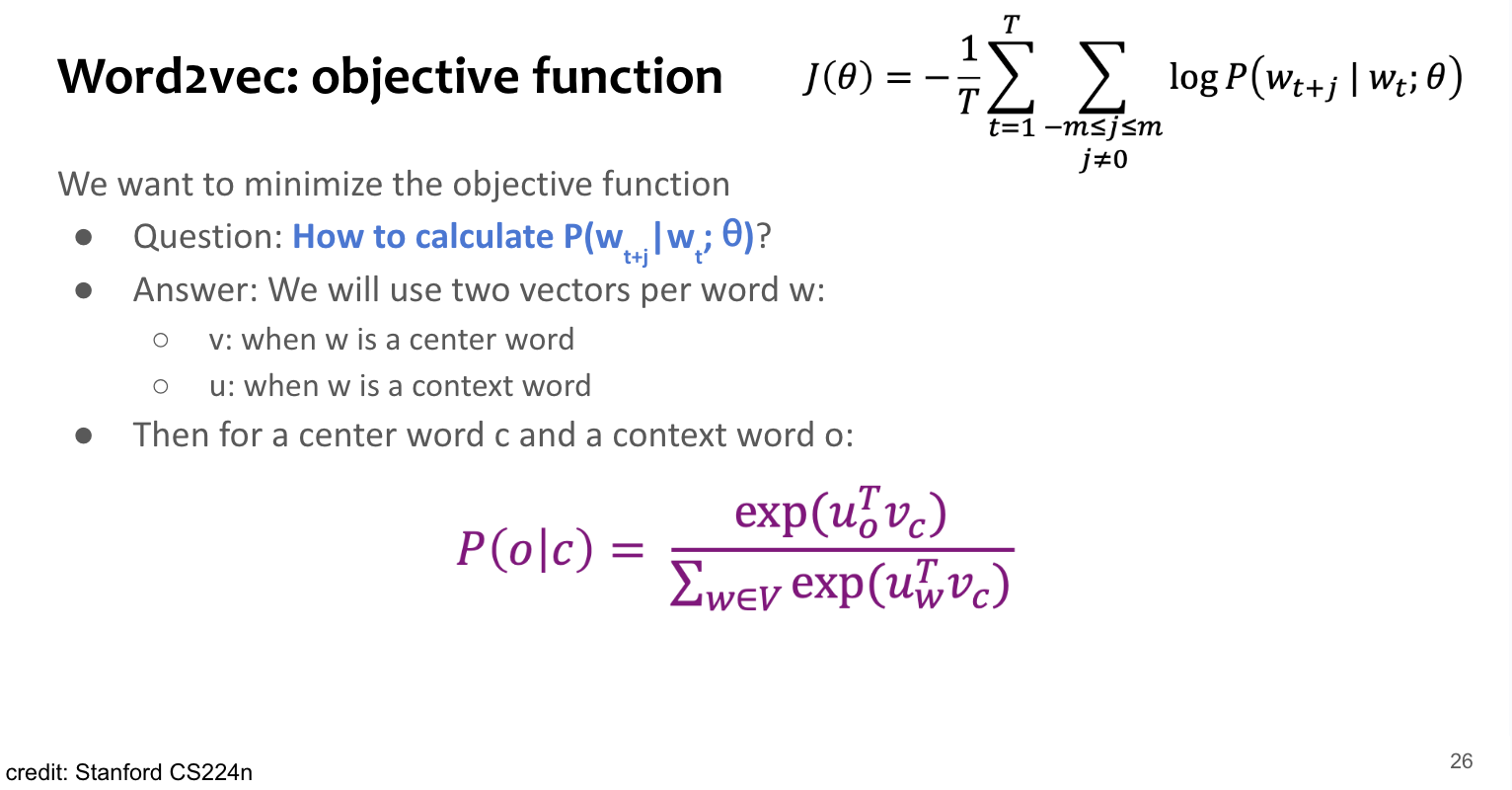
Optimization target 즉, parameter는 모든 단어들의 vector embedding 자체. → voca size 만큼의 d-dimensional vector x 2(center version, context version)
즉,
where : vector dimension, : voca size
Question
Why 2 vectors?
- easy to optimize.
- average both at the end.
Summary
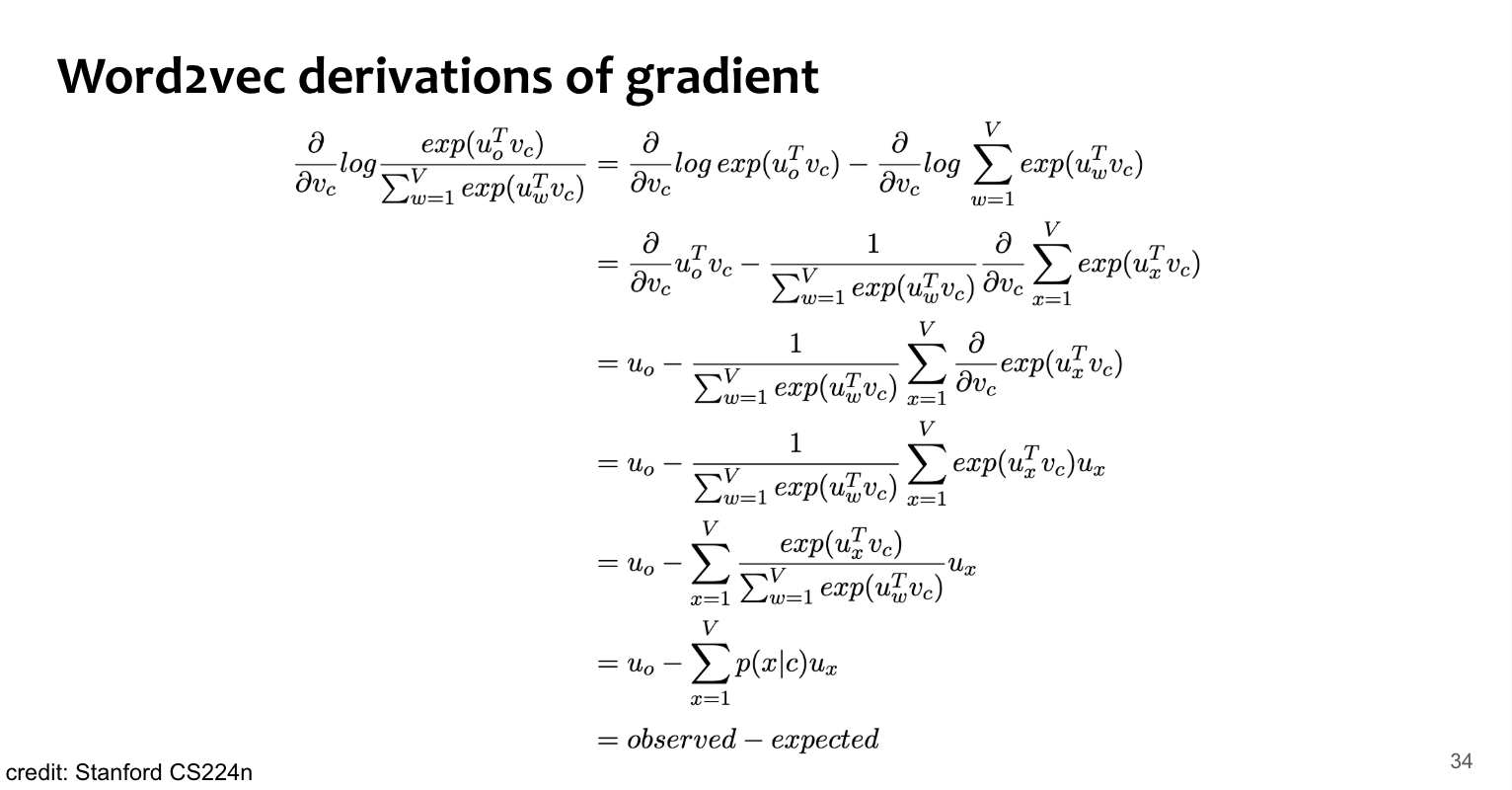
위 식을 통해 gradient를 계산해보면,
Check
- 위에 건 v에 대한 미분. u에 대한 미분도 해볼 것.
Tip
Negative sampling이 training에 도움을 준다. (efficient vs naive softmax)
Model Variants(Type)
Skip-grams(SG)
- predict context by using center.
- course cover this .
Continuous Bag of Words(CBOW)
- predict center by using context.
Negative Sampling
Summary
위 식 중 확률 는 아래처럼 softmax항으로 생겼는데,
denominator에서 sum term이 voca size라 연산량이 크다.따라서 naive하게 softmax를 사용하지 않고, negative sampling을 사용한다.
Important
Main Idea: train binary logistic regression for a true pair(center word and a word in its context window) vs several “noise” pairs (the center word paired with a random word)
Quote
From “Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality” (Mikolov et al. 2013)
- k개의 negative samples(using word occurance probabilities)
- Aim: 실제 context 내부에서 발견되는 단어들의 확률은 maximize, 반대로 negative sample 항들에 대한 확률은 minimize.
Tip
가 negative sample 추출 시 사용되는 확률 분포이자, occurance distribution인데, 이를 그대로 사용하는 것보다 해서 사용하는 것이 경험적으로 더 좋다고 한다.
- 3/4 power 걸어주면, 저 빈도 단어들이 조금 더 추출되는 효과.
SG(stochastic gradient) with neg sampling
NOTE
업데이트 대상인 vector representation들은 voca size만큼 있으니, 이 한 번의 업데이트 시 현재 주목하는 단어들만 update하면 되는 거지, 나머지 단어들은 건드릴 필요가 없음. → stochastic process를 해야 함.
We might only update the word vectors that “actually appear”!
Solution:
- either you need sparse matrix update operations to only update certain rows of full embedding matrices U and V,
- or you need to keep around a hash for word vectors
If you have millions of word vectors and do distributed computing, it is important to not have to send gigantic updates around!